Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (34): 5558-5564.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1449
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advance in research on peri-implantitis in diabetic patients
- 1四川大学华西口腔医学院,四川省成都市 610041;2四川大学华西口腔医院,四川省成都市 610041
-
Received:2019-06-13Online:2019-12-08Published:2019-12-08 -
Contact:Pei Xibo, Associate professor, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wu Jiaxin, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Distinguished Young Scholars, No. 81601316 (to PXB); the Youth Clinical Research Fund of Chinese Stomatological Association, No. CSA-B2018-09 (to PXB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Jiaxin, Pei Xibo. Advance in research on peri-implantitis in diabetic patients[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5558-5564.
share this article
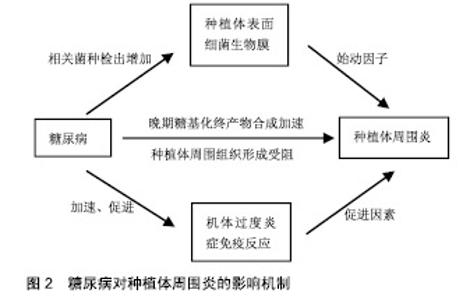
2.1 种植体周围炎 美国牙周学会、欧洲牙周学会专家联合发布的牙周病疾病新分类(以下称为“共识”)中表明,种植体周围炎是发生于牙种植体周围组织中一种与牙菌斑相关的病理状态。相关危险因素如糖尿病和吸烟对于种植体周围炎的影响尚无定论[15-16],临床研究认为其对种植体周围炎的发展有促进作用[12,17-18],因此接受牙种植术的糖尿病患者应进行相关预防和治疗,尽量降低发生种植体周围炎的风险。 2.2 糖尿病对种植体周围炎的影响机制 种植体周围炎是由细菌作用和宿主防御之间的不平衡引起的[5]。因此,糖尿病对种植体表面细菌生物膜和机体免疫-炎症系统的影响,可能是糖尿病患者种植体周围炎发病率较高的内在原因,见图2。"
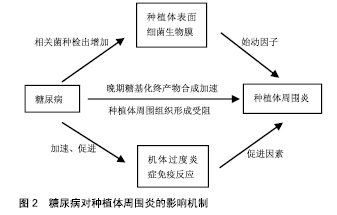

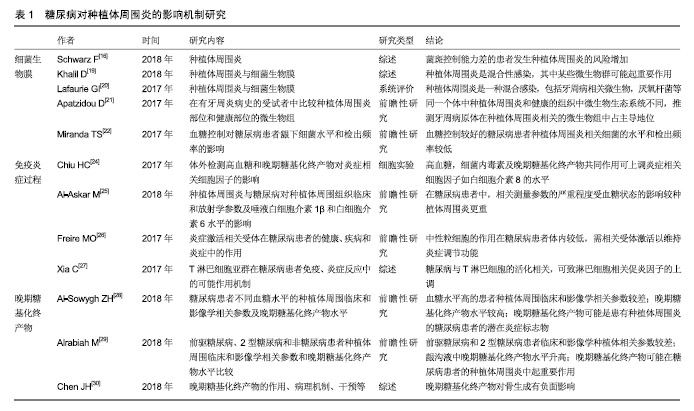
2.2.1 微生物 细菌生物膜可以在种植体上形成,对种植体周围软、硬组织的健康有不利影响,是引起种植体周围炎的重要因素[16,19-20]。 共识表明种植体周围炎没有特异性的细菌[15]。目前导致种植体周围炎发生发展的微生物群仍无科学数据[19]。相关研究表明,牙龈卟啉单胞菌、放线菌、普氏菌等与种植体周围炎的发生密切相关[5,16,20-21]。与血糖控制较好(糖化血红蛋白<8%)的患者相比,糖化血红蛋白≥8%的糖尿病患者具核梭杆菌的平均检出数量及福赛斯坦菌、具核梭杆菌、牙龈卟啉单胞菌等种植体周围炎相关细菌的检出频率更高[22]。因此,良好的血糖控制降低了种植体周围炎相关微生物水平,进而减少种植体周围炎的发生概率。 2.2.2 免疫-炎症过程 种植体周围炎未鉴定出特异性致炎细胞因子[15]。目前与种植体周围炎相关细胞因子的研究主要集中于白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α等[16]。白细胞介素1β是种植体周围炎的重要炎性因子,可以协同其他炎性因子抑制骨的重建,并随着炎症的治疗而出现下降趋势[23]。糖化加速了炎症过程,导致种植体周围炎相关促炎细胞因子的产生增加[24]。研究表明,糖尿病患者唾液中白细胞介素1β的检测结果高于非糖尿病患者[25]。 种植体周围炎是细菌对种植体周围组织的攻击与宿主免疫炎症反应之间相互作用的结果。糖尿病患者具有更强的炎症反应[25],这可能与中性粒细胞功能下调进而导致细菌的低效清除[26],以及淋巴细胞相关促炎因子的上调等机制有关[27]。因此糖尿病患者与正常患者相比产生慢性炎症、进行性组织破坏的可能性更大。 2.2.3 晚期糖基化终产物抑制骨整合 晚期糖基化终产物是由蛋白质、脂质和核酸的非酶促糖化和氧化形成的促炎分子,可增加促炎细胞因子的表达,引起许多慢性退行性疾病[24]。高血糖可以加速晚期糖基化终产物的形成,种植体周围龈沟液中的晚期糖基化终产物水平随着2型糖尿病患者血糖水平的升高而升高[28]。晚期糖基化终产物积聚于糖尿病的各种组织,抑制人间充质干细胞的增殖,诱导细胞凋亡,从而抑制种植体软组织和骨组织的形成;成骨细胞和破骨细胞对晚期糖基化终产物的反应可能导致种植体周围骨整合情况不佳[29-30]。 高血糖状态通过多种机制影响骨代谢[31]。糖尿病患者骨愈合过程中,由于成骨细胞的分化、增殖和骨形成能力受到抑制,骨愈合能力降低,使种植体周围炎的发生率及严重程度较无糖尿病患者增加[32-33]。但当糖尿病得到良好控制时,种植体植入手术并发症的发生率与健康患者相似,提高了牙种植的成功率[14,34]。美国糖尿病学会(ADA)2017年糖尿病健康指南中建议糖化血红蛋白控制在7.5%以下,伴有多种慢性疾病的糖尿病患者糖化血红蛋白应控制在8.0%以下[35]。也有研究机构以糖化血红蛋白=6.8%为界分为中度或控制不佳的糖尿病(糖化血红蛋白6.8%或更高)和糖尿病控制良好的受试者(糖化血红蛋白低于6.8%)[36-37]。 目前已有一些研究为糖尿病对种植体周围炎的机制提供了相关证据,见表1。 "

