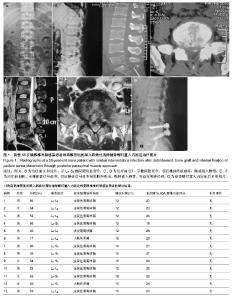
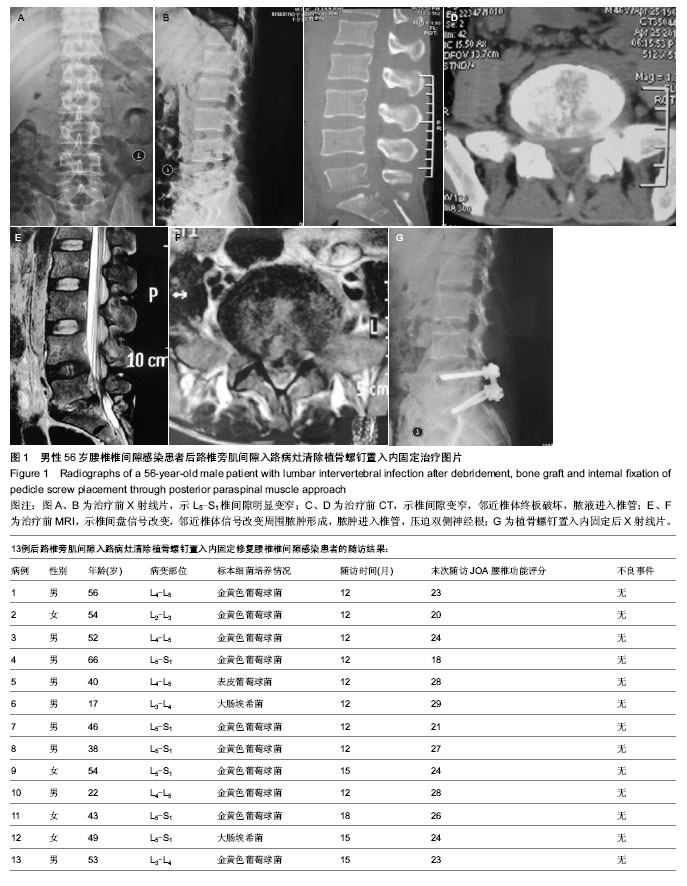
| [1] Mann S, Schutze M, Sola S, et al. Nonspecific pyogenic spondylodiscitis:clinical manifestations,surgical treatment, and outcome in 24 patients. Neurosurg Focus. 2004;17(1): E3-6.
[2] Borowski AM, Crow WN, Hadjipavlou AG, et al. Interventional radiology case conference: the University of Texas Medical Branch.Percutaneous management of pyogenic spondylodiscitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 170(6): 1587-1592.
[3] Tyler KL. Acute pyogenic diskitis(spondylodiskitis)in adults. Rev Neurol Dis. 2008;5(1):8-13.
[4] 崔旭,马远征,陈兴,等. 脊柱结核前后路不同术式的选择及其疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(10):807-812.
[5] Kim KT, Lee SH, Suk KS, et al. The quantitative analysis of tissue injury markers after mini-open lumbar fusion. Spine. 2006;31(6): 712-716.
[6] Kawaguchi Y, Matsui H, Tsuji H. Back muscle injury after posterior 1umbar spine surgery: a histologic and enzymatic analysis. Spine. 1996; 21(8): 941-944.
[7] Suwa H, Hanakita J, Ohshita N, et al. Postoperative changes in paraspinal muscle thickness after various lumbar back surgery procedures. Neurol Med. 2000;40(3):151-154.
[8] Schwender JD, Holly LT, Rouben DP, et al. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion technical feasibility and initial results. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18 (Suppl): S1-6.
[9] 陈晓陇,尚平,温月凤,等.椎旁肌间隙入路与传统后正中入路在胸腰椎后路手术中的应用比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012, 22 (10): 925-930.
[10] Wiltse LL, Bateman JG, Hutchinson RH, et al.The paraspinal sacrospinalis-splitting approach to the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968;50(5):919-926.
[11] 刘玉军,李学民,朱瑜琪.闭式抗生素灌洗治疗腰椎间盘术后椎间隙感染的效果[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(7):554-556.
[12] Kayani I, Syed I, Saifuddin A, et al. Vertebral osteomyelitis withoutdisc involvement. Clin Radiol. 2004;59(10):881-891.
[13] Williams RL, Fukui MB, Mehzer CC, et al. Fungal spinal osteomyelitis in the immunocompromised patient: MR findings in three cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999;20(3): 381-385.
[14] Lury K, Smith JK, Castillo M. Imaging of spinal infections. Semin Roentgenol. 2006;41(4):363-379.
[15] Kurtz SM, Lau E. Ong KL, et al. Infection risk for primary and revision instrumented lumbar spine fusion in the Medicare population. J Neurosury Spine. 2012;17(4):342-347.
[16] Petilon JM, Glassman SD, Dimar JR,et al. Clinical outcomes after lumbar fusion complicated by deep wound infection:a case-control study. Spine. 2012;37(16):1370-1374.
[17] Walters R,Verong-Roberts B,Ffaser R,et al.Therapeutic use of cephazolin to prebent complications of spine surgery. Inflammopharmacology. 2006;14(3/4):138-143.
[18] Viale P, Furlanut M, Scudeuer L, et al. Treatment of pyngenic (nontuberculous) spondylodiscitis with tailored high-dose evofloxacin plus rifampicin. Int J Antimierob Asents. 2009;4: 379-382.
[19] 张亮.椎间隙感染后椎间盘内抗生素药物浓度与软骨终板弥散功能改变的相关研究[D].第二军医大学,2012.
[20] Walters R, Moore R, Fraser R. Penetrat ion of cephazolin in human lumbar in tervertebral disc. Spine. 2006; 31(5): 567-570.
[21] 姚长海,侯树勋,史亚民,等.脊柱椎间隙感染的内固定治疗[D]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(12):1163-1165.
[22] Hadjipavlou AG, Madr JT, Necessary JT, et al. Hematogenic pyogenic spinal infections and their surgical management. Spine. 2000;25(13):1668.
[23] 刘铁龙,严望军,章允志,等.继发性腰椎间盘炎的诊治分析[ J].脊柱外科杂志,2008,6(5):277-280.
[24] 唐焕章,徐皓,姚晓东.一期病灶清除植骨内固定治疗原发性椎间隙感染[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(13):969-972.
[25] 蔡卫华,张宁,金正帅.原发性腰椎间隙感染的诊断与治疗[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(2):132-137.
[26] Lehovsky J. Pyogenic vertebral osteom yelitis/disc infection. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 1999;13(1):59 -75.
[27] Lim JK, Kim SM, Jo DJ, et al.Anterior interbody grafting and instrumentation tor advanced spondylodisctis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2008;43(1):5-10.
[28] 赵斌,王浩,许帆,等.后路椎旁肌间隙人路治疗胸、腰椎结核[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2014,34(2):116-120.
[29] 曹武,万双林,虞和君,等.肌间隙入路椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].浙江医学,2008,30(1):58-60.
[30] Kuriyama N, Ito H. Electromyographic functional analysis of the lumbar spinal muscles with low back pain. Nippon Med Sch. 2005;72(3):165-173.
[31] Issack PS, Boachie-Adjei O. Surgical correction of kyphotic deformity in spinal tuberculosis.Int Orthop. 2012;36(2):353-357. |