| [1] Hirabayashi K, Watanabe K, Wakano K, et al. Expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spinal stenotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983;8(7): 693-699.
[2] Hardman J, Graf O, Kouloumberis PE, et al. Clinical and functional outcomes of laminoplasty and laminectomy. Neurol Res. 2010;32(4): 416-420.
[3] 牛硕,孙宇.系统性回顾改良颈椎椎管扩大椎板成形术的疗效及其对轴性症状的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2012,22(1):72-76.
[4] O'Brien MF, Peterson D, Casey AT, et al. A novel technique for laminoplasty augmentation of spinal canal area using titanium miniplate stabilization. A computerized morphometric analysis. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(4): 474-483; discussion 484.
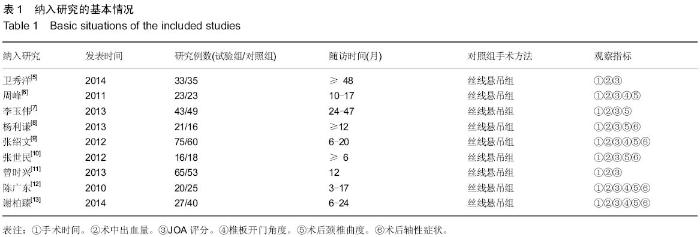
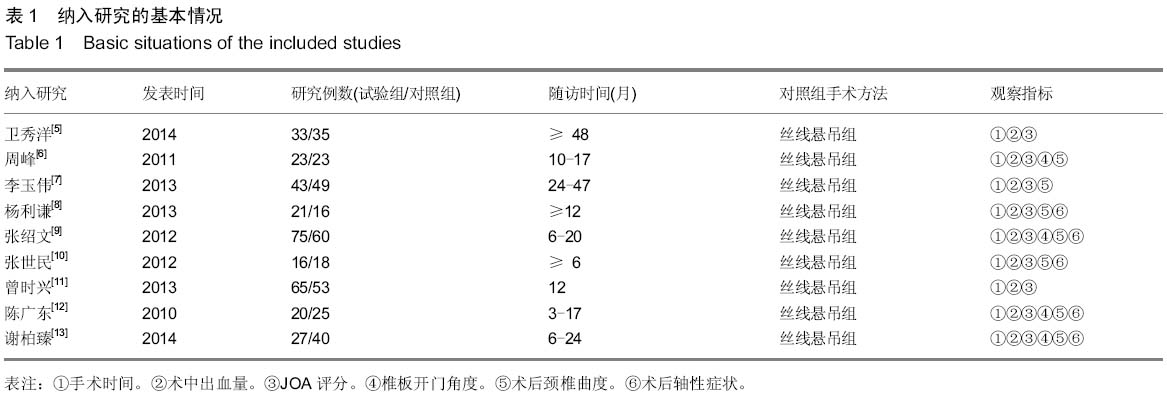
