Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (17): 2775-2781.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.17.027
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomarkers of deep venous thrombosis after total joint arthroplasty
Chen Hui, Wang Yan
- Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, China
-
Online:2015-04-23Published:2015-04-23 -
Contact:Wang Yan, M.D., Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Chen Hui, Studying for doctorate, Department of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Medical School of Chinese PLA, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:the National High-tech R&D Program (863 Program), No. 2006AA02A136, 2011AA030101
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Hui, Wang Yan . Biomarkers of deep venous thrombosis after total joint arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(17): 2775-2781.
share this article
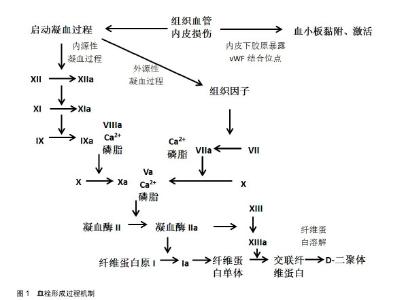
2.1 凝血相关标志物 2.1.1 D-二聚体 D-二聚体是稳定型纤维蛋白经纤溶酶水解所产生的特异性降解产物[5]。纤维蛋白原经凝血酶转化为可溶性的纤维蛋白单体,后者自发聚合形成可溶性的纤维蛋白聚合物。凝血酶在钙离子的作用下激活交联纤维蛋白聚合物的ⅩⅢ因子,形成交联纤维蛋白。然后在活化ⅩⅢ因子的介导下,纤溶酶降解交联纤维蛋白,生成包括D-二聚体在内的多种交联纤维蛋白降解产物。监测血浆中D-二聚体值有助于下肢深静脉血栓的诊断[6-8]。 目前D-二聚体检查是临床上评估静脉血栓栓塞症最常用的检测指标之一。急性深静脉血栓患者中血液中D-二聚体水平会显著升高,近年来学者也进行了大量研究。Bounameaux 等[9]对膝关节置换后患者行静脉造影,D-二聚体水平敏感性和特异性分别为73.5%和 58.8%。Khaira等[10]评估血浆D-二聚体水平相较于静脉造影敏感性和特异性分别为96%和40%。Watanabe等[11]研究发现,行多排计算机断层CT扫描的无症状深静脉血栓患者中,血栓组的D-二聚体水平在置换后第4天比无血栓组显着增高,敏感性和特异性分别为75%和63%。表明D-二聚体对深静脉血栓诊断的准确性较好,也就是说可以提高疑似深静脉血栓患者诊断的准确性。所以,作者得出结论血浆D-二聚体正常可排外深静脉血栓诊断,也就是说D-二聚体不能作为深静脉血栓诊断的特异性指标。因为继发性纤维蛋白溶解功能亢进如肝脏疾病、怀孕、肿瘤、近期的创伤或手术、大量出血以及多处创伤等情况也可导致血浆D-二聚体的升高[12-15]。Bounameaux等[9]研究指出单独的D-二聚体检测就可以排除门诊1/3深静脉血栓可疑患者,节约大量的花费及时间。2014年欧洲心脏病学会发布的急性肺栓塞诊断和管理指南指出,D-二聚体的特异性随着年龄的增长下降[16]。Douma等[17]的多中心、前瞻性研究发现,如果患者年龄超过50岁,使用年龄校正过的D-二聚体(年龄×10 μg/L),用以代替以往临界值标准500 μg/L,排除肺栓塞的可能性6.4%升至29.7%,没有其他假阴性的发现。总的来说,D-二聚体可以作为深静脉血栓诊断的排外检查指标。 2.1.2 Ⅷ因子 凝血因子Ⅷ是一种高分子糖蛋白辅助因子,由2 332个氨基酸残基组成,由血管、肾小球内皮细胞和肝脏血窦细胞合成和释放入血液[18]。在循环血液中,Ⅷ因子与血管性血友病因子(von Willebrand factor,vWF)以稳定复合体的形式存在,凝血酶是生成Ⅷa因子的惟一激活剂[19]。在凝血级联反应中,Ⅷa因子作为辅因子与Ⅸa因子结合。便可以在血小板表面迅速激活X因子生成大量的Ⅹa因子,从而连接Va因子进一步将凝血酶原转化为凝血酶,最后将纤维蛋白原转化为纤维蛋白,由ⅩⅢ a因子令纤维素发生交联形成稳固的血凝块。 