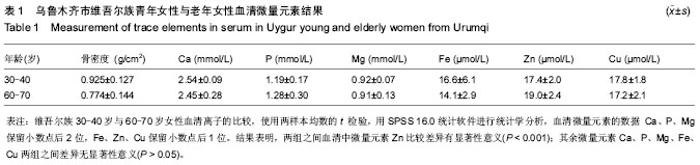
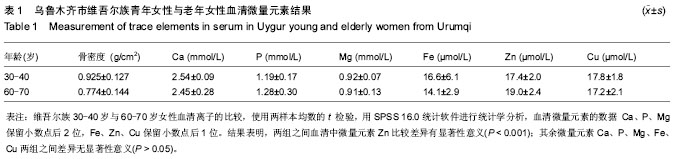
| [1] 常小霞,吴洁,任慕兰.微量元素与绝经后骨质疏松症[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2006,12(6):635-638.
[2] 茹选良.锌与骨代谢的研究进展[J].临床骨科杂志,1998,1(1): 32-34.
[3] 马蓓蕾,蔡美琴.微量元素与骨质疏松防治的研究进展[J].中国临床营养杂志,2005,13(5):319-325.
[4] Hyun TH, Barrett-Connor E, Milne DB. Zinc intakes and plasma concentrations in men with osteoporosis: the Rancho Bemardo Stuy.Am J Clin Nutr.2004;80(3):715-721.
[5] 孙体健,尚晓虹,董进,等.人发中钙、磷、锌元素含量与骨质疏松症关系的探讨[J].山西医科大学学报,1998,29(2):126-127.
[6] Hill T, Meunier N, Andriollo-Sanchez M, et al. The relationship between the zinc nutritive status and biochemical markers of bone turnover in older European adults: the ZENITH study. Eur J Clin Nutr.2005;59(Suppl 2):S73-S78.
[7] 孟迅吾.营养与原发性骨质疏松症//顾景范.现代临床营养学[M].北京:科学出版社,2003:600-601.
[8] 周琦.补充铜、镁锰和锌防治骨质疏松的研究进展[J].中国临床营养杂志, 2003,11(4):312-314.
[9] Liu G, Men P, Kenner GH, et al. Age-associated iron accumulation in bone: implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis and a new target for prevention and treatment by Chelation.Bionmetals.2006;19:245-251.
[10] Cornis J, Callon NE, Naot D, et al. Lactofemin is a potent regulator of bone cell activity and increases bone formation in vivo. Endocrinology.2004;145: 4366-4374.
[11] 伊晟,肖艳红,李英,等.血清IL-8、BGP、PTH-M和铁离子浓度与男性老年骨质疏松症的关系[J].标记免疫分析与临床. 2013, 20(4):275-276.
[12] 赵理平.骨代谢与铁代谢指标相关性的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(3):273.
[13] Sadat-Ali M,Sultan O, Al-Turki H,et. Does high serum iron level induce low bone mass in sickle cell anemia. Biometals. 2011;24(1):19-22.
[14] Wallach S. Relation of magnesium to osteoporosis and calcium urolithiasis. Magnes Trace Elem. 1991-1992; 10(2-4): 281-286.
[15] 陈照坤.影响骨质疏松症的微量元素研究进展[J].护士进修杂志,2005,20(6):509.
[16] 黄焕新,李秀美,胡俊波.骨质疏松症的防治[J].广东微量元素科学, 2003,10(1):63.
[17] 田玉慧,史明珠,李万里,等.膳食矿物质与骨密度关系调查[J].中国公共卫生,2002,18(7):836-837.
[18] 葛可佑.中国营养科学全书[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2004: 1638.
[19] 薛延.骨质疏松症诊断与治疗指南[M].北京:科学出版社, 1999: 208-213.
|