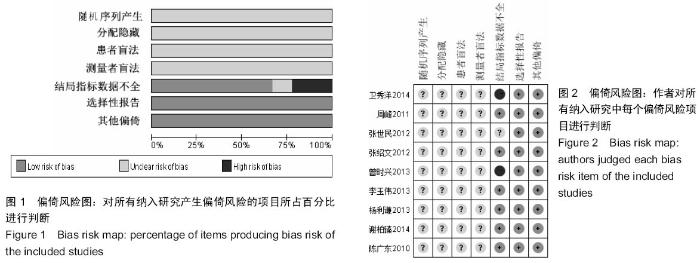
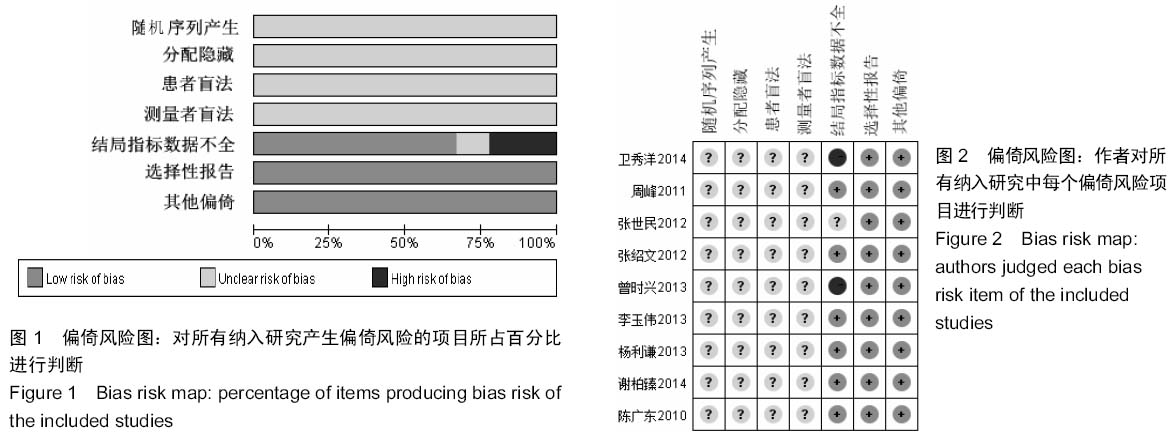
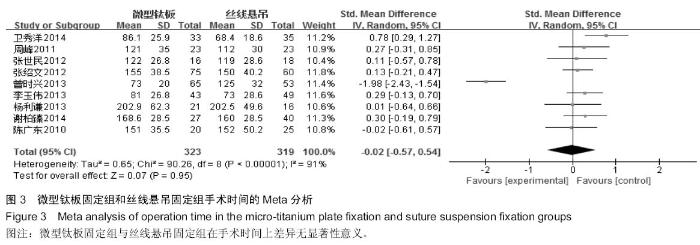
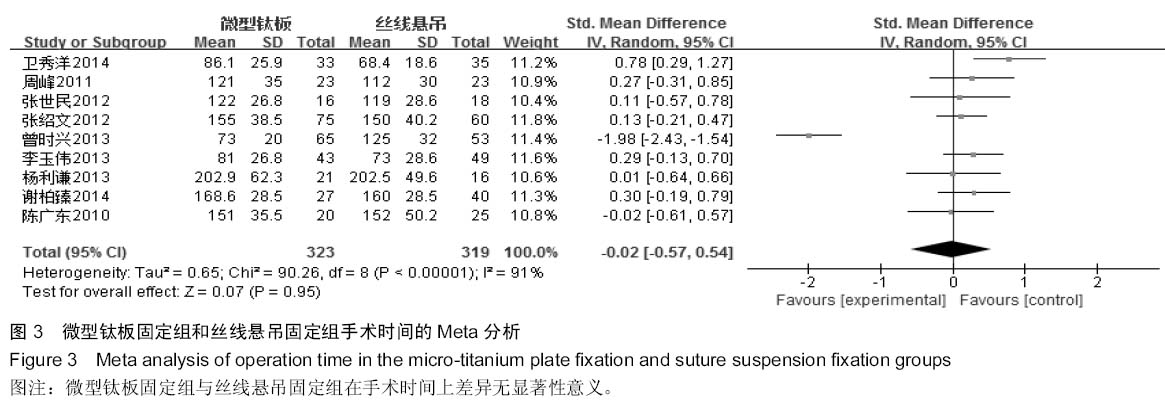
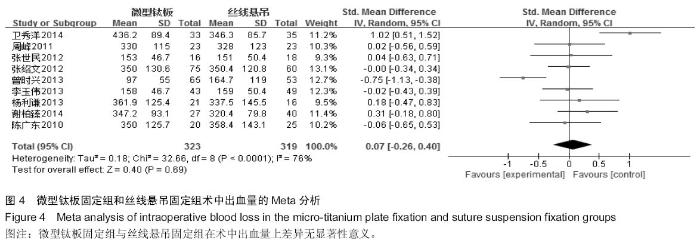
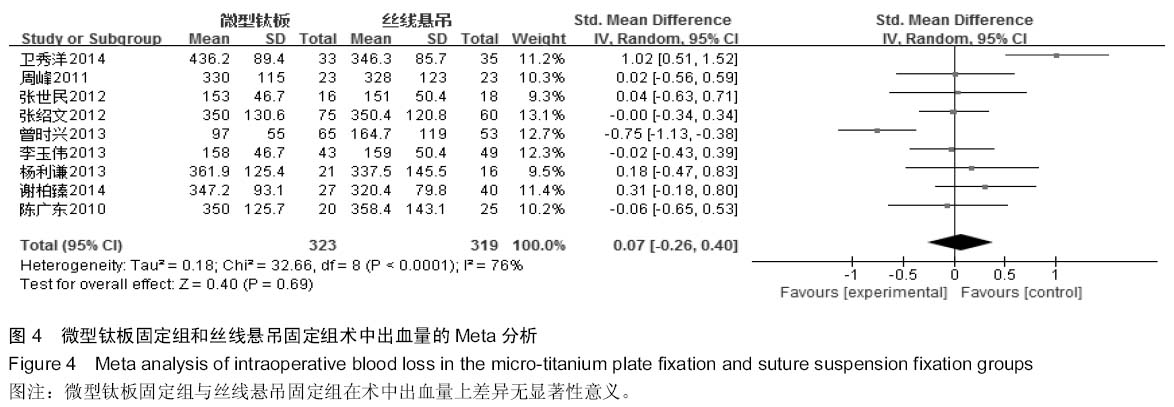
[5] 卫秀洋,陈勇忠,王金星,等. 3种颈椎后路单开门椎管扩大成形术的临床效果评价[J]. 中医正骨,2014,18(12): 19-24.
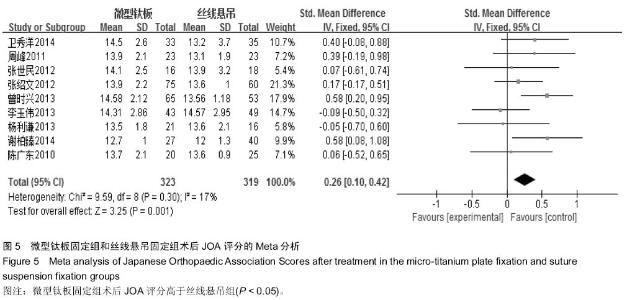
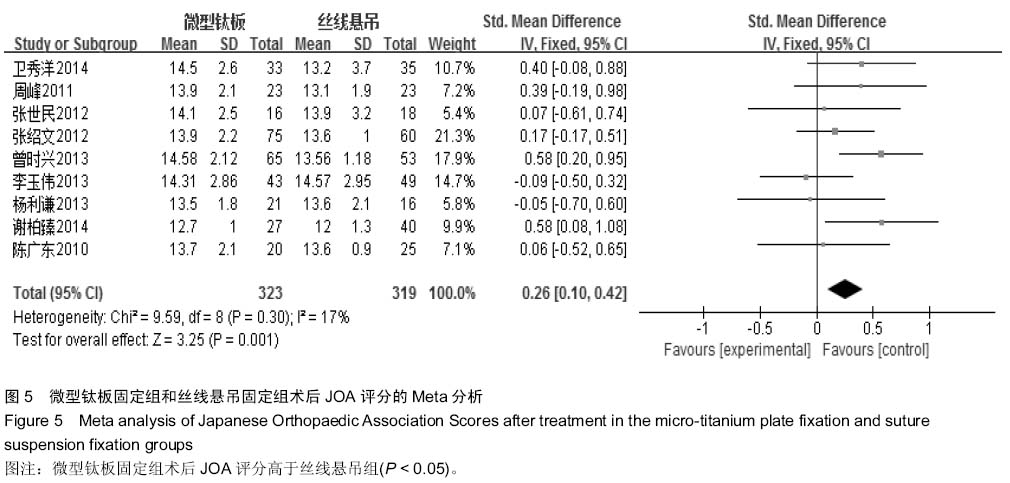
