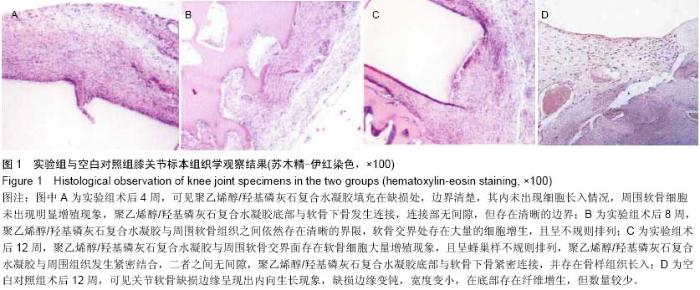
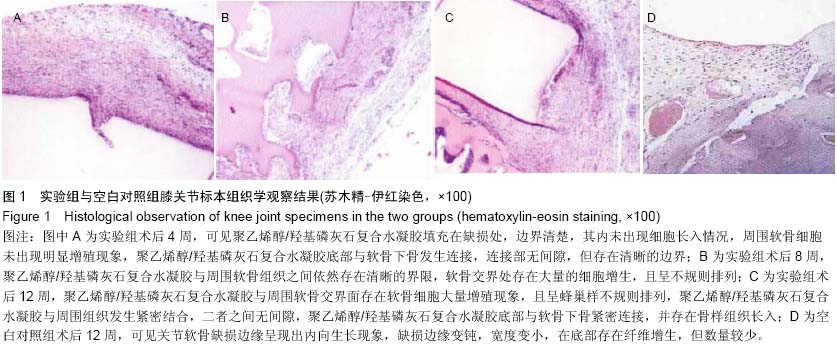
| [1] 卢华定,蔡道章,刘青,等.聚乙烯醇/羟基磷灰石复合水凝胶移植修复兔膝关节软骨缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(21): 1701-1703.
[2] 宁志刚.以COLⅡ为主要组分的软骨基质仿生水凝胶研制[D].第三军医大学,2012.
[3] 张一.Ⅱ型胶原水凝胶—细胞复合物(可注射型组织工程软骨)修复关节软骨缺损动物实验研究[D].第三军医大学,2012.
[4] 张一,田晓滨,李波,等.Ⅱ型胶原水凝胶-骨髓MSCs复合物兔膝关节腔成软骨实验研究[C].//第25届全国脊柱脊髓学术会议暨2013年贵州省骨科年会论文集,2013:269-270.
[5] 聚乙烯醇/羟基磷灰石复合水凝胶移植修复兔膝关节软骨缺损[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(34):184-186,189.
[6] 张一,田晓滨,李波,等.Ⅱ型胶原水凝胶-骨髓基质干细胞复合物在兔膝关节腔内成软骨的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014, 16(2):145-150.
[7] 蔡宏,娄思权,王志国,等.聚乙烯醇水凝胶弹性体复合物修复关节软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2004,19(5): 337- 339.
[8] 张一,田晓滨,李波,等.Ⅱ型胶原水凝胶-骨髓MSCs复合物兔膝关节腔成软骨实验研究[C].//第九届西部骨科论坛论文集,2013: 165-165.
[9] 李锋,周海宇,苏永琳,等.人膝关节软骨与聚乙烯醇水凝胶人工软骨压缩实验比较研究[J].医用生物力学,2009,24(6): 448-451, 457.
[10] 蔡宏.聚乙烯醇水凝胶复合物修复关节软骨缺损的实验研究[D].北京大学,2004.
[11] 张弩,陈廖斌.复合基质细胞衍生因子-1β、转化生长因子-β1的新型温敏性壳聚糖水凝胶修复兔关节软骨缺损[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,27(10):1529-1531.
[12] 沈艳秋,张德坤,葛世荣,等.PVA/HA复合水凝胶的结构和摩擦学性能[J].材料研究学报,2008,22(3):257-261.
[13] 郭忠鹏,彭超,蒋电明等.三种生物材料修复兔关节软骨缺损的性能对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(16): 2870-2874.
[14] Barbucci R,Fini M,Giavaresi G,et al.Hyaluronic acid hydrogel added with ibuprofen-lysine for the local treatment of chondral lesions in the knee: in vitro and in vivo investigations.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2005;75(1):42-48.
[15] 郭涛,杨天府,肖杰,等.新型生物复合材料聚乙烯醇/纳米羟基磷灰石+聚酰胺66修复关节软骨及软骨下骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(14):2623-2627.
