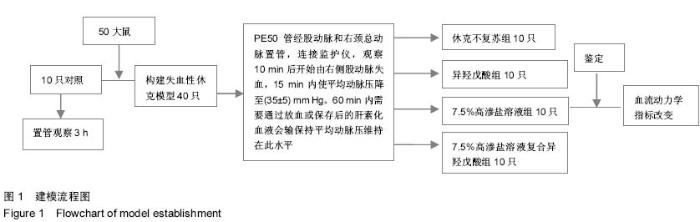
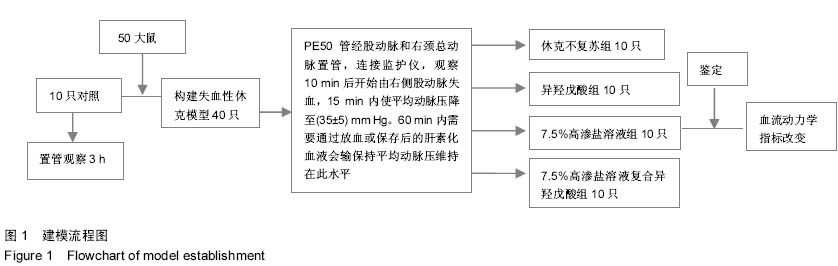
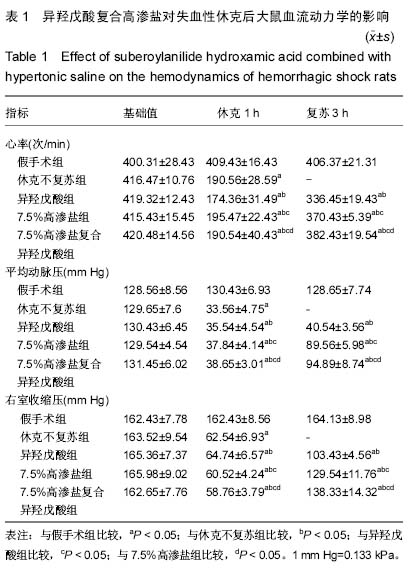
| [1] 刘志国,徐冰心,李建忠,等.液体复苏时机对烫伤休克大鼠内脏血管通透性的影响[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2006,14(10):811- 813.
[2] Paes-da-Silva F, Gonzalez AP, Tibiriçá E. Effects of fluid resuscitation on mesenteric microvascular blood flow and lymphatic activity after severe hemorrhagic shock in rats. Shock. 2003;19(1):55-60.
[3] Lu YQ, Gu LH, Jiang JK, et al. Effect of hypertonic versus isotonic saline reauscit-ation on heme oxygenase-1 expression in visceral organs following hemorrhagic shock in rats. Biomed Environ Sci. 2013;26(8):684-688.
[4] Gonzales ER, Chen H, Munuve RM, et al. Hepatoprotection and lethality rescue by histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid in fatal hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma. 2008;65(3): 554-565.
[5] 朱捷,帅小军,何晓冉.高渗盐水对创伤失血性休克患者T细胞免疫的影响[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2009,18(4):376-379.
[6] Shang Y, Jiang Y, Ze-jun D, et al. Valproic acid attenuates the multiple-organ dysfunction in a rat model of septic shock. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010;123(19):2682.
[7] Finkelstein RA, Li Y, Liu B, et al. Treatment with histone deacetylase inhibitor attenuates MAP kinase mediated liver injury in a lethal model of septic shock. J Surg Res. 2010; 163(1): 146-154.
[8] DuBose JJ, Kobayashi L, Lozornio A, et al. Clinical experience using 5% hypertonic saline as a safe alternative fluid for use in trauma. J Trauma. 2010;68(5):1172-1177.
[9] Cotton BA, Guy JS, Moms JA Jr, el al. The cellular, metabolic, and systemic consequences of aggressive fluid resuscitation strategies. Shock. 2006;26(2):115-121.
[10] Zacharias N, Sailhamer EA, Li Y, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent apoptosis following lethal hemorrhagic shock in rodent kidney cells. Resuscitation. 2011;82(1): 105-109.
[11] Liu Z, Li Y, Liu B, et al. Synergistic effects of hypertonic saline and valproic acid in a lethal rat two-hit model. J Trauma. 2013; 74(4):991-998.