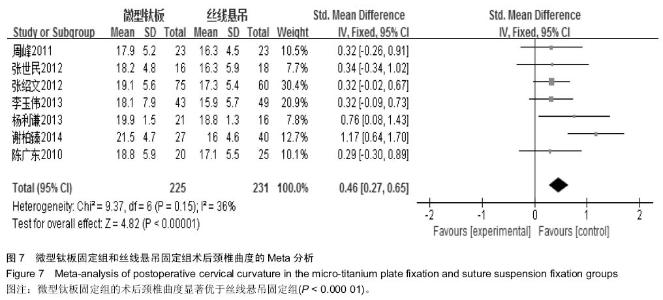
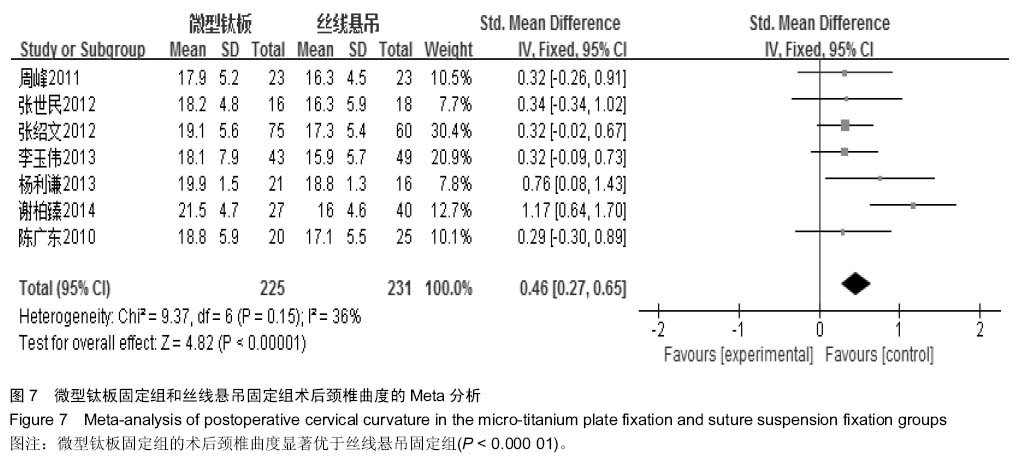
[6] 周峰,杨惠林,王根林,等.颈椎单开门微型钛板固定与缝线悬吊固定治疗颈椎病[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(21):1761-1764.
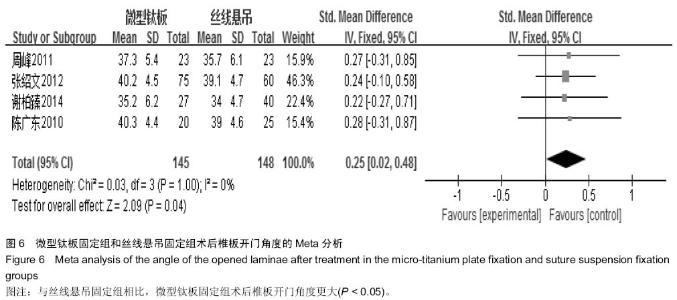
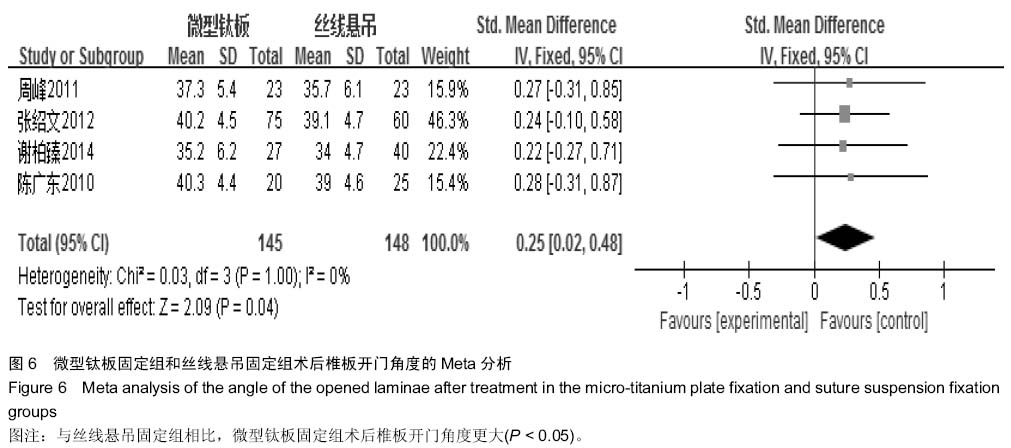
[7] 李玉伟,王海蛟,严晓云,等.颈椎单开门椎管扩大成形术不同椎板固定方法治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013, 23(11):973-978.