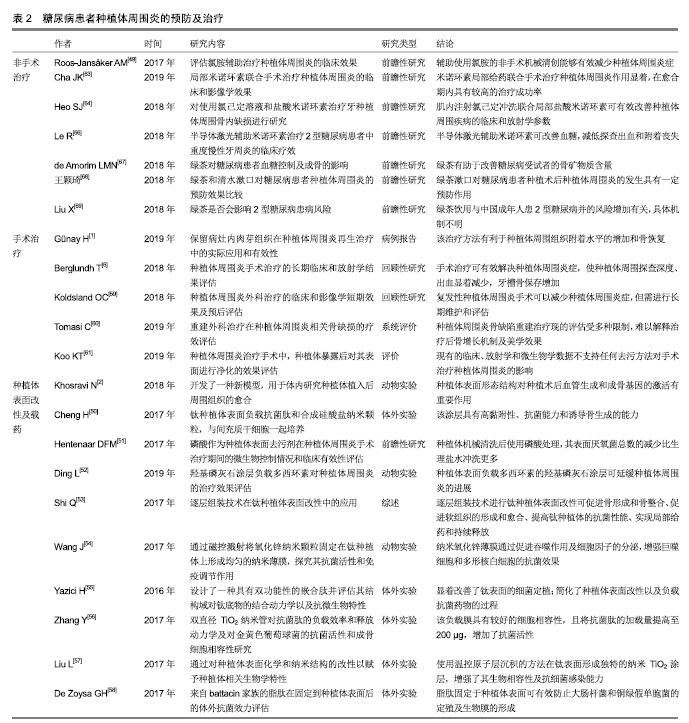
2.3 诊断及早期检测 早期诊断、检测和干预是管理种植体周围炎的关键[38-39]。种植体周围炎的诊断标准为:(有初始检查数据)轻探出血和(或)溢脓,探诊深度较初始检查增加,最初骨重建之外存在骨质丧失;(无初始检查数据)轻探出血和(或)溢脓,探诊深度≥6 mm,牙槽嵴处骨丧失≥3 mm[15]。目前,临床对种植体周围炎的诊断通常以机体的炎症反应为标准,如牙周探诊出血、溢脓及骨丧失等[40],但微观的诊断仍无确切标准。研究者们对种植体周围炎的微观诊断进行了一系列探究。 研究证明,细胞因子浓度随种植体植入后不同时期的愈合情况而变化[23]。龈沟液中各种生物标记物如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和NO等有望作为常规检查期间判断牙种植体状态的指标[41]。活化的基质金属蛋白酶8是进行性种植体周围疾病的生物标志物,能够辅助预测种植体周围炎的临床活动性及治疗效果[42],有助于种植体周围炎的诊断和临床疗效评估等[23]。附着于种植体的菌斑微生物特征也有助于疾病的预测。Parolin等[43]设计出一种可以快速可靠地表征口腔中菌群的DNA检测探针——OralArray,并开发了针对种植体周围炎相关物种(放线菌)的探针组,有助于早期预测种植体周围炎。 糖尿病特征性和相关产物同样可能作为种植体周围炎的预测方法。Gomez-Moreno等[44]研究表明,通过监测糖化血红蛋白水平可评估种植体周围炎的进展。曹杨[45]的研究证明,糖尿病患者行种植修复术后种植体周围龈沟液中骨桥蛋白水平明显高于健康者,且骨桥蛋白的水平与种植体牙周状况呈正相关性。 2.4 预防及治疗 种植体周围炎进展较快,需及时给予治疗措施[46]。其治疗目标是控制炎症,阻止骨丢失,促进骨整合[3]。由于种植体周围炎特征的相关研究仍处于早期阶段,目前无普遍接受的治疗方法[5]。常规用于种植体周围炎的多种干预措施,如术前抗生素、机械干预(超声波、刮治等)和化学试剂(氯己定等)同样适用于糖尿病患者[47-48]。氯胺辅助治疗等新方法也在不断研究 中[49]。此外,实现良好的血糖控制对于降低种植术后并发症的风险至关重要[31]。近年来,以糖尿病模型探究种植体周围炎的治疗也逐渐成为研究热点。 2.4.1 种植体周围菌斑及炎症的控制 种植体表面改性及载药:预防术后感染和促进种植体周围骨整合是牙种植成功的关键因素。骨整合通过种植体与骨组织之间直接接触而完成,种植体表面形态结构对种植术后血管生成和成骨基因的激活有重要作用[2]。种植体周围炎的外科治疗结果也受到种植体表面特征的影响[6]。对种植体进行表面处理及抗菌药物装载,是控制局部感染、促进种植体周围骨整合的一种重要方式[50-53]。 Wang等[54]通过磁控溅射将氧化锌纳米颗粒固定在钛上形成均匀的纳米薄膜,并通过体内外实验证明了纳米氧化锌薄膜可以通过促进吞噬作用及细胞因子分泌来增强巨噬细胞和多形核白细胞的抗菌效果。Cheng等[50]在钛表面负载了抗菌肽和合成硅酸盐纳米颗粒,改性后的钛表现出良好的抗微生物活性及抑制生物膜形成的特性,当与人间充质干细胞一起培养时,硅酸盐纳米颗粒可增强周围组织中的新骨形成。 近年来出现了一些新型的、更高效的种植体表面改性和负载方式。Yazici等[55]设计了一种具有双功能性的嵌合肽,一端与钛具有高亲和力以结合于种植体表面,另一端可结合抗菌肽而具有抗菌活力。该方法简化了种植体表面改性及负载抗菌药物的过程。Zhang等[56]利用双直径TiO2纳米管负载抗菌肽,具有较好的细胞相容性,且将抗菌肽的加载量提高至200 μg,增加了抗菌活性,但随之增加的细胞毒性是限制其临床应用的重要因素。Liu等[57]首次引入温控原子层沉积的方法在钛表面形成独特的纳米TiO2涂层结构,该方法能够对涂层表面纳米形态和表面能进行精细控制,增强其生物相容性及抗细菌感染能力。De Zoysa等[58]首次在钛表面合成了来自battacin家族的脂肽作为抗菌涂层,有效防止了大肠杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌的定殖及生物膜的形成。但脂肽自身的毒性是否会对人体造成其他伤害,仍需进一步实验证明。 随着糖尿病患病人数的进一步增多,针对糖尿病患者的种植体表面改性和载药临床应用需求将会随之增加。在表面改性和载药技术不断发展改进的同时,如何对糖尿病影响下的种植体周围炎进行改善是未来关注的重点。 手术治疗:手术方法是种植体周围炎,尤其是晚期的种植体周围炎病例的重要治疗手段,血糖控制较好的糖尿病患者也可进行常规手术治疗。手术治疗方法有翻瓣清创、种植体表面去污配合骨移植、生物介质等方 法[1]。研究证明机械抗感染措施和手术治疗可有效解决种植体周围炎症性病变,且有效期较长[6],但在较严重的病例中效果减弱[59]。种植体周围炎骨缺陷的重建治疗有效性尚无明确解释,且相关美学效果也无定论[60]。目前种植体周围炎无统一的手术治疗方法,已有的手术治疗方法仍在不断探索改进中[1,61]。 非手术治疗:临床应用的种植体周围炎非手术治疗方式包括非手术机械清创、辅助药物治疗、激光和抗菌光动力疗法及联合治疗等,有助于减轻种植体周围炎临床症状如探诊深度增加及出血[39,49,62]。针对糖尿病患者的种植体周围炎非手术治疗研究也有了一些新的进展。盐酸米诺环素是半合成四环素,有较强的抗菌性。研究表明局部应用米诺环素可在种植术后的愈合期产生积极作用,以提高种植成功率[63-64],且在糖尿病种植体周围炎治疗中有良好效果,能控制炎症反应并促进牙周组织的恢复[65]。