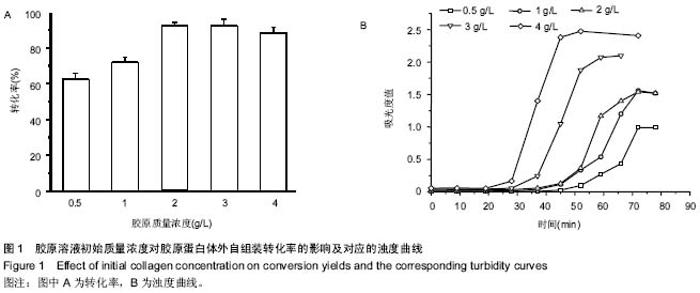
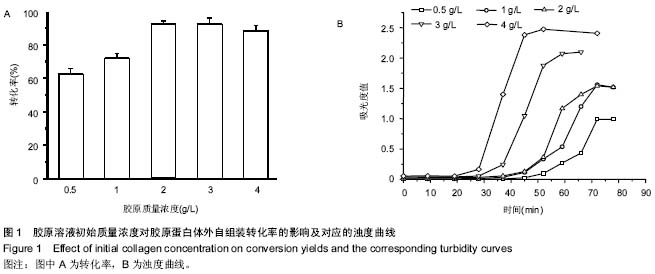
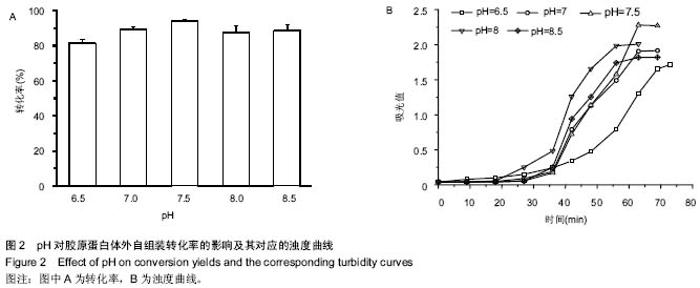
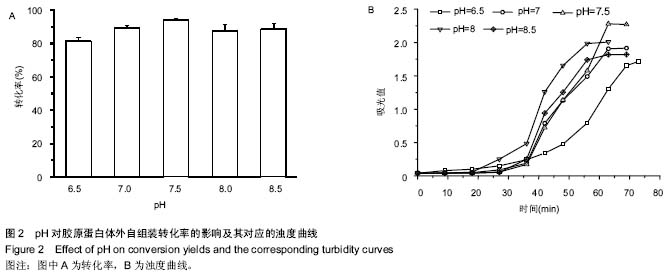
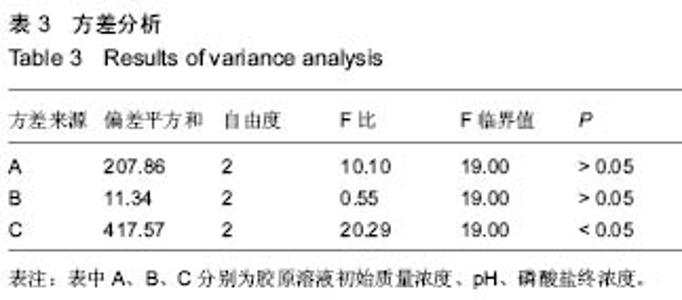
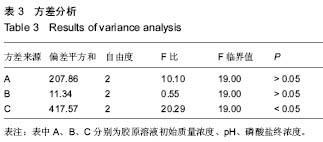
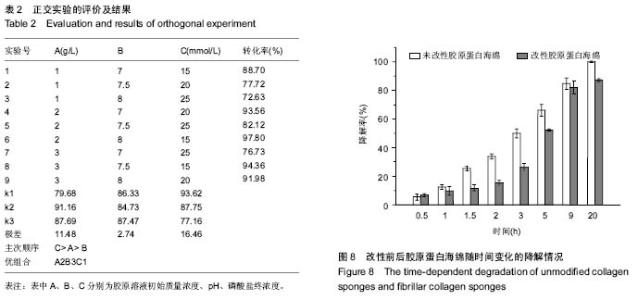
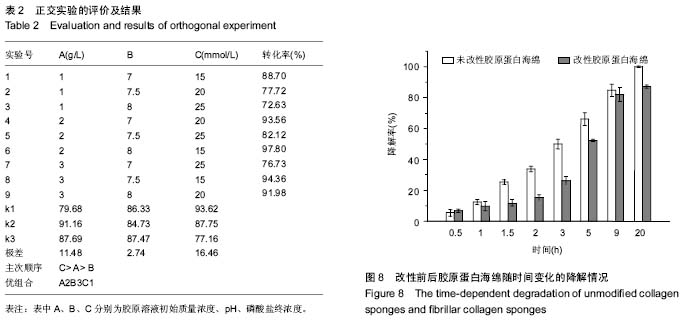
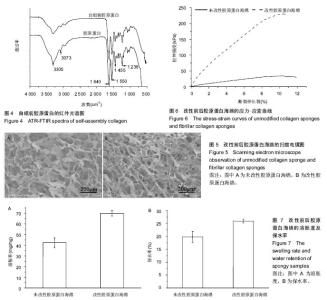
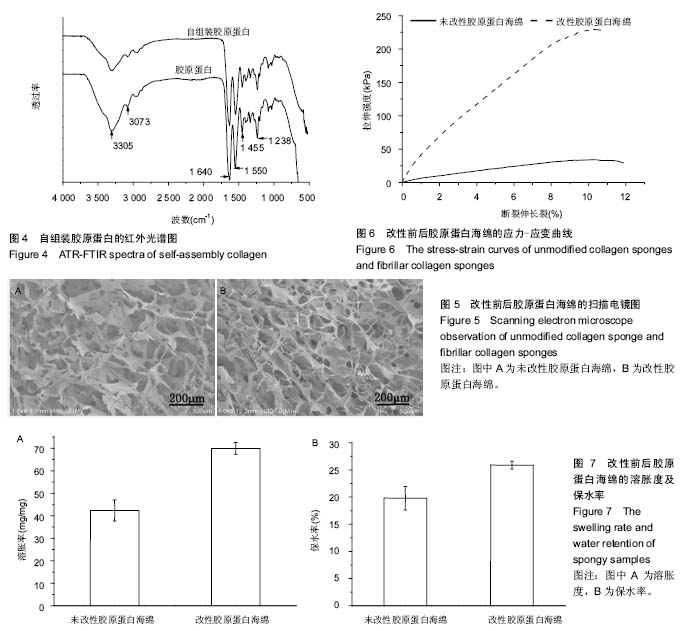
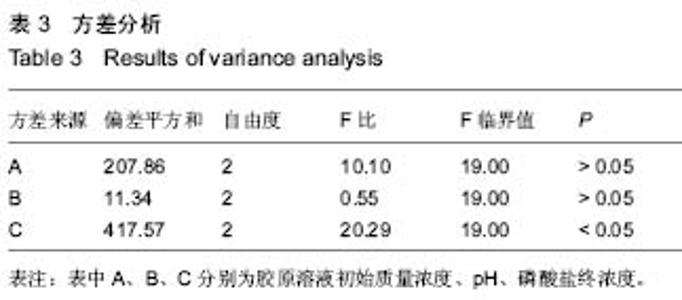
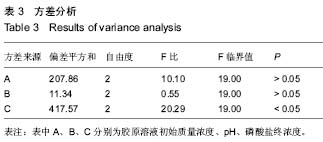
| [1] Eisenbud D,Hettrick H,Evans C,et al. The interdisciplinary CWS, 5 years later. Adv Skin Wound Care.2004;17(7): 336-340.
[2] Palsson BO,Bhatia SN.Tissue Engineering.Pearson Pentice Hall,2003:261-269.
[3] FengX,Tonnesen MG,Mousa S,et al.Fibrin and collagen differentially but synergistically regulate sprout angiogenesis of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells in 3-dimensional matrix.Int J Cell Biol.2013;2013:1-11.
[4] Shen W,Chen X,Hu Y,et al.Long-term effects of knitted silk-collagen sponge scaffold on anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and osteoarthritis prevention. Biomaterials. 2014;35(28):8154-8163.
[5] Perumal S,Ramadass Sk,Madhan B.Sol-gel processed mupirocin silica microspheres loaded collagen scaffold: a synergistic bio-composite for wound healing.Eur J Pharm Sci.2014;52:26-33.
[6] Sun CY,Che YJ,Lu SJ.Preparation and application of collagen scaffold-encapsulated silver nanoparticles and bone morphogenetic protein 2 for enhancing the repair of infected bone. Biotechnol Lett. 2015;37(2):467-473.
[7] Roy S,Driggs J,Elgharably H,et al.Platelet-rich fibrin matrix improves wound angiogenesis via inducing endothelial cell proliferation.Wound Repair Regen. 2011;19(6):753-766.