高水平的Ⅷ因子是首次和再发静脉血栓栓塞症的一个独立剂量依赖危险因素[20]。Ota等[21]对68名静脉血栓栓塞症患者及40名对照组进行平均随访期为52.6个月的Ⅷ因子水平回顾性研究,Logistic回归分析得出在日本人群中高水平的血浆Ⅷ因子是静脉血栓栓塞症的危险因素,而且高于75%水平的Ⅷ因子对静脉血栓栓塞症发生有显著影响。Kraaijenhagen等[22]研究发现Ⅷ因子水平每增10×103 IU/L,初次患静脉血栓栓塞症的风险增加10%。此外,Ⅷ因子水平每增10×103 IU/L,静脉血栓栓塞症复发的风险增加了24%。Ⅷ因子水平和静脉血栓栓塞症再发危险性呈非线性关系。Tichelaar等[23]研究发现尤其是在Ⅷ因子水平持续增高的住院患者中,其水平可部分受到急性期反应影响,也就是说Ⅷ因子水平增高是原因而不是静脉血栓栓塞症所引起的后果。 而目前一些学者在基因层面研究血栓与Ⅷ因子之间的关系。高水平Ⅷ因子通过降低活化蛋白C的抗凝作用,从而导致活化蛋白C抵抗和随后的高凝状态。Soria等[24]研究指出活化蛋白C抵抗和Ⅷ因子水平是血栓形成的主要潜在危险因素,它们共同受到18号染色体数量性状位点的影响。Viel等[25]研究发现92714C > G (rs1800291)与Ⅷ因子水平显著相关。92714C>G是一个非同义单核苷酸多态性编码B结构域替代D1241E。Emmerechts等[26]通过建立小鼠静脉血栓栓塞模型,部分抑制Ⅷ因子或可以提供抗血栓作用,同时避免过度抗凝。这些试验数据为血栓的预防诊治提供了有效简单安全的策略。 2.1.3 凝血酶生成 凝血酶是凝血级联加速的关键,它是血小板、Ⅴ因子和Ⅷ因子的激活剂,而且是正反馈循环重要组成,用以产生更多的凝血酶,将纤维蛋白原转化为纤维蛋白,最终形成血凝块。凝血级联反应激活后血浆中可检测出凝血酶生成。凝血酶生成可通过多种方式表达,包括滞后时间(即从反应开始到凝血酶开始生成所经历的时间),凝血酶生成峰值及凝血酶生成潜力(即凝血酶生成曲线下的积分面积,反映单位时间凝血酶生成的量)等[27]。 许多研究证实凝血酶生成是静脉血栓栓塞症的危险因素之一,而且可以作为预测指标评估静脉血栓栓塞症。Ryland等[28]一项前瞻性队列研究表明对于有静脉血栓栓塞症史的患者凝血酶生成潜力和凝血酶生成峰值显著增高,且凝血酶生成和Ⅷ因子水平呈显著相关。但相反的,Haas等[29]的前瞻性队列研究表明单独的凝血酶生成不适合作为深静脉血栓的排外指标;仅在老年人中由于滞后时间指标的加入排外深静脉血栓或许会明显增加。所以可以将D-二聚体和凝血酶生成相结合,以提高诊断及排除静脉血栓栓塞症的敏感性、特异性。 2.1.4 纤维蛋白单体 血栓形成包括血小板活化、凝血系统增强及纤维蛋白形成等阶段。血栓形成时纤维蛋白原转化成包括纤维蛋白单体、纤维蛋白(原)降解产物及D-二聚体在内的纤维蛋白,其中纤维蛋白单体产生的最早,故其可作为如关节置换后深静脉血栓早期诊断的一种有意义的生物标记物[30]。Caliezi等[31]的研究纤维蛋白单体水平以 3.5 g/L为临界值,诊断深静脉血栓的敏感性、特异性及阴性预测值为100%(95% CI: 94%-100%), 35.6% (95% CI:23%-48%) 及100% (95% CI:86%-100%)。 而D-二聚体产生稍晚,但较稳定,持续时间长。所以纤维蛋白单体可被看作是血栓形成前的检测标志物,D-二聚体可被看作是血栓形成后的检测标志物。Dopsaj等[32]绘制受试者工作曲线,得出纤维蛋白单体及D二聚体联合检测组结果相较于单独D-二聚体组更为可靠。故日常临床工作中,两者联用可提高深静脉血栓预测的准确性(图1)。 2.2 炎性标志物 2.2.1 P-选择素 P-选择素是一种相对分子质量为140 000的跨膜糖蛋白,为细胞黏附分子选择素之一,主要分布于静息血小板(α颗粒)和内皮细胞的Weibel- Palade小体中。目前许多学者致力于研究其与凝血、血栓形成的关系[33-37]。当血小板和内皮细胞受到刺激(如受损)时,血小板活化,P-选择素从胞质中迅速转移至细胞膜并融合,在血小板及内皮细胞的细胞膜表面表达,成为血小板活化的特征标志之一。P-选择素的水平大多与血小板激化有关,而且P-选择素的上调与血栓栓塞的发生率相关。有报道P-选择素表达上调使得发生血栓栓塞的危险上升1.7倍[38]。P-选择素糖蛋白配体1是P-选择素在白细胞上的主要配体,他们的黏附介导了白细胞的最初趋集以及单核细胞/巨噬细胞等白细胞、血小板与血管内皮之间的作用,参与血栓形成过程[39]。 另外,P-选择素刺激还可以增加单核细胞上组织因子的表达,并介导组织因子转移至血小板。组织因子与血中FVIIa结合形成FVIIa/组织因子复合物,始动血栓形成过程中的凝血反应[40]。有研究表明包括磷脂酰丝氨酸在内的P-选择素的表达可增加单核细胞中表面依赖凝血酶生成[41],显示可能存在另外的凝血机制。 