[8] 杨利谦,尚咏,虞攀峰.颈椎单开门椎管扩大术缝线悬吊与钛板固定疗效比较[J].山西医科大学学报, 2013,44(4): 307-310.
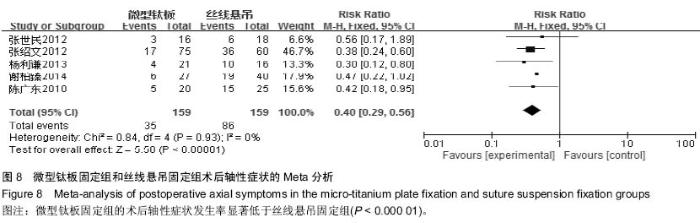
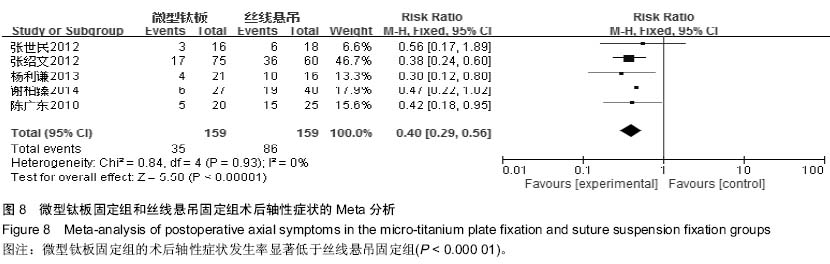
[9] 张绍文,樊成虎,温剑涛.微型钛板法单开门颈椎管扩大成形术治疗脊髓型颈椎病的临床疗效观察.中华中医药学会骨伤科分会2012年学术年会,2012. 2012-01-01;141-144. Available from: http://d.g.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_7964949.aspx.
[10] 张世民,周卫,李星,等.微型钛板固定颈椎单开门椎管扩大成形术的临床应用[J].中国骨伤, 2012,25(1): 4-8.
[11] 曾时兴,詹世强,昌耘冰,微型钛板内固定在颈椎后路单开门术中的应用及疗效比较[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2013,31(5): 582-585.
[12] 陈广东,杨惠林,王根林,等.微型钛板在颈椎单开门椎管扩大椎板成形术中的应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(10):850-854.
[13] 谢柏臻,华强,赵慧毅.微型钛板在颈椎后路椎板成形中的应用:近期随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(35):5681-5686.
[14] Higgins JPT. Cochrane Handbook for SystematicReviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated Macch 2011].The Cochrane Collaboration. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochranehandbook.org, 2011.
[15] Tanaka J,Seki N, Tokimura F, et al. 0perative results of canal expansive laminoplasty for cervical spondylodic myelopathy in eldly patients. Spine. 1999;24(22):2308-2312.
[16] Deutsch H, Mummaneni PV, Rodts GE, et al. Posterior cervical laminoplasty using a new plating system: technical note. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(4): 317-320.
[17] Park AE, Heller JG. Cervical laminoplasty: use of a novel titanium plate to maintain canal expansion--surgical technique. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(4): 265-271.
[18] Freedman B,Heller J,Rhee J. Cervical laminoplasty myths and realities: a meta-analysis of outcomes and complications. Spine. 2009;9: 23.
[19] Fukui K, Kataoka O, Sho T, et al. Pathomechanism, pathogenesis, and results of treatment in cervical spondylotic myelopathy caused by dynamic canal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1990;15(11):1148-1152.
[20] 孙宇,张凤山,潘胜发.锚定法改良单开门椎管成形术及其临床应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,14(9):517-519.
[21] Schulz KF, Moher D, Altman DG. CONSORT 2010 comments. Lancet. 2010;376(9748): 1222-1223. |