[16] 范家兵.滑膜组织来源的间充质干细胞复合水凝胶支架材料体外构建组织工程化关节软骨[D].中山大学,2010.
[17] 张一,田晓滨,佘荣峰,等.快速构建一体化可注射型组织工程软骨修复猪关节软骨缺损[C].//第25届全国脊柱脊髓学术会议暨2013年贵州省骨科年会论文集,2013:270-271.
[18] 肖万军,范广字.几丁质凝胶与同种异体软骨细胞复合修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(19): 3633-3636.
[19] 刘文忠,夏亚一,汪玉良,等.水凝胶材料复合物修复软骨缺损的组织学评鉴[J].兰州大学学报:医学版,2006,32(4):26-29,33.
[20] 王岩,李德华.骨髓间充质干细胞复合多肽凝胶及成软骨生成因子修复兔关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(1): 30-36.
[21] 王金明,章庆国,张娇,等.温固化水凝胶负载骨髓基质干细胞修复兔关节骨软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国美容医学,2008,17(3): 389-392.
[22] 王金明,章庆国,张娇,等.温固化水凝胶负载骨髓基质干细胞修复兔关节软骨缺损的实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2008, 4(2):65-68.
[23] 郑裕东,王迎军,陈晓峰,等.聚乙烯醇/羟基磷灰石复合水凝胶软骨植入材料的研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2003,20(3): 401-403, 465.
[24] 许凤兰,李玉宝,王学江等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇复合水凝胶的制备和性能研究[J].功能材料,2004,35(4):509-512.
[25] 牟元华.新型一体化骨与软骨组织嵌层修复材料的设计与研制[D].四川大学,2006.
[26] 郭涛,杨天府,肖杰,等.新型生物复合材料聚乙烯醇/纳米羟基磷灰石+聚己二酰己二胺修复关节软骨及软骨下骨缺损的生物力学研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(6): 1051- 1054.
[27] 郑裕东,杨槐,王迎军,等.PVA/HA复合水凝胶人工软骨材料的体内外生物活性研究[C].2005年全国高分子学术论文报告会论文摘要集,2005.
[28] 两种不同关节软骨替代材料对兔肝肾功能毒性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(42):8241-8244.
[29] 吴刚,郑裕东,刘青,等.聚乙烯醇/羟基磷灰石复合软骨植入材料性能的研究[C].//2002年材料科学与工程新进展-2002年中国材料研讨会论文集,2002:410-413.
[30] 王教训.聚乙烯醇软骨支架材料的制备及其性能评价[D].哈尔滨工业大学,2012.
[31] 郭涛,杨天府,吴佳齐,等.体内实验评价新型关节软骨修复材料聚乙烯醇/纳米羟基磷灰石+聚酰胺66的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(1):31-34.
[32] 郭涛,杨天府,肖杰,等.生物复合材料聚乙烯醇/纳米羟基磷灰石+聚酰胺66的制备及力学性能评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(45):8859-8862.
[33] 郭涛,杨天府,肖杰,等.新型生物复合材料聚乙烯醇/纳米羟基磷灰石+聚酰胺66修复兔关节软骨缺损[J].中华创伤杂志,2009, 25(8):748-750.
[34] 吴佳奇.新型多孔PVA及其复合物修复兔膝关节骨软骨缺损的实验研究[D].四川大学,2007.
[35] 朱晓丽.生物活性羟基磷灰石的溶胶-凝胶制备及其在人工关节软骨中的应用[D].华南理工大学,2002.
[36] Mishra D,Bhunia B,Banerjee I,et al.Enzymatically crosslinked carboxymethyl-chitosan/gelatin/nano- hydroxyapatite injectable gels for in situ bone tissue engineering application. Mater Science Eng C.2011;31(7):1295-1304.
[37] Tavakol S,Kashani IR,Azami M,et al.In vitro and in vivo investigations on bone regeneration potential of laminated hydroxyapatite/gelatin nanocomposite scaffold along with DBM.J Nanopart Res.2012;14(12):1265.
[38] 刘金龙,张德坤,葛世荣,等.多孔生物陶瓷与PVA水凝胶复合材料的制备与力学性能分析[J].医用生物力学,2011,26(4):341-348.
[39] 潘育松.n-HA/PVA凝胶关节软骨修复材料制备与性能研究[D].南京理工大学,2007.
[40] 戴祖明,张德坤,陈凯等.PVA/HA复合水凝胶力学性能分析及有限元模拟[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(3):344-350. |