许多体外实验研究表明P-选择素在血栓形成机制上起重要作用[42]。Myers等[43]研究显示P-选择素及E-选择素缺失的转基因动物组相较于野生型动物组血栓发生率低,后者P-选择素呈高凝集状态。亦有研究显示静脉血栓栓塞症患者在应激状态或下发生静脉血栓栓塞症后数月可溶性P-选择素增高[44-45]。尽管一些研究表明P-选择素不失为一种简便经济的诊断深静脉血栓的指标[46]。而对于另外一些研究P-选择素作为深静脉血栓的诊断指标仍存在争议[43]。Shi等[47]研究显示患者接受全髋关节置换后发生深静脉血栓组与未发生深静脉血栓组之间的P-选择素差异无显著性意义,P-选择素可能不能作为预测髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓发生的指标。 2.2.2 炎性因子 目前越来越多的静脉血栓栓塞症研究指向了C-反应蛋白、白细胞介素如白细胞介素1β,白细胞介素6,白细胞介素8,白细胞介素10等炎性因子[48]。炎性因子可影响组织因子的表达,组织因子是外源凝血途径的启动子,导致血栓形成。 静脉血栓栓塞症可致C-反应蛋白水平增高[49]。不同研究机构的实验研究对于C-反应蛋白与静脉血栓栓塞症是否有关系结论不一。有研究指出C-反应蛋白可作为静脉血栓栓塞症诊断的潜在评估指标[50-51]。但Tsai等[52]研究指出C-反应蛋白基线水平与静脉血栓栓塞症的发展无明显关系。所以单独的血浆C-反应蛋白不能作为深静脉血栓的诊断指标[53]。肿瘤坏死因子α,白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8等促炎性因子被认为是静脉血栓栓塞症的风险因素,而抗炎因子白细胞介素10趋势下降[54]。Downing等[55]研究发现中和白细胞介素10会增加炎症和血栓形成,补充外源性的白细胞介素10可以降低炎症和血栓形成。因此白细胞介素10可以作为静脉血栓栓塞症的治疗用药。 2.2.3 细胞膜微粒 国际血栓与止血协会定义细胞膜微粒为大小在0.1-1.0 μm之间小膜囊泡,来源于血小板、白细胞、红细胞几千血管内皮细胞凋亡或激活后的释放,其脂质双层的外层中表达带有负电荷的磷脂酰丝氨酸,可为凝血过程提供所必需的负离子磷脂表面,也可加速细胞-细胞间的信息交流。细胞膜微粒可以通过各自特定亲本细胞的表面抗原成分进行检测[56-57]。 近年来,细胞膜微粒被认为在抗炎、血凝及血管功能方面发挥作用[58]。Morel等[59]研究发现血管损伤,凝血等疾病状态时细胞膜微粒水平上调,显示细胞膜微粒等与绝大部分心血管危险因素有关,表明预后不佳。细胞膜微粒也成为血管损伤有价值的检测标志。 此外,细胞膜微粒是组织因子的主要载体,他们共同构成组织因子微粒,组织因子微粒作为启动子,大量聚集在血小板表面形成血栓。Ramacciotti等[60]建立的小鼠血栓栓塞模型中细胞膜微粒集聚与组织因子活化呈高度相关。组织因子微粒的升高或可作为患者血栓确诊一个有效指标。 2.2.4 白细胞计数 血中白细胞可受外界影响刺激进行强力的凝血,从而激活外源性凝血途径。白细胞黏附和移行可在早期启动深静脉血栓。Stoffel等[61]的回顾性研究评估白细胞计数与分成3组的100名正行细胞减灭的血液肿瘤患者血栓形成的关系。结果证实白血球增多与血栓形成之间存在密切关系。但也有研究认为原发性血小板增多症患者的白细胞计数与血栓形成之间无明显相关性[62]。 2.3 分子生物学及遗传学层面生物标志物 2.3.1 遗传因素 研究报道抗凝血酶、蛋白C及其辅因子蛋白S缺乏,莱顿第五因子突变,凝血酶原202010A突变,高同型半胱氨酸血症等可能是血栓形成的遗传学因素。P-选择素、Ⅷ因子、炎症细胞因子的单核苷酸多态性被证实与静脉血栓栓塞症的发生有关[63],也就是说这些生物标志物确实对静脉血栓栓塞症的发病机制有影响。 2.3.2 血清游离小分子核糖核酸(microRNAs) 游离microRNAs存在于各种体液中,而且近期许多研究表明其可作为许多疾病的生物标志物。Qin等[64]应用Taqman microRNA芯片技术及实时PCR技术分析深静脉血栓患者血清,得出血清microRNAs(miR-582,miR-195和miR-532)可成为深静脉血栓检测新的的生物标志物,而且为包括人工关节置换在内的骨科手术后深静脉血栓的发病机制提供机理性的认识。 "
| [1]Parvizi J, Parmar R, Raphael IJ, et al. Proximal deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolus following total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(9):1846-1848.
