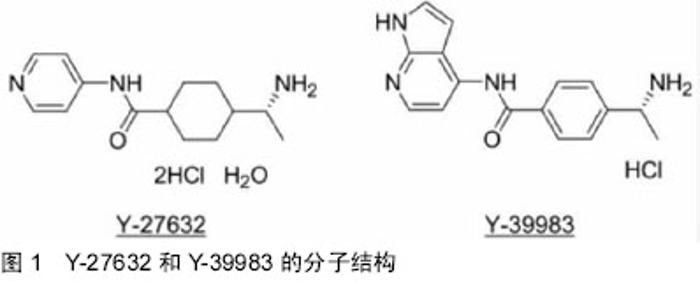
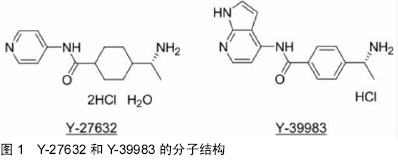
| [1] Mueller BK,Mack H,Teusch N.Rhokinase,a promising drug target for neuro logical disorders.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2005; 4:387-398.
[2] 段为钢,袁胜涛,廖红,等. Rho激酶及其抑制剂的研究进展[J].药学学报,2007, 42(10):1013-1022.
[3] Moffatt SL,Cartwright VA,Stumpf TH.Centennial review of corneal transplantation.Clin Experiment Ophthalmol.2005; 33:642-657.
[4] Thompson RW Jr, Price MO, Bowers PJ, et al. Long-term graft survival after penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:1396-1402.
[5] Panda A,Vanathi M,Kumar A,et al.Corneal graft rejection.Surv Ophthalmol.2007;52: 375-396.
[6] Golchet G, Carr J, Harris MG. Why don’t we have enough cornea donors? A literature review and survey. Optometry. 2000;71:318-328.
[7] Olson MF. Applications for ROCK kinase inhibitio .Curr Opin Cell Biol.2008; 20(2):242-248.
[8] Hahmann C, Schroeter T.Rho-kinase inhibitors as therapeutics: from pan inhibition to isoform selectivity.Cell Mol Life Sci.2010; 67(2):171-177.
[9] Tanaka T, Nishimura D, Wu RC, et al. Nuclear Rho kinase, ROCK2, targets p300 acetltransferase. Biol chem. 2006; 281(22);15320-15329.
[10] Kiento K, Kidley AJ. Rocks: multifunctional kinase in cell beliaviour.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2003;4(6):446-456.
[11] Rao PV, Deng PF, Kumar J, et al. Modulation of aqueous liumor outflow facility by the Rho kinase-specific inhibitor Y-27632.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2001;42 (5):1029-1037.
[12] 李斌. ROCK抑制剂Y-27632对角膜上皮的保护性作用及其机制的初步研究[D].济南大学,2013.
[13] Okumura N, Nakano S, Kay EP, et al. Involvement of cyclin D and p27 in cell proliferation mediated by ROCK inhibitors Y-27632 and Y-39983 during corneal endothelium wound healing.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2014;55(1):318-329.
[14] 蒙青青,刘苏. ROCK抑制剂在眼科基础及临床应用研究进展[J]. 眼科新进展,2013;09:894-897.
[15] Nakajima E, Nakajima T, Minagawa Y, et al.Contribution of ROCK in contraction of trabecular meshwork:proposed mechanism for regulating aqueous outflow in monkey and human eyes. Pharm Sci.2005;94:701-708.
[16] Tokushige H, Inatani M, Nemoto S, et al. Effects of topical administration of y-39983, a selective rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, on ocular tissues in rabbits and monkeys.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2007;48:3216-3222.
[17] Ishizaki T, Uehata M, Tamechika I,et al.Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor ofRho-associated kinases.Mol Pharmacol.2000;57 (5):976-983.
[18] Sangwan VS. Limbal stem cells in health and disease.Biosci Rep. 2001;21(4):385-405.
[19] Davanger M, Evensen A. Role of the pericorneal papillary structure in renewal of corneal epithelial. Nature.1971;229: 560-561.
[20] Nagasaki T,Zhao J.Centripetal movement of corneal epithelial cells in the normal adult mouse.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44(2):558-566.
[21] Collinson JM,Morris L,Reid AI, et al. Clonal analysis of patterns of growth, stem cell activity, and cell movement during the development and maintenance of the murine corneal epithelium.Dev Dyn.2002;224(4):432-440.
