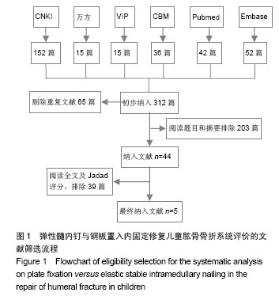
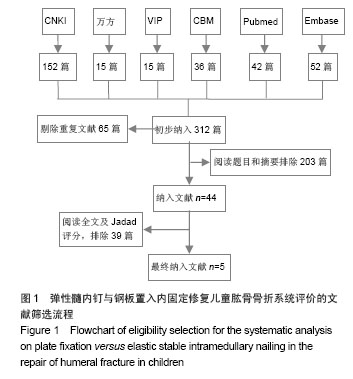
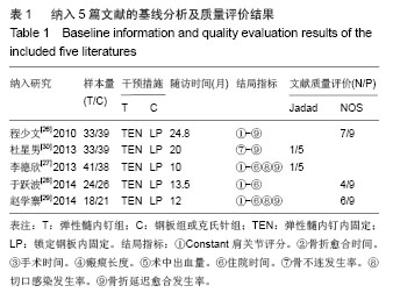
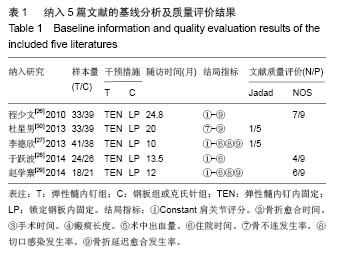
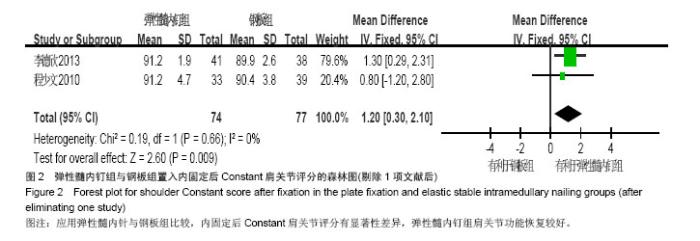
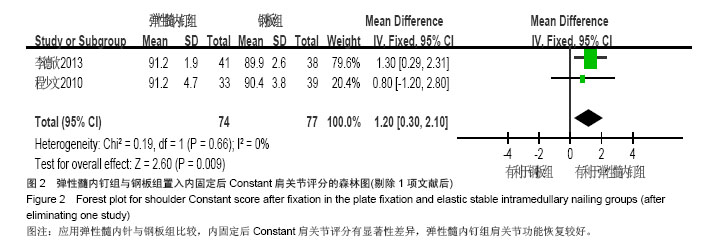
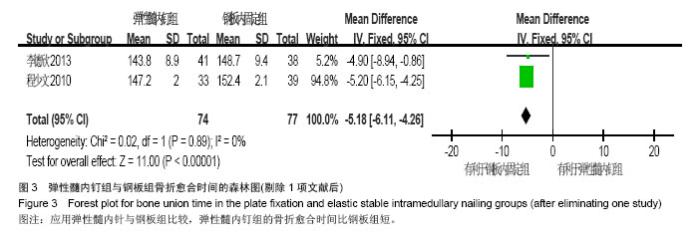
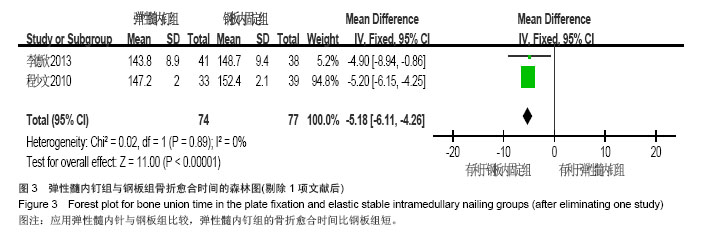
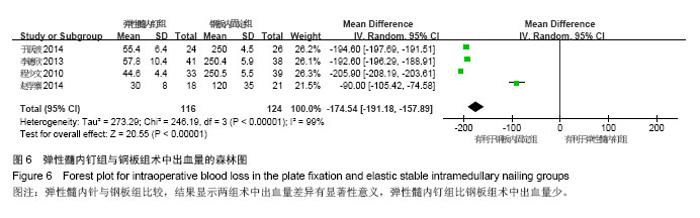
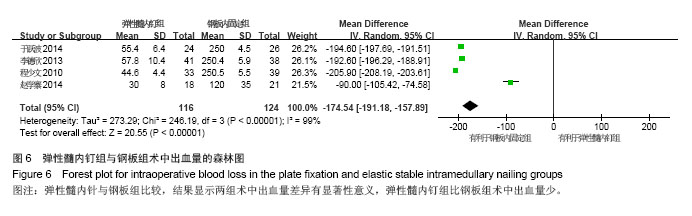
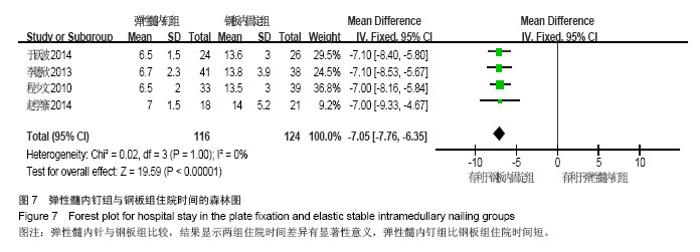
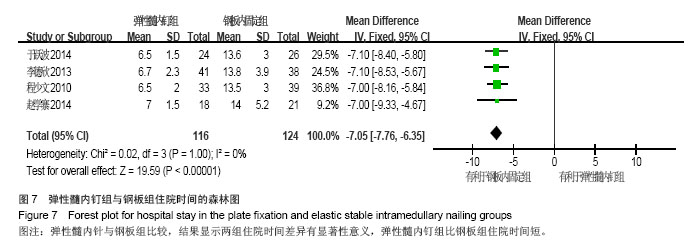
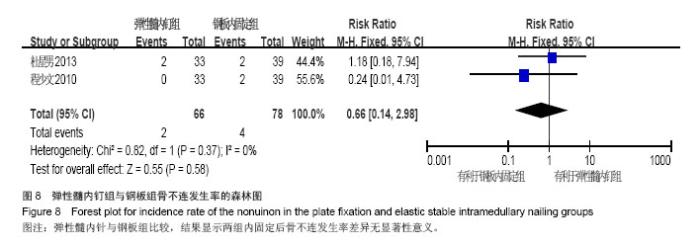
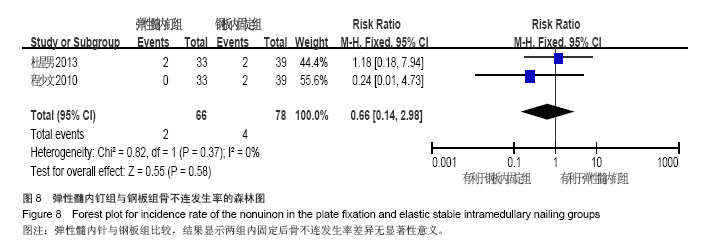
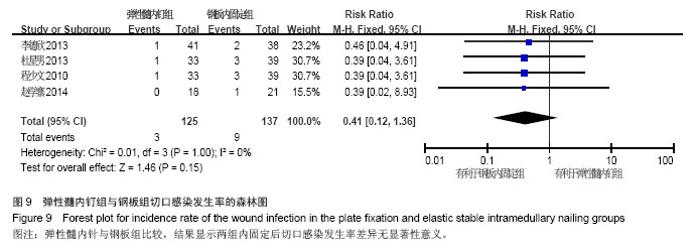
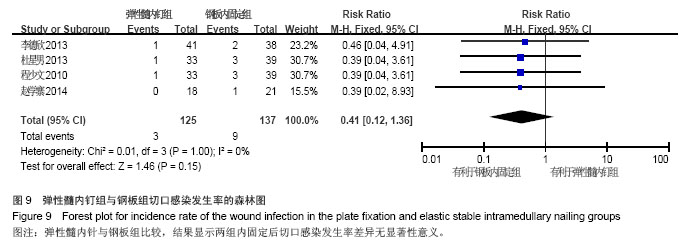
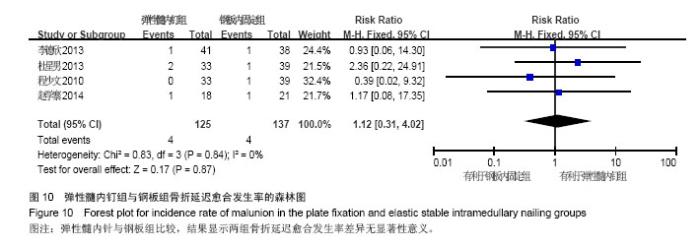
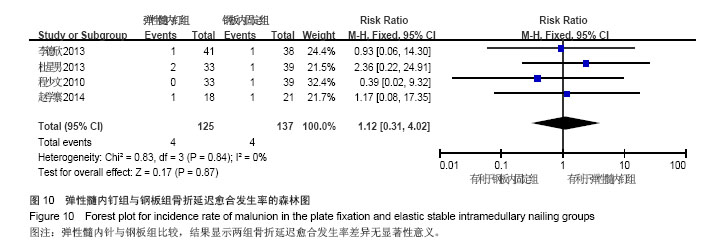
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (17): 2782-2788.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.17.028
Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation for the repair of humeral fractures in children: a meta-analysis
Lv Gang, Meng Qing-cai, Miao De-sheng, Ma Lei
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2015-04-23Published:2015-04-23 -
Contact:Meng Qing-cai, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Lv Gang, Master, Chief physician, Associate professor, Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lv Gang, Meng Qing-cai, Miao De-sheng, Ma Lei . Elastic stable intramedullary nailing versus plate fixation for the repair of humeral fractures in children: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(17): 2782-2788.