[2]Januel JM, Chen G, Ruffieux C, et al. Symptomatic in-hospital deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism following hip and knee arthroplasty among patients receiving recommended prophylaxis: a systematic review. JAMA. 2012; 307(3):294-303.
[3]Mont MA, Jacobs JJ. AAOS clinical practice guideline: preventing venous thromboembolic disease in patients undergoing elective hip and knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(12):777-778.
[4]Baarslag HJ, van Beek EJ, Koopman MM, et al. Prospective study of color duplex ultrasonography compared with contrast venography in patients suspected of having deep venous thrombosis of the upper extremities. Ann Intern Med. 2002; 136(12):865-872.
[5]Adam SS, Key NS, Greenberg CS. D-dimer antigen: current concepts and future prospects. Blood. 2009;113(13): 2878-2887.
[6]Cronan JJ. Deep vein thrombosis: imaging diagnosis and related controversies. Ultrasound Clin. 2011;6(4):421-433.
[7]Cosmi B, Palareti G. Update on the predictive value of D-dimer in patients with idiopathic venous thromboembolism. Thromb Res. 2010;125 Suppl 2:S62-65.
[8]Righini M, Bounameaux H. Clinical relevance of distal deep vein thrombosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008;14(5):408-413.
[9]Bounameaux H, Miron MJ, Blanchard J, et al. Measurement of plasma D-dimer is not useful in the prediction or diagnosis of postoperative deep vein thrombosis in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1998;9(8): 749-752.
[10]Khaira HS, Mann J. Plasma D-dimer measurement in patients with suspected DVT--a means of avoiding unnecessary venography. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 1998; 15(3): 235-238.
[11]Watanabe H, Madoiwa S, Sekiya H, et al. Predictive blood coagulation markers for early diagnosis of venous thromboembolism after total knee joint replacement. Thromb Res. 2011;128(6):e137-143.
[12]Castro DJ, Pérez-Rodríguez E, Montaner L, et al. Diagnostic value of D dimer in pulmonary embolism and pneumonia. Respiration. 2001;68(4):371-375.
[13]Perrier A. D-dimer for suspected pulmonary embolism: whom should we test? Chest. 2004;125(3):807-809.