[22] Thoft RA,Rriend J.The X,Y,Z hypothesis of corneal epithelial maintenance. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.1983;24:1442-1443.
[23] Yin J, Yu FS.Rho kinases regulate corneal epithelial wound healing. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2008;295: C378-C387.
[24] 马玲.ROCK抑制剂在角膜缘干细胞体外扩增和保存中的作用研究[D].青岛大学,2012.
[25] Okumura N, Koizumi N, Kay EP, et al. The ROCK inhibitor eye drop accelerates corneal endothelium wound healing.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2013;54(4):2493-2502.
[26] Okumura N, Koizumi N, Ueno M, et al. Enhancement of corneal endothelium wound healing by Rho-associated kinase(ROCK) inhibitor eye drops.Br J Ophthalmol. 2011; 95:1006-1009.
[27] Shanyi L, Chan W, Ying D, et al. The stimulatory effect of ROCK inhibitor on bovine cornealendothelial cells.Tissue Cell.2013;45(6):387-396.
[28] Koizumi N, Sakamoto Y, Okumura N, et al. Cultivated corneal endothelial cell sheet transplantation in a primate model.Invest Ophthalmol.Vis Sci.2007;48:4519-4526.
[29] Koizumi N,Sakamoto Y,Okumura N,et al.Cultivated corneal endothelial transplantation in a primate: possible future clinical application in corneal endothelial regenerative medicine. Cornea.2008;27:Suppl 1:S48-S55.
[30] Okumura N,Koizumi N,Ueno M,et al. ROCK inhibitor converts corneal endothelial cells into a phenotype capable of regenerating in vivo endothelial tissue.Am J Pathol.2012; 181(1): 268-277.
[31] Griffith LG, Swartz MA. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2006;7:211-224.
[32] Abbott A. Cell culture: biology's new dimension. Nature.2003; 424: 870-872.
[33] Yamada K, Kamihira M, Iijima S. Enhanced cell aggregation and liver functions using polymers modified with a cell-specific ligand in primary hepatocyte cultures. Biosci Bioeng. 1999;88:557-562.
[34] Han Y, Liu XM, Liu H, et al. Cultivation of recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells grown as suspended aggregates in stirred vessels. Biosci Bioeng.2006; 102: 430-435.
[35] Bi YL, Zhou Q, Du F, et al. Regulation of functional corneal endothelial cells isolated from sphere colonies by Rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor. Exp Ther Med.2013; 5(2):433-437.
[36] Tokushige H, Inatani M, Nemoto S, et al.Effects of topical administration of y-39983, a selective rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor, on ocular tissues in rabbits and monkeys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2007;48:3216-3222.
[37] Mimura T,Yamagami S,Yokoo S, et al. Sphere Therapy for Corneal Endothelium Deficiency in a Rabbit Model. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2005;9(46): 3128-3135.
[38] Honjo M, Tanihara H, Inatani M, et al.Effects of rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 on intraocular pressure and outflow facility. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2001;42:137-144.
[39] Waki M, Yoshida Y, Oka T, et al. Reduction of intraocular pressure by topical administration of an inhibitor of the Rhoassociated protein kinase.Curr Eye Res.2001;22: 470-474.
[40] 邱敬华. H-1152降眼压治疗青光眼的实验研究[D].南华大学, 2007.
[41] Wang RF1, Williamson JE, Kopczynski C, et al.Effect of 0.04% AR-13324, a ROCK, and norepinephrine transporter inhibitor, on aqueous humor dynamics in normotensive monkey eyes. J Glaucoma.2015;24(1):51-4.
[42] Lee JG, Kay EP.PI3-kinase/Rac1 and ERK1/2 regulate FGF-2-mediated cell proliferation through phosphorylation of p27 at Ser10 by KIS and at Thr187 by Cdc25A/Cdk2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2011;52:417-426.
[43] Lee HT, Kay EP. Regulatory role of PI 3-kinase on expression of Cdk4 and p27, nuclear localization of Cdk4, and phosphorylation of p27 in corneal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2003;44:1521-1528.
[44] Yamamoto M, Marui N, Sakai T, et al. ADP-ribosylation of the rhoA gene product by botulinum C3 exoenzyme causes Swiss 3T3 cells to accumulate in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Oncogene.1993;8:1449-1455.
[45] Olson MF, Ashworth A, Hall A. An essential role for Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases in cell cycle progression through G1. Science.1995;269:1270-1272. |