share this article
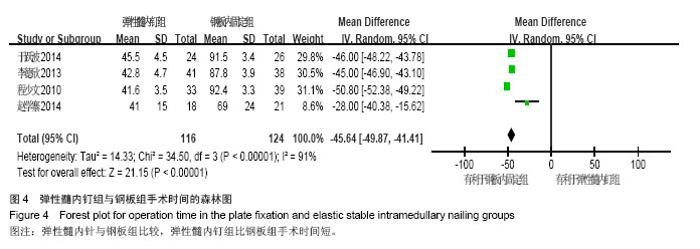
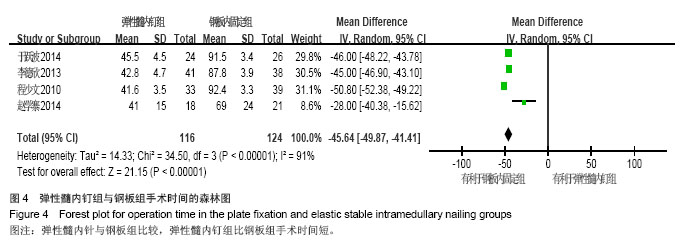
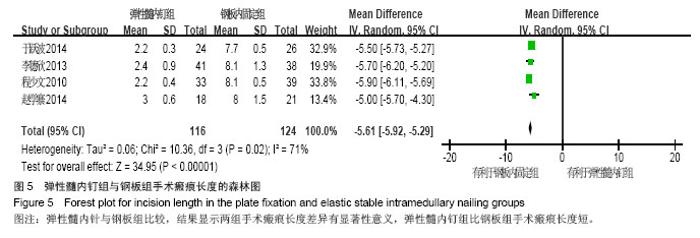
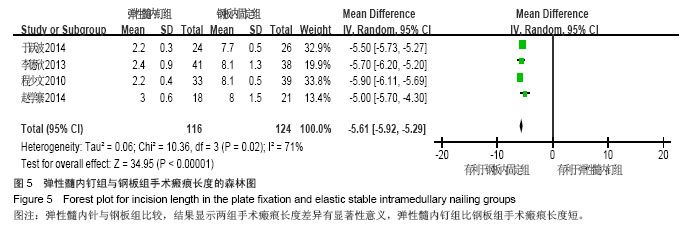
| [1]Beaty JH. Fractures of the proximal humerus and shaft in children. Instr Course Lect. 1992;41:369-372. [2]Jubel A, Andermahr J, Isenberg J, et al. Experience with elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) of shaft fractures in children. Orthopade. 2004;33(8):928-935. [3]Steffner RJ, Lee MA. Emerging concepts in upper extremity trauma: humeral shaft fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2013; 44(1):21-33. [4]Lascombes PT, Journeau HP. Use and abuse of flexible intramedullary nailing in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop. 2006;26(6):827-834. [5]Schaffer K, Bohm R, Dietz HG. [Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children]. Unfallchirurg. 2007;110(10):852-858. [6]徐璐杰,朱建.儿童长骨骨折弹性髓内针治疗后骨延迟愈合及不愈合[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2012,33(1):38-41. [7]慕明章,唐伟,杨建平.克氏针髓内交叉固定治疗儿童肱骨干骨折 [J].中华小儿外科杂志,2006, 27(9):495-496. [8]董展,楼跃,唐凯,等.弹性髓内钉微创治疗小儿肱骨干骨折33例 [J].中华创伤杂志,2014,30(4):333-335. [9]王小林,邵景范,杨小进,等. 弹性髓内针固定治疗大龄儿童严重移位肱骨近端骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(3):345-348. [10]肖健,邱晗,陈蕾.闭合复位弹性髓内针固定治疗儿童四肢长骨粉碎性骨折[J].长春中医药大学学报, 2013,29(4):680-681,687. [11]孙祥水,楼跃,唐凯,等.弹性髓内针逆行髓内固定治疗大龄儿童肱骨近端骨折 [J].南京医科大学学报•自然科学版, 2013,33(4): 537-539. [12]周曙光,陈建雯,俞辉国.