[14]Mountain D, Jacobs I, Haig A. The VIDAS D-dimer test for venous thromboembolism: a prospective surveillance study shows maintenance of sensitivity and specificity when used in normal clinical practice. Am J Emerg Med. 2007;25(4): 464-471.
[15]Ho CH. Can very high level of D-dimer exclusively predict the presence of thromboembolic diseases? J Chin Med Assoc. 2011;74(4):151-154.
[16]Konstantinides SV. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(45):3145-3146.
[17]Douma RA, le Gal G, Söhne M, et al. Potential of an age adjusted D-dimer cut-off value to improve the exclusion of pulmonary embolism in older patients: a retrospective analysis of three large cohorts. BMJ. 2010;340:c1475.
[18]O'Donnell J, Tuddenham EG, Manning R, et al. High prevalence of elevated factor Ⅷ levels in patients referred for thrombophilia screening: role of increased synthesis and relationship to the acute phase reaction. Thromb Haemost. 1997;77(5):825-828.
[19]Tanaka KA, Key NS, Levy JH. Blood coagulation: hemostasis and thrombin regulation. Anesth Analg. 2009;108(5): 1433-1446.
[20]Jenkins PV, Rawley O, Smith OP, et al. Elevated factor Ⅷ levels and risk of venous thrombosis. Br J Haematol. 2012; 157(6):653-663.
[21]Ota S, Yamada N, Ogihara Y, et al. High plasma level of factor Ⅷ: an important risk factor for venous thromboembolism. Circ J. 2011;75(6):1472-1475.
[22]Kraaijenhagen RA, in't Anker PS, Koopman MM, et al. High plasma concentration of factor Ⅷc is a major risk factor for venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost. 2000;83(1):5-9.
[23]Tichelaar V, Mulder A, Kluin-Nelemans H, et al. The acute phase reaction explains only a part of initially elevated factor Ⅷ:C levels: a prospective cohort study in patients with venous thrombosis. Thromb Res. 2012;129(2): 183-186.
[24]Soria JM, Almasy L, Souto JC, et al. A new locus on chromosome 18 that influences normal variation in activated protein C resistance phenotype and factor Ⅷ activity and its relation to thrombosis susceptibility. Blood. 2003;101(1): 163-167.
[25]Viel KR, Machiah DK, Warren DM, et al. A sequence variation scan of the coagulation factor Ⅷ (FⅧ) structural gene and associations with plasma FⅧ activity levels. Blood. 2007; 109(9):3713-3724.
[26]Emmerechts J, Vanassche T, Loyen S, et al. Partial versus complete factor Ⅷ inhibition in a mouse model of venous thrombosis. Thromb Res. 2012;129(4):514-519.
[27]Hemker HC, Giesen P, Al Dieri R, et al. Calibrated automated thrombin generation measurement in clotting plasma. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2003;33(1):4-15.
[28]Ryland JK, Lawrie AS, Mackie IJ, et al. Persistent high factor Ⅷ activity leading to increased thrombin generation - a prospective cohort study. Thromb Res. 2012;129(4):447-452.
[29]Haas FJ, Schutgens RE, Kluft C, et al. A thrombin generation assay may reduce the need for compression ultrasonography for the exclusion of deep venous thrombosis in the elderly. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2011;71(1):12-18.
[30]Horan JT, Francis CW. Fibrin degradation products, fibrin monomer and soluble fibrin in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2001;27(6):657-666.
[31]Caliezi C, Fünfsinn N, Mauron T, et al. Performance of a new fibrin monomer assay to exclude deep vein thrombosis in symptomatic outpatients. Thromb Haemost. 1999;81(1): 50-53.
[32]Dopsaj V, Bogavac-Stanojevic N, Vasic D, et al. Excluding deep venous thrombosis in symptomatic outpatients: is fibrin monomer aid to D-dimer analysis? Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2009;20(7):546-551.
[33]Ley K. The role of selectins in inflammation and disease. Trends Mol Med. 2003;9(6):263-268.
[34]McEver RP. Adhesive interactions of leukocytes, platelets, and the vessel wall during hemostasis and inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86(3):746-756.
[35]Furie B, Furie BC. Role of platelet P-selectin and microparticle PSGL-1 in thrombus formation. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10(4): 171-178.