半导体激光辅助米诺环素可改善血糖,减低探查出血和附着丧失[66],有望成为糖尿病种植体周围炎的临床治疗方法。 绿茶可能对糖尿病受试者的骨矿物质含量有改善作用[67]。王颖琦等[68]研究证明,绿茶对糖尿病患者种植术后的口腔维护具有积极的作用。也有研究认为饮用茶水无益于糖尿病血糖的控制,甚至可能加重2型糖尿病患病的风险[69]。其具体机制需进一步探索。 口腔护理行为:预防种植体周围炎的关键是患者自身口腔卫生措施的执行和医护人员在随访中的正确指导,以及考虑到个体潜在风险和具体情况的个性化支持治疗[3]。个性化的治疗方案设计可提高患者的自我保健意识,减少或延缓种植体周围炎的发生发展。临床上,医护人员需要帮助患者了解种植术后并发症的风险,以及牙菌斑控制和定期随访的重要性[4]。 目前已有很多钛种植体表面改性和载药用于抗菌和促进骨整合的研究,见表2。 2.4.2 血糖控制 糖尿病患者应主动监测血糖变化,并及时进行处理。美国糖尿病协会对糖尿病患者血糖的控制提出了如下建议:生活方式管理(合理饮食,增强体质,戒烟和心理调节等)、药物治疗及去代谢手术等[35,37]。血糖的管理有利于糖尿病患者种植体周围炎的控制:一方面,血糖的降低使骨整合的抑制作用减少,减轻种植体周围的骨破坏[30-31],同时降低了种植体周围细菌水平和致炎细胞因子水平,有利于炎症的预防和控制[22,24];另一方面,糖尿病患者控制血糖的生活方式管理中,体质锻炼、戒烟等同样有利于种植体周围炎的预防和改善[70]。"
| [1]Günay H,Staufenbiel I,Geurtsen W,et al.The granulation tissue preservation technique in regenerative therapy of peri-implantitis—a treatment concept with case reports.Introducing DZZ Int.2019;1(1):4-15.[2]Khosravi N,Maeda A,DaCosta RS,et al. Nanosurfaces modulate the mechanism of peri-implant endosseous healing by regulating neovascular morphogenesis.Commun Biol.2018;1(1):72-84.[3]Berglundh T,Jepsen S,Stadlinger B,et al.Peri-implantitis and its prevention.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(2):150-155.[4]Rokn A,Aslroosta H,Akbari S,et al.Prevalence of peri-implantitis in patients not participating in well-designed supportive periodontal treatments: a cross-sectional study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(3): 314-319.[5]Valente NA,Andreana S.Peri-implant disease: what we know and what we need to know.J Periodont Implant Sci.2016;46(3):136-151.[6]Berglundh T, Wennström JL, Lindhe J. Long-term outcome of surgical treatment of peri-implantitis. A 2-11-year retrospective study.Clin Oral Implants Res.2018;29(4):404-410.[7]Ting M, Craig J, Balkin BE, et al. Peri-implantitis: a comprehensive overview of systematic reviews.J Oral Implantol.2018;44(3):225-247.[8]Urakami T, Kuwabara R, Yoshida K. Economic Impact of Diabetes in Japan.Curr Diab Rep.2019;19(1):2-5.[9]American Diabetes Association.Economic costs of diabetes in the US in 2017.J Diabetes Care. 2018;41(5):917-928.[10]Cho NH,Shaw JE,Karuranga S,et al.IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045.Diabetes Res Clin Pract.2018;138:271-281.[11]Hu XF,Wang L,Xiang G,et al.Angiogenesis impairment by the NADPH oxidase-triggered oxidative stress at the bone-implant interface: Critical mechanisms and therapeutic targets for implant failure under hyperglycemic conditions in diabetes.J Acta Biomaterialia. 2018;73: 470-487.