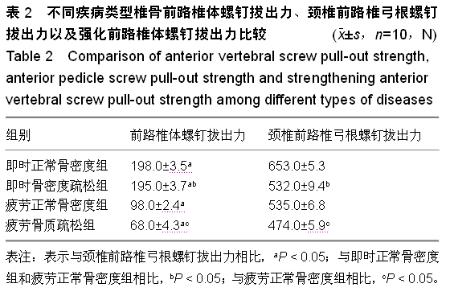
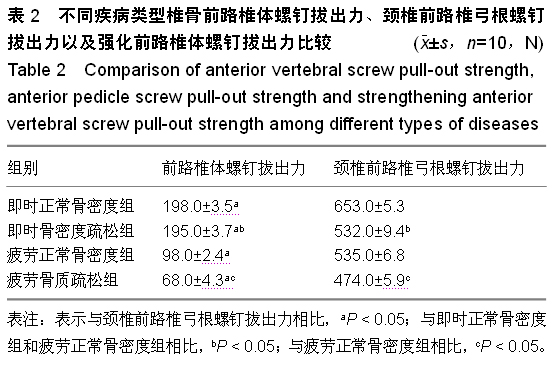
| [1] 袁文.脊髓型颈椎病手术入路与术式的选择-对多节段脊髓型颈椎病手术方案选择的要素[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(7): 483-484.
[2] 陈文瑶,李新志.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(3):226-229.
[3] 王秀会,王子平,夏胜利,等.骨质疏松性骨折的治疗选择与内固定失败原因分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(9):717-719.
[4] 陈跃平,朱勇,黄有荣.注射式憐酸韩骨水泥加固颈椎前路螺钉的生物力学研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2007,24(3):386-388.
[5] Bames AH, Eguizabal JA, Acosta FJ, et al. Biomechanical pullout strength and stability of the cervical artificial pedicle screw. Spine (Phila Pa1976). 2009;34(1):E16-E20.
[6] 杨惠林,王志荣,王根林,等.可灌注骨水泥椎弓根螺钉的生物力学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(3):241-247.
[7] Kiner DW, Wybo CD, Sterba W, et al. Biomechanical analysis of different techniques in revision spinal instrumentation: larger diameter screws versus cement augmentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(24):2618-2622.
[8] 吴增晖,郑轶,章凯,等.经口前路枢椎椎弓根螺钉固定的临床应用解剖学[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2009,27(5):505-507.
[9] 邓斌,袁峰,郭开今,等.下颈椎颈前路反向椎弓根螺钉内固定的解剖学研究[J].徐州医学院学报,2010,30(8):520-523.
[10] 郑轶,吴增晖,章凯,等.经口前路寰椎椎弓根螺钉的应用解剖学研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2010,32(4):399-401.
[11] 徐荣明,赵刘军,马维虎,等.下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉内面定解剖学测量及临床应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(12):1337-1343.
[12] 吴峰,尹庆水.经口咽前路寰枢椎复位钢板縲钉固定强度的生物力学评价[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010,28(5):575-577.
[13] Christensen DM, Eastlack RK, Lynch JJ, et al. CI anatomy and dimensions relative to lateral mass screw placement. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(8):844-848.
[14] 任绍东,马邦兴,屠永刚.寰椎的应用解剖及对寰椎椎弓根钉置钉方法的探讨[J].解剖学研究,2011,33(1):44-48.
[15] 王建华.对枢椎椎弓根复合体与解剖学椎弓根的认识[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(4):319-321.
[16] 顾勇杰,胡勇,徐荣明,等.枢椎前路椎弓根螺钉固定通道的安全因素分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,27(2):125-127.
[17] Koller H, Schmidt R, Mayer M, et al. The stabilizing potential of anterior,posterior and combined techniques for the reconstruction of a 2 level cervical corpectomy model: biomechanical study and first results of ATPS prototyping. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(12):2137-2148.
[18] 赵刘军,徐荣明,马维虎,等.下颈椎损伤前路椎弓根螺 钉固定的初步临床运用[J].中华创伤杂志,2012,28(9):780-784.
[19] Yukawa Y, Kato F, Ito K, et al. Anterior cervical pedicle screw and plate fixation using fluoroscope assisted pedicle axis view imaging:a preliminary report of a new cervical reconstruction technique. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(6):911-916.
[20] 赵刘军,李杰,蒋伟宇,等.下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉固定系统与普通前路椎体螺钉固定系统的静力学比较[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(2): 118-122.
[21] Zhao L, Xu R, Hu T, et al. Quantitative evaluation of the location of the vertebral artery in relation to the transverse foramen in the lower cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(4):373-378.
[22] Jeon SW, Jeong JH, Choi GH, et al. Clinical outcome of posterior fixation of the C1 lateral mass and C2 pedicle by polyaxial screw and rod. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2011.
[23] 池永龙,林焱,毛方敏,等.几种椎弓根钉内固定器的生物力学测试与临床应用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2001,11(3):78-80.
[24] Meyer D, Meyer F, Kretschmer T, et al. anslaminar screws of the axis--an alternative technique for rigid screw fixation in upper cervical spine instability. Neurosurg Rev. 2012;35(2): 255-261.
[25] Pelton MA, Schwartz J, Singh K. Subaxial cervical and cervicothoracic fixation techniques--indications, techniques, and outcomes. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012;43(1):19-28.
[26] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.脊柱骨折经伤椎椎弓根置钉附加横连短节段固定的稳定性测试[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(9): 745-749.
[27] 胡樵,黄勇,赵东升,等.胸腰椎骨折伤椎椎弓根内固定的生物力学研究[J].河北医学,2008,14(7):757-758.
[28] 魏美钢,王坤正,侯德门,等.椎弓根螺钉器械横杆作用的生物力学研究[J].西安医科大学学报,2002,23(1):47-49.
[29] 殷渠东,郑祖根,蔡建平,等.椎弓根螺钉固定相对稳定性的体外生物力学试验[J].江苏医药,2005,31(2):119-122.
[30] 武启军,王自立,戈朝晖,等.脊柱单节段前中柱切除后不同节段椎弓根螺钉内固定的稳定性测试[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010, 20(4): 267-269.
[31] 王志荣,杨惠林,王根林.胸腰椎椎弓根螺钉内固定系统的设计进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008(10):791-794.
[32] Nakashima H, Yukawa Y, Imagama S, et al. Complications of cervical pedicle screw fixation for nontraumatic lesions: a multicenter study of 84 patients. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012; 16(3): 238-247.
[33] Ishikawa Y, Kanemura T, Yoshida G, et al. Intraoperative, full-rotation, three-dimensional image (O-arm)-based navigation system for cervical pedicle screw insertion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;15(5):472-478.
[34] 高明,刘庆余,陈建宇,等.CT三维重建技术对颈椎理想椎弓根螺钉的选择及意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010,1(24):61-64. |