[12] 杨瑞,李亚洁.行大鼠股动脉插管术的体会[J].护理研究,2004, 18(3):429-430.
[13] Wiggers HC, Ingraham RC. Hemorrhagic shock; definition and criteria for its diagnosis. J Clin Invest. 1946;25(10)30-36.
[14] Santry HP, Alam HB. Fluid resuscitation: past, present, and the future. Shock. 2010;33(3):229-241.
[15] Thompson R, Greaves I. Hypertonic saline-hydroxyethyl starch in trauma resuscitation. J R Army Med Corps. 2006; 152(1):6-12.
[16] Machiedo GW, Zaets SB, Berezina TL, et al. Trauma-hemorrtiagic shock- induced red blood cell damage leads to decreased microcirculatory blood flow. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(3):1000-1010.
[17] Li HB, Wang GZ, Gong J, et al. BML-111 attenuates hemorrhagic shock-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in rats. J Surg Res. 2013;183(2):710-719.
[18] Mihaescu A, Santén S, Jeppsson B, et al. p38 Mitogen- activated protein kinase signalling regulates vascular inflammation and epithelial barrier dysfunction in an experimental model of radiation-induced colitis. British J Surg. 2010;97(2):226-234.
[19] 望亭松,陆一鸣,喻中城.高渗氯化钠羟乙基淀粉40治疗失血性休克的初步研究[C].第17届世界灾难及急救医学学术会议暨第14次全国急诊医学学术年会论文汇编.2011.
[20] 余高锋,庞红宇,郭娜,等.不同溶液小容量复苏对内毒素休克大鼠肾组织病理和氧化应激的影响[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2012, 17(6):491-495.
[21] Zarychanski R, Abou-Setta A M, Turgeon A F, et al. Association of hydroxyethyl starch administration with mortality and acute kidney injury in critically ill patients requiring volume resuscitation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2013;309(7):678-688.
[22] Kim HJ, Lee KH. The effectiveness of hypertonic saline and pentoxifylline (HTS–PTX) resuscitation in haemorrhagic shock and sepsis tissue injury: comparison with LR, HES, and LR-PTX treatments. Injury. 2012;43(8):1271-1276.
[23] 李荣国,王剑,王小欧,等.7.5%高渗盐水用于创伤性失血性休克早期复苏的观察[J].现代临床医学,2012,38(3):182-184.
[24] Besnard AG, Togbe D, Couillin I, et al. Inflammasome-IL-1-Th 17 response in allergic lung inflammation. J Mol Cell Biol. 2012;4(1):3-10.
[25] Shih CC, Chen SJ, Chen A, et al. Therapeutic effects of hypertonic saline on peritonitis-induced septic shock with multiple organ dys¬function syndrome in rats. Crit Care Med. 2008;36(6):1864-1872.
[26] Bouglé A, Harrois A, Duranteau J. Resuscitative strategies in traumatic hemorrhagic shock. Ann Int Care. 2013;3(1):1-9.
[27] Oreopoulos GD, Bradwell S, Lu Z, et al. Synergistic induction of IL-10 by hypertonic saline solution and lipopolysaccharides in murine peritoneal macrophages. Surgery. 2001;130(2): 157-165.
[28] Wohlauer M, Moore EE, Silliman CC, et al. Nebulized hypertonic saline attenuates acute lung injury following trauma and hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med. 2012;40(9):2647.
[29] Junger WG, Rhind SG, Rizoli SB, et al. Resuscitation of traumatic hemorrhagic shock patients with hypertonic saline-without dextran-inhibits neutrophil and endothelial cell activation. Shock. 2012;38(4):341.
[30] Kochanek AR, Fukudome E Y, Li Y, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor treatment attenuates MAP kinase pathway activation and pulmonary inflammation following hemorrhagic shock in a rodent model. J Surg Res. 2012;176(1):185-194.
[31] Li Y, Alam HB. Creating a pro-survival and anti-inflammatory phenotype by modulation of acetylation in models of hemorrhagic and septic shock. Recent Advances on Model Hosts. Springer, New York, USA. 2012:107-133.
[32] Zacharias N, Sailhamer EA, Li Y, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent apoptosis following lethal hemorrhagic shock in rodent kidney cells. Resuscitation. 2011;82(1): 105-109.
|