[12]Monje A,Catena A,Borgnakke WS.Association between Diabetes Mellitus/Hyperglycemia and Peri-Implant Diseases: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Periodontol.2017;44(6):636-648.[13]Zeev O,Jonathan B,Shlomo M,et al.The Effect of Moderately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes on Dental Implant Survival and Peri-implant Bone Loss: A Long-Term Retrospective Study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2018;33(2):389-394.[14]Naujokat H, Kunzendorf B, Wiltfang J.Dental implants and diabetes mellitus—a systematic review.Int J Implant Dent.2016;2(1):5-14.[15]Berglundh T Armitage G,Araujo MG,et al. Peri‐implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri‐Implant Diseases and ConditionsJ Clin Periodontol.2018;45(S20):S286-S291.[16]Schwarz F,Derks J,Monje A,et al.Peri-implantitis.J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(S20):S246-S266.[17]Mazel A,Belkacemi S,Tavitian P, et al.Peri‐implantitis risk factors: A prospective evaluation.J J Investig Clin Dent.2019;10(2):e12398.[18]Papi P,Letizia C,Pilloni A,et al.Peri-implant diseases and metabolic syndrome components: a systematic review.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2018;22(4):866-875.[19]Khalil D,Hultin M.Peri-implantitis microbiota[M]//An Update of Dental Implantology and Biomaterial.Intech Open.2018:81-93.[20]Lafaurie GI,Sabogal MA,Castillo DM,et al.Microbiome and microbial biofilm profiles of peri-implantitis: a systematic review.J Periodontol. 2017;88(10):1066-1089.[21]Apatzidou D,Lappin DF,Hamilton G,et al.Microbiome associated with peri-implantitis versus periodontal health in individuals with a history of periodontal disease.J Oral Microbiol. 2017;9(sup1):1325218.[22]Miranda TS,Feres M,Retamal-Valdés B,et al.Influence of glycemic control on the levels of subgingival periodontal pathogens in patients with generalized chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes.J Appl Oral Sci.2017;25(1):82-89.[23]Renvert S, Widén C, Persson RG. Cytokine and microbial profiles in relation to the clinical outcome following treatment of peri-implantitis. Clin Oral Implants Res.2017;28(9):1127-1132.[24]Chiu HC, Fu MMJ, Yang TS, et al. Effect of high glucose, Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide and advanced glycation end-products on production of interleukin-6/-8 by gingival fibroblasts.J Periodont Res.2017;52(2):268-276.