[8] W?odarczyk-Biegun MK,Werten MW,de Wolf FA,et al. Genetically engineered silk-collagen-like copolymer for biomedicalapplications:Production,characterization and evaluation of cellular response.Acta Biomater. 2014;10(8): 3620-3829.
[9] Murphy CM,Matsiko A,Haugh MG,et al.Mesenchymal stem cell fate is regulated by the composition and mechanical properties of collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2012;11:53-62.
[10] Maeda M,Tanis S,Sano A,et al.Microstructure and release characteristics of the minipellet, a collagen based drug delivery system for controlled release of protein drugs.J Controlled Rel.1999;62:313-324.
[11] Seal BL,OteroTC,Panitch A.Polymeric biomaterials for tissue and organ regeneration.Mater Sci Eng.2001;34:147-230.
[12] 付小兵,吴志谷.现代创伤敷料理论与实践[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2007:651.
[13] 牟善松,马德安,屠美,等.以胶原为基质的组织工程支架材料的制备及组织相容性研究[J].第一军医大学学报,2002,22(10): 878-882.
[14] Park SN,Park JC,Kim HO,et al.Characterization of porous collagen/hyaluronicacid scaffold modified by 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide cross-linking. Biomaterials.2002;23(4):1205-1212.
[15] Jiang D,Yang J,Jiang S.Properties and biocompatibility of collagen scaffold modified by genipin cross-linked L-lysine.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi.2014; 31(4):818-821.
[16] Li Y,Asadi A,Monroe MR,et al.pH effects on collagen fibrillogenesis in vitro: electrostatic interactions and phosphate binding.Mater Sci Eng C. 2009;29:1643-1649.
[17] de Wild M1,Pomp W,Koenderink GH.Thermal Memory in Self-Assembled Collagen Fibril Networks. Biophys J.2013; 105(1):200-210.
[18] Stamov D,Grimmer M,Salchert K,et al.Heparin intercalation into reconstituted collagen I fibrils: Impacton growth kinetics and morphology. Biomaterials.2008; 29(1):1-14.
[19] Raspanti M,Viola M,Sonaggere M,et al.Collagen Fibril structure is affected by collagen concentrationand decorin. Biomacromolecules.2007;8(7):2087-2091.
[20] Fang M,Goldstein EL,Matich EK,et al.Type I collagen self-assembly: the roles of substrate and concentration. Langmuir.2013;29(7):2330-2338.
[21] Franz CM,Muller DJ.Studying Collagen Self-Assembly by Time-Lapse High-Resolution Atomic Force Microscopy. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;736:97-107.
[22] Yan M,Li B,Zhao X,et al.Effect of concentration, pH and ionic strength on the kinetic self-assembly of acid-soluble collagen from walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) skin.Food Hydrocolloids.2012;29(1):199-204.
[23] Stephanopoulos N,Ortony JH,Stupp SI.Self-Assembly for the Synthesis of Functional Biomaterials.Acta Mater.2013;61(3): 912-930.
[24] Dehsorkhi A,Castelletto V,Hamley IW,et al.The effect of pH on the self-assembly of a collagen derived peptide amphiphile. Soft Mater.2013;9:6033-6036.
[25] Silver FH,Freeman JW,Seehra GP.Collagen self-assembly and the development of tendon mechanical properties.J Biomech.2003;36(10):1529-1553.
[26] Silver FH,Freeman JW,Seehra GP.Collagen self-assembly and the development of tendon mechanical properties. Biomaterials.2005;26(14): 1623-1632.
[27] McCall AS,Cummings CF,Bhave G,et al.Bromine is an essential trace element for assembly of collagen IV scaffolds in tissue development and architecture. Cell.2014;157(6): 1380-1392.
[28] Stuart K,Panitch A.Characterization of Gels Composed of Blends of Collagen I, Collagen III, and Chondroitin Sulfate. Biomacromolecules.2009;10(1):25-31.
[29] 方林,黄红海.ATR-FTIR光谱技术在高聚物研究中的应用[J].化学工程师,2008,33(3): 33-36.
[30] Ganim Z,Chung HS,Smith AW,et al. Amide I two-dimensionnal infrared spectroscopy of proteins.Acc Chem Res.2008;41(3):432-441.
[31] Chang MC,Tanaka J.FTIR study for hydroxyapatite/collagen nanocomposite cross-linked by glutaraldehyde. Biomaterials. 2002;23(24):4811-4818. |