[36]Théorêt JF, Yacoub D, Hachem A, et al. P-selectin ligation induces platelet activation and enhances microaggregate and thrombus formation. Thromb Res. 2011;128(3):243-250.
[37]Miszti-Blasius K, Debreceni IB, Felszeghy S, et al. Lack of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 protects mice from thrombosis after collagen/epinephrine challenge. Thromb Res. 2011;127(3): 228-234.
[38]Fijnheer R, Frijns CJ, Korteweg J, et al. The origin of P-selectin as a circulating plasma protein. Thromb Haemost. 1997;77(6): 1081-1085.
[39]Zarbock A, Müller H, Kuwano Y, et al. PSGL-1-dependent myeloid leukocyte activation. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86(5): 1119-1124.
[40]André P, Hartwell D, Hrachovinová I, et al. Pro-coagulant state resulting from high levels of soluble P-selectin in blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13835-13840.
[41]del Conde I, Nabi F, Tonda R, et al. Effect of P-selectin on phosphatidylserine exposure and surface-dependent thrombin generation on monocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005; 25(5):1065-1070.
[42]Myers D Jr, Farris D, Hawley A, et al. Selectins influence thrombosis in a mouse model of experimental deep venous thrombosis. J Surg Res. 2002;108(2):212-221.
[43]Myers DD, Hawley AE, Farris DM, et al. P-selectin and leukocyte microparticles are associated with venous thrombogenesis. J Vasc Surg. 2003;38(5):1075-1089.
[44]Rectenwald JE, Myers DD Jr, Hawley AE, et al. D-dimer, P-selectin, and microparticles: novel markers to predict deep venous thrombosis. A pilot study. Thromb Haemost. 2005; 94(6):1312-1317.
[45]Blann AD, Noteboom WM, Rosendaal FR. Increased soluble P-selectin levels following deep venous thrombosis: cause or effect? Br J Haematol. 2000;108(1):191-193.
[46]Smith A, Quarmby JW, Collins M, et al. Changes in the levels of soluble adhesion molecules and coagulation factors in patients with deep vein thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 1999; 82(6):1593-1599.
[47]Shi D, Xu X, Xu Z, et al. P-selectin: an unpredicted factor for deep vein thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:783967.
[48]Zacho J, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Nordestgaard BG. C-reactive protein and risk of venous thromboembolism in the general population. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(8): 1672-1678.
[49]Roumen-Klappe EM, den Heijer M, van Uum SH, et al. Inflammatory response in the acute phase of deep vein thrombosis. J Vasc Surg. 2002;35(4):701-706.
[50]Bucek RA, Reiter M, Quehenberger P, et al. C-reactive protein in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. Br J Haematol. 2002;119(2):385-389.
[51]Rabinovich A, Cohen JM, Cushman M, et al. Inflammation markers and their trajectories after deep vein thrombosis in relation to risk of post-thrombotic syndrome. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(3):398-408.
[52]Tsai AW, Cushman M, Rosamond WD, et al. Coagulation factors, inflammation markers, and venous thromboembolism: the longitudinal investigation of thromboembolism etiology (LITE). Am J Med. 2002;113(8):636-642.
[53]Fox EA, Kahn SR. The relationship between inflammation and venous thrombosis. A systematic review of clinical studies. Thromb Haemost. 2005;94(2):362-365.
[54]Poredos P, Jezovnik MK. In patients with idiopathic venous thrombosis, interleukin-10 is decreased and related to endothelial dysfunction. Heart Vessels. 2011;26(6):596-602.
[55]Downing LJ, Strieter RM, Kadell AM, et al. IL-10 regulates thrombus-induced vein wall inflammation and thrombosis. J Immunol. 1998;161(3):1471-1476.
[56]Enjeti AK, Lincz LF, Seldon M. Detection and measurement of microparticles: an evolving research tool for vascular biology. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2007;33(8):771-779.
[57]Burger D, Schock S, Thompson CS, et al. Microparticles: biomarkers and beyond. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013;124(7): 423-441.
[58]Noci MV, Ramírez R, Lluch M, et al. Changes in endothelial microparticles and endothelial progenitor cells in obese patients in response to surgical stress. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(5):353-358.
[59]Morel O, Toti F, Hugel B, et al. Procoagulant microparticles: disrupting the vascular homeostasis equation? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(12):2594-2604.