[25]Al-Askar M,Ajlan S,Alomar N,et al.Clinical and Radiographic Peri-Implant Parameters and Whole Salivary Interleukin-1β and Interleukin-6 Levels among Type-2 Diabetic and Nondiabetic Patients with and without Peri-Implantitis.Med Princ Pract.2018;27(2):133-138.[26]Freire MO,Dalli J,Serhan CN,et al.Neutrophil resolvin E1 receptor expression and function in type 2 diabetes.J Immunol. 2017;198(2): 718-728.[27]Xia C, Rao X, Zhong J.Role of Tlymphocytes in type 2 diabetes and diabetes-associated inflammation.J Diabetes Res.2017;2017:1-6.[28]Al-Sowygh ZH, Ghani SMA, Sergis K, et al. Peri‐implant conditions and levels of advanced glycation end products among patients with different glycemic control.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(3): 345-351.[29]Alrabiah M,Al-Aali KA,Al-Sowygh ZH, et al.Association of advanced glycation end products with peri‐implant inflammation in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018;20(4):535-540.[30]Chen JH,Lin X, Bu C,et al.Role of advanced glycation end products in mobility and considerations in possible dietary and nutritional intervention strategies.Nutr Metab (Lond).2018;15(1):72-89.[31]Napoli N, Chandran M, Pierroz DD, et al. Mechanisms of diabetes mellitus-induced bone fragility.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4): 208-219.[32]Ghiraldini B,Conte A,Casarin RC, et al. Influence of Glycemic Control on Peri‐Implant Bone Healing: 12‐Month Outcomes of Local Release of Bone‐Related Factors and Implant Stabilization in Type 2 Diabetics.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2016;18(4): 801-809.[33]Zhou W, Tangl S, Reich KM, et al. The Influence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Osseointegration of Titanium Implants With Different Surface Modifications—A Histomorphometric Study in High-Fat Diet/Low-Dose Streptozotocin–Treated Rats.J Implant Dent. 2019; 28(1):11-19.[34]Al-Shibani N, Al-Aali KA, Al-Hamdan RS, et al.Comparison of clinical peri-implant indices and crestal bone levels around narrow and regular diameter implants placed in diabetic and non-diabetic patients: A 3-year follow-up study.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(2): 223-421.[35]American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2017 abridged for primary care providers.Clin Diabetes. 2017;35(1):5-26.[36]Baum A, Scarpa J, Bruzelius E, et al. Targeting weight loss interventions to reduce cardiovascular complications of type 2 diabetes: a machine learning-based post-hoc analysis of heterogeneous treatment effects in the Look AHEAD trial.