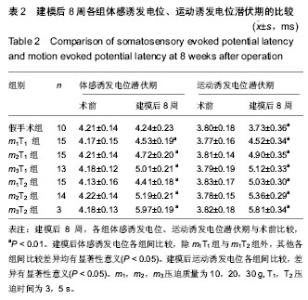
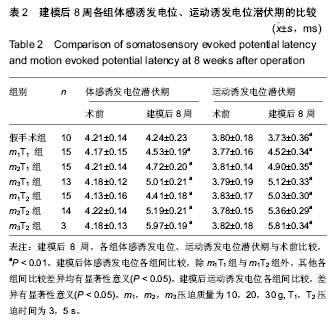
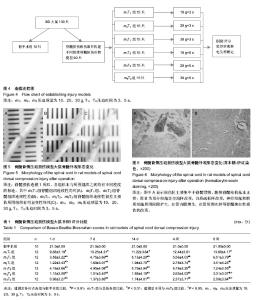
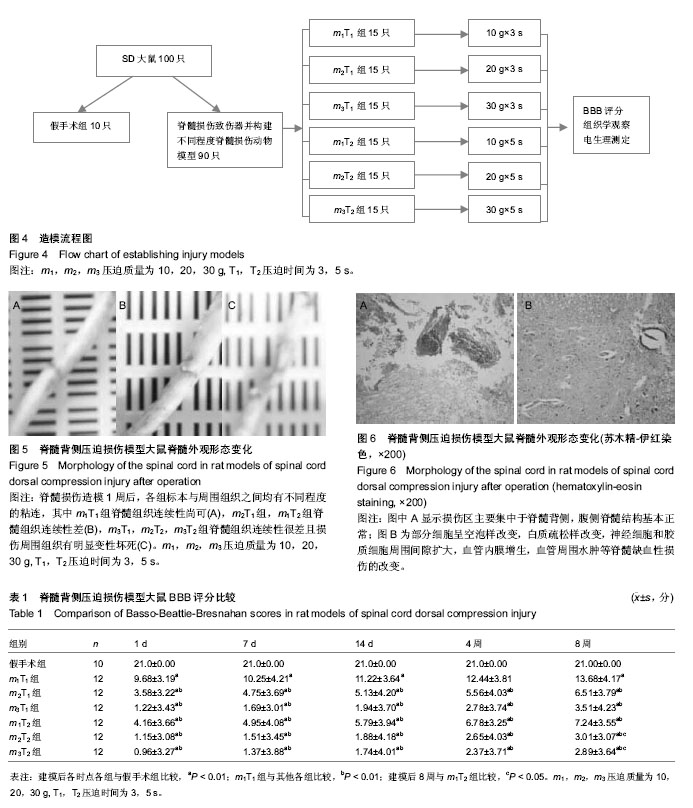
| [1] Margolis JM, Juneau P, Sadosky A, et al. Health care resource utilization and medical costs of spinal cord injury with neuropathic pain in a commercially insured population in the United States. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(12): 2279-2287.
[2] Vawda R, Fehlings MG. Mesenchymal cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: current future perspectives. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8:25-38.
[3] Varma AK, Das A, Wallace G, et al.Spinal cord injury: a review of current therapy, future treatments, and basic science frontiers. Neurochem Res. 2013;38:895-905.
[4] Nagoshi N, Fehlings MG. Investigational drugs for the treatment of spinal cord injury: review of preclinical studies and evaluation of clinical trials from Phase I to II. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015:1-14.
[5] Hamid S, Hayek R. Role of electrical stimulation for rehabilitation and regeneration after spinal cord injury: an overview. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(9):1256-1269.
[6] Kaptanoglu E, Tuncel M, Palaoglu S, et al. Comparison of the effects of melatonin and methylprednisolone in experimental spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg. 2000;93(Suppl 1):S77-S84.
[7] Fairbanks CA, Schreiber KL, Brewer KL, et al. Agmatine reverses pain induced by inflammation, neuropathy, and spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(19): 10584-10589.
[8] Mann CM, Lee JHT, Hillyer J, et al. Lack of robust neurologic benefits with simvastatin or atorvastatin treatment after acute thoracic spinal cord contusion injury. Exp Neurol. 2010;221(2): 285-295.