[60]Ramacciotti E, Hawley AE, Farris DM, et al. Leukocyte- and platelet-derived microparticles correlate with thrombus weight and tissue factor activity in an experimental mouse model of venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. 2009;101(4):748-754.
[61]Stoffel N, Rysler C, Buser A, et al. Leukocyte count and risk of thrombosis in patients undergoing haematopoietic stem cell transplantation or intensive chemotherapy. Thromb Haemost. 2010;103(6):1228-1232.
[62]Passamonti F, Rumi E, Arcaini L, et al. Prognostic factors for thrombosis, myelofibrosis, and leukemia in essential thrombocythemia: a study of 605 patients. Haematologica. 2008;93(11):1645-1651.
[63]Hou H, Ge Z, Ying P, et al. Biomarkers of deep venous thrombosis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2012;34(3):335-346.
[64]Qin J, Liang H, Shi D, et al. A panel of microRNAs as a new biomarkers for the detection of deep vein thrombosis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2015;39(2):215-221.
[65]Geersing GJ, Zuithoff NP, Kearon C, et al. Exclusion of deep vein thrombosis using the Wells rule in clinically important subgroups: individual patient data meta-analysis. BMJ. 2014; 348:g1340.
[66]Ramacciotti E, Blackburn S, Hawley AE, et al. Evaluation of soluble P-selectin as a marker for the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2011;17(4): 425-431. |
| [1] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [2] | Cheng Jun, Tan Jun, Zhao Yun, Cheng Fangdong, Shi Guojia. Effect of thrombin concentration on the prevention of postoperative cerebrospinal leakage by fibrin glue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 570-575. |
| [3] | Cheng Chongjie, Yan Yan, Zhang Qidong, Guo Wanshou. Diagnostic value and accuracy of D-dimer in periprosthetic joint infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3921-3928. |
| [4] | Liu Zhiwei, Xie Rui, Sun Kai, Li Kaiming, Wang Xiongwei, Zhan Jiawen, Zhu Liguo. Interpretation of diagnostic criteria for cervicogenic headache: challenges and understandings in diagnosis and differential diagnosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3746-3751. |
| [5] | Fang Yi, Zhao Wenzhi, Pan Deyue, Han Xin, Zhang Lu, He Hongtao, Shi Feng, Tian Tingxiao. Acromioclavicular joint dislocation: how to achieve anatomical reduction, sustained stability and micro-motion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 796-802. |
| [6] | Cao Houran, Deng Peng, Ye Pengcheng, Jie Ke, Zeng Jianchun, Feng Wenjun, Chen Jinlun, Qi Xinyu, Li Jie, Tan Xueqiu, Zhang Haitao, Zeng Yirong. Platelet count as a novel potential predictor of periprosthetic joint infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4795-4801. |
| [7] | Liu Mengyuan1, Fang Fang2. Risk factors for multi-drug resistant organisms infection after liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1109-1114. |
| [8] | Han Guangtao, Li Haohuan. Influence of the concept of fast track surgery on the physiological and psychological rehabilitation of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5760-5765. |
| [9] | Li Cheng, Andrej Trampuz. Application and significance of joint puncture in the diagnosis and treatment of periprosthetic joint infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5868-5874. |
| [10] | Cui Jiaming, Yang Dazhi. Treatment strategies for spinal metastases: advantages of 3D printing and precise treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5875-5881. |
| [11] | Wang Jicheng1, 2, Liu Shizhang1, Zhao Song1, 2, Yi Zhi1. Relationship between miRNA and occurrence and development of chondrosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5697-5702. |
| [12] | Wu Jiaxin, Pei Xibo. Advance in research on peri-implantitis in diabetic patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5558-5564. |
| [13] | Luo Hong1, Liu Fang1, Li Shunhua1, Qiu Bing1, Liu Fuyao1, Zhang Yu2, Ma Limin3. Significance of gait analysis in the diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4969-4973. |
| [14] | Mo Fan1, Zhao Jinmin2, Sha Ke2, Yang Yuan1, Huang Weifeng1, Wei Wu1, Xie Qi1. Treatment and research progress of adult brachial plexus injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 5072-5078. |
| [15] | Kong Lingyao, Li Tao, Zeng Xinglin, Li Jian, Xiong Yan. Synovial chondromatosis: how to improve the diagnosis accuracy and clearance rate of tumor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4570-4575. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||