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.2017;5(10):808-815.[37]Care D.Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2019.Diabetes Care. 2019;42(1):S81-S89.[38]Neely AL,Maalhagh-Fard A.Successful Management of Early Peri-implant Infection and Bone Loss Using a Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach.Clin AdvPeriodont.2018;8(1):5-10.[39]Wang CW,Renvert S,Wang HL.Nonsurgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis.Implant Dent. 2019;28(2):155-160.[40]Hirooka H,Renvert S.Diagnosis of Peri-implant Disease.Implant Dent.2019;28(2):144-149.[41]Bielemann AM, Marcello-Machado RM, Cury AADB, et al. Systematic review of wound healing biomarkers in peri-implant crevicular fluid during osseointegration.Arch Oral Biol.2018;89:107-128.[42]Al-Majid A, Alassiri S, Rathnayake N, et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 as an Inflammatory and Prevention Biomarker in Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases.Int J Dent.2018;2018:1-27.[43]Parolin C,Giordani B,Palomino RAÑ,et al. Design and validation of a DNA-microarray for phylogenetic analysis of bacterial communities in different oral samples and dental implants.Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 6280-6291.[44]Gómez-Moreno G,Aguilar-Salvatierra A,Rubio Roldán J,et al.Peri‐implant evaluation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a 3-year study.Clin Oral Implants Res.2015;26(9):1031-1035.[45]曹杨.糖尿病患者种植体周围龈沟液中骨桥蛋白水平的研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2016.[46]Salvi GE,Cosgarea R,Sculean A.Prevalence and mechanisms of peri-implant diseases.J Dent Res.2017;96(1):31-37.[47]Kadkhoda Z,Amarlu Z,Eshraghi S,et al.Antimicrobial effect of chlorhexidine on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans biofilms associated with peri-implantitis.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2016;10(3):176-180.[48]Gerits E,Verstraeten N,Michiels J.New approaches to combat Porphyromonas gingivalis biofilms.J Oral Microbiol. 2017;9(1): 1300366-1300377.[49]Roos-Jansåker AM, Almhöjd US, Jansson H.Treatment of peri-implantitis: clinical outcome of chloramine as an adjunctive to non-surgical therapy, a randomized clinical trial.Clin Oral Implants Res.2017;28(1):43-48. [50]Cheng H,Yue K,Kazemzadeh-Narbat M,et al.Mussel-Inspired Multifunctional Hydrogel Coating for Prevention of Infections and Enhanced Osteogenesis.J ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(13): 11428-11439.