弹性髓内针治疗儿童长骨骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(4):306-308. [13]杨宜,舒世琼,鲍同柱.弹性钛髓内钉固定治疗儿童肱骨髁上骨折肘内翻畸形矫治中的应用研究[J].中国医药导报, 2012, 9(26):58-59. [14]王伟,程少文,彭磊,等.弹性髓内钉在儿童肱骨骨折中的应用[J]. 临床小儿外科杂志,2011,10(1):30-32. [15]蔡豪祺,王志刚,蔡海清,等.钛制弹性髓内钉治疗儿童肱骨高位髁上骨折及交界性骨折[J].中华小儿外科杂志, 2011, 32(11):845-849. [16]刘俊才,王月敏,纪春生,等.应用钛制弹性髓内针微创治疗儿童长骨骨折[J].黑龙江医学, 2010,10(9):694-695. [17]胡孔才,曹进,诸葛天瑜,等.闭合复位弹性髓内钉内固定治疗儿童肱骨干骨折[J].中医正骨,2010, 22(9):58-59. [18]Lefevre Y, Journeau P, Angelliaume A, et al. Proximal humerus fractures in children and adolescents. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(1 Suppl):S149-156. [19]Khan A, Athlani L, Rousset M, et al. Functional results of displaced proximal humerus fractures in children treated by elastic stable intramedullary nail. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(2):165-172. [20]Canavese F, Athlani L, Marengo L, et al. Evaluation of upper-extremity function following surgical treatment of displaced proximal humerus fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2014;23(2):144-149. [21]Sessa S, Lascombes P, Prevot J, et al. Centro-medullary nailing in fractures of the upper end of the humerus in children and adolescents. Chir Pediatr. 1990;31(1):43-46. [22]Higgins J, Green S (Editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011, Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org. [23]Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17(1):1-12. [24]Ga Shea BW, O'connell D. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale(NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses, URL:http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_ epidemiology/oxford.asp. [25]Constant CR, Murley HG. A clinical method of functional assessment of shoulder. Clin Orthop. 1987;214:160-164. [26]程少文,王伟,林忠勤,等.弹性髓内钉与锁定钢板内固定治疗儿童肱骨骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2010, 18(11): 26-28. [27]李德欣.弹性髓内钉与锁定钢板内固定治疗儿童肱骨骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中国当代医药, 2013, 20(19):22-23. [28]于跃波.弹性髓内钉与锁定钢板内固定治疗儿童肱骨骨折的疗效比较[J]. 医学信息, 2014, 28(5):156-156,157. [29]赵学寨.弹性髓内钉与接骨板治疗大龄儿童肱骨干骨折的对比研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2014, 13(11):948-950. [30]杜星男.弹性髓内钉与锁定钢板内固定治疗儿童肱骨骨折的疗效比较[J].中国保健营养(下旬刊), 2013, 23(11):6352. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [8] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [9] | Zhang Jing, Wang Bin, Lü Xin. Application of anatomic intramedullary nail in tubular bone fractures of limbs: stronger holding force and anti-rotation ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 917-922. |
| [10] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [11] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [12] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [13] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [14] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [15] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||