[9] Lee JHT, Tigchelaar S, Liu J, et al. Lack of neuroprotective effects of simvastatin and minocycline in a model of cervical spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2010;225(1):219-230.
[10] Erichsen HK, Hao JX, Xu XJ. Comparative actions of the opioid analgesics morphine,methadone and codeine in rat models of peripheral and central neuropathic pain. Pain. 2005; 116(3):347-358.
[11] Marques SA, Garcez VF, Del Bel EA, et al. A simple, inexpensive and easily reproducible model of spinal cord injury in mice: morphological and functional assessment. J Neurosci Methods. 2009;177(1):183-193.
[12] Ito T, Ohtori S, Inoue G, et al. Glial phosphorylated p38 MAP kinase mediates pain in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation and induces motor dysfunction in a rat model of lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(2):159-167.
[13] Wang G, Thompson SM. Maladaptive homeostatic plasticity in a rodent model of central pain syndrome: thalamic hyperexcitability after spinothalamic tract lesions. J Neurosci. 2008;28(46):11959-11969.
[14] Hashimoto T, Fukuda N. New spinal cord injury model produced by spinal cord compression in the rat. J Pharmacol Methods. 1990;23(3):203-212.
[15] Caudle KL, Atkinson DA, Brown EH, et al. Hindlimb stretching alters locomotor function after spinal cord injury in the adult rat. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2015;29(3):268-277.
[16] Wong JK, Sharp K, Steward O. A straight alley version of the BBB locomotor scale. Exp Neurol. 2009;217(2):417-420.
[17] Anderson TE. A controlled pneumatic technique for experimental spinal cord contusion. J Neurosci Methods. 1982;6:327-233.
[18] Vijayaprakash KM, Sridharan N. An experimental spinal cord injury rat model using customized impact device: a cost-effective approach. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013; 4(3): 211-213.
[19] Moriyama H, Tobimatsu Y, Ozawa J, et al. Amount of torque and duration of stretching affects correction of knee contracture in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(11):3626-3636.
[20] Vijayaprakash KM, Sridharan N. An experimental spinal cord injury rat model using customized impact device: A cost?effective approach. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013;3(4): 211-213.
[21] Koffler J, Samara RF, Rosenzweig ES. Using templated agarose scaffolds to promote axon regeneration through sites of spinal cord injury. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1162:157-165.
[22] Zheng B, Lee JK, Xie F. Genetic mouse models for studying inhibitors of spinal axon regeneration. Trends Neurosci. 2006;29:640-646.
[23] Nishi RA, Liu H, Chu Y, et al. Behavioral, histological, and ex vivo magnetic resonance imaging assessment of graded contusion spinal cord injury in mice. J Neurotrauma. 2007;24: 674-689.
[24] Leroux LG, Bredow S, Grosshans D, et al. Molecular imaging detects impairment in the retrograde axonal transport mechanism after radiation-induced spinal cord injury. Mol Imaging Biol. 2014;7:1145-1149.
[25] Hoschouer EL, Yin FQ, Jakeman LB. L1 cell adhesion molecule is essential for themaintenance of hyperalgesia after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2009;1(216):22-34.
[26] Kim P, Haisa T, Kawamoto T, et al. Delayed myelopathy induced by chronic compression in the rat spinal cord. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:503-511.
[27] Barros Filho TE, Molina AE. Analysis of the sensitivity and reproducibility of the Basso, Beattie, Bresnahan (BBB) scale in Wistar rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2008;63(1):103-108.
[28] Scheff SW, Saucier DA, Cain ME. A statistical method for analyzing rating scale data: the BBB locomotor score. J Neurotrauma. 2002;19(10):1251-1260.
[29] Talac R, Friedman JA, Moore MJ, et al. Animal models of spinal cord injury for evaluation of tissue engineering treatment strategies. Biomaterials. 2004;25:1505-1510.
[30] Ferguson AR, Hook MA, Garcia G, ey al. A simple post hoc transformation that improves the metric properties of the BBB scale for rats with moderate to severe spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2004;21(11):1601-1613.
[31] Mets GA, Curt A, van de Ment H, et al. Validation of the weisht-drop contusion model in rats:a comparative study of human spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000;17:1-17.
[32] Fukuda S, Nakamura T, Kishigami Y, et al. New canine spinal cord injury model free from laminectomy. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 2005;14:171-180. |