[51]Hentenaar DFM,De Waal YCM,Strooker H,et al.Implant decontamination with phosphoric acid during surgical peri-implantitis treatment: a RCT.Int J Implant Dent.2017;3(1):33-41.[52]Ding L,Zhang P,Wang X,et al.A doxycycline‐treated hydroxyapatite implant surface attenuates the progression of peri‐implantitis: A radiographic and histological study in mice.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2019;21(1):154-159.[53]Shi Q,Qian Z,Liu D,et al Surface modification of dental titanium implant by layer-by-layer electrostatic self-assembly.J Front Physiol. 2017;8: 574-580.[54]Wang J,Zhou H,Guo G,et al. Enhanced anti-infective efficacy of ZnO nanoreservoirs through a combination of intrinsic anti-biofilm activity and reinforced innate defense.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(39): 33609-33623.[55]Yazici H, O’Neill MB, Kacar T, et al. Engineered chimeric peptides as antimicrobial surface coating agents toward infection-free implants. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016;8(8):5070-5081.[56]Zhang Y,Zhang L,Li B,et al.Enhancement in Sustained Release of Antimicrobial Peptide from Dual-Diameter-Structured TiONanotubes for Long-Lasting Antibacterial Activity and Cytocompatibility.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2017;9(11):9449-9461.[57]Liu L,Bhatia R,Webster TJ.Atomic layer deposition of nano-TiO2 thin films with enhanced biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity for orthopedic implants.Int J Nanomedicine.2017;12:8711-8723.[58]De Zoysa GH, Sarojini V.Feasibility Study Exploring the Potential of Novel Battacin Lipopeptides as Antimicrobial Coatings.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2017;9(2):1373-1383.[59]Koldsland OC,Wohlfahrt JC,Aass AM.Surgical treatment of peri‐implantitis: Prognostic indicators of short‐term resultsJ Clin Periodontol.2018;45(1):100-113.[60]Tomasi C,Regidor E,Ortiz-Vigón A,et al.Efficacy of reconstructive surgical therapy at peri‐implantitis‐related bone defects. A systematic review and meta‐analysis.J Clin Periodontol. 2019. doi:10.1111/jcpe.13070.[61]Koo KT, Khoury F, Keeve PL, et al. Implant Surface Decontamination by Surgical Treatment of Periimplantitis: A Literature Review.J Implant dentistry. 2019;28(2):173-176.[62]Mills MP,Rosen PS,Chambrone L,et al.American academy of periodontology best evidence consensus statement on the efficacy of laser therapy used alone or as an adjunct to non-surgical and surgical treatment of periodontitis and peri-implant diseases.J Periodontol. 2018;89(7):737-742.[63]Cha JK,Lee JS,Kim CS.Surgical Therapy of Peri-Implantitis with Local Minocycline: A 6-Month Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.J Dent Res.2019;98(3):288-295.[64]Heo SJ,Kim HJ,Joo JY,et al.Simplified nonsurgical treatment of peri-implantitis using chlorhexidine and minocycline hydrochloride.J Periodontal Implant Sci.2018;48(5):326-333.[65]陈希楠,何添荣,杨芳,等.米诺环素治疗糖尿病患者种植体周围感染的临床效果分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2019,29(5):741-744.[66]Le R,Zhe Z,Daxu L,et al.Clinical efficacy of semiconductor laser-assisted minocycline in moderate-to-severe chronic periodontitis patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Trop J Pharm Res. 2018;17(6): 1165-1170.[67]de Amorim LMN, Vaz SR, Cesário G, et al. Effect of green tea extract on bone mass and body composition in individuals with diabetes.J Funct Foods.2018;40:589-594.[68]王颖琦,孙艳芳,李春娥,等.绿茶漱口预防糖尿病患者种植体周围炎的临床研究[J].世界最新医学信息文摘(电子版),2018,18(18):1-2.[69]Liu X,Xu W,Cai H,et al.Green tea consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes in Chinese adults: the Shanghai Women’s Health Study and the Shanghai Men’s Health Study.Int J Epidemiol. 2018;47(6): 1887-1896.[70]ArRejaie AS,Al-Aali KA,Alrabiah M,et al.Proinflammatory cytokine levels and peri‐implant parameters among cigarette smokers, individuals vaping electronic cigarettes, and non-smokers.J Periodontol. 2019;90(4):367-374. |
| [1] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [2] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [8] | Yang Yang, Yao Yu, Shen Xiaotian, Liu Jiajia, Xue Jianhua. Expression and significance of interleukin-21 in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 690-694. |
| [9] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [10] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [11] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [12] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [13] | Xu Xiaoming, Chen Yan, Song Qian, Yuan Lu, Gu Jiaming, Zhang Lijuan, Geng Jie, Dong Jian. Human placenta derived mesenchymal stem cell gel promotes the healing of radiation skin damage in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3976-3980. |
| [14] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [15] | Bi Qingwei, Liu Chengpu, Li Yan, Zhao Wenwen, Han Mei. Structure analysis of platelet-rich fibrin derived from two centrifugation procedures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3534-3539. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||