Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (9): 1463-1469.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.09.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis for the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty
Li Fei-xiong1, Wang Zhi-yong2, Zhang Zhi-qiang2
- 1Fenyang Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Fenyang 032200, Shanxi Province, China
2The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2015-01-08Online:2015-02-26Published:2015-02-26 -
Contact:Zhang Zhi-qiang, The Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Fei-xiong, Master, Attending physician, Fenyang Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Fenyang 032200, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Fei-xiong, Wang Zhi-yong, Zhang Zhi-qiang. Meta-analysis for the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(9): 1463-1469.
share this article
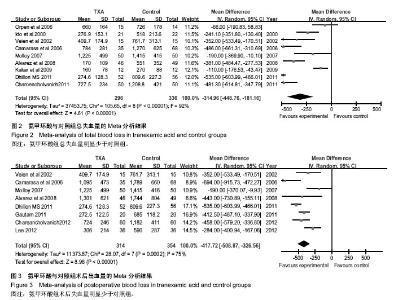
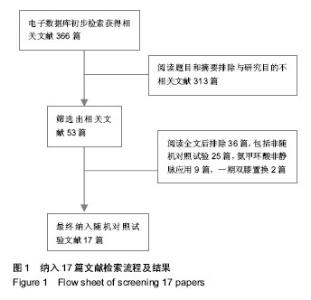
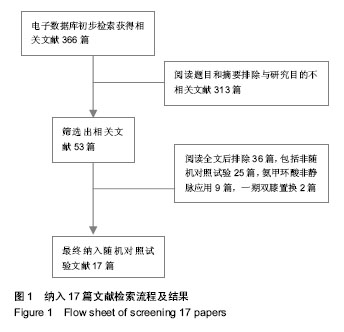
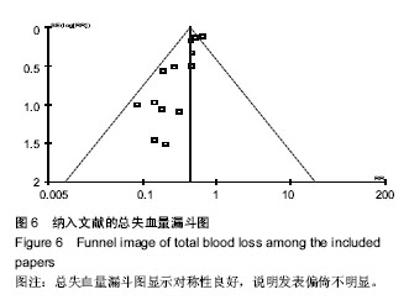
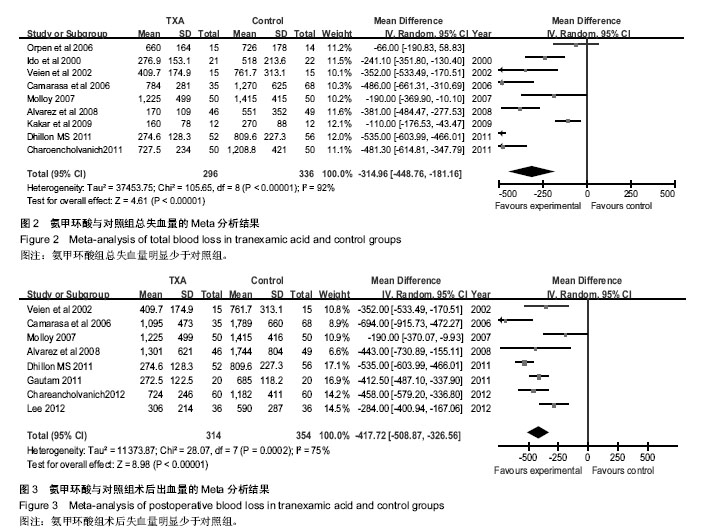
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 总失血量 本文研究结果包括全膝关节置换术中及术后失血量,共纳入9篇文献,氨甲环酸与对照组总量分别为296 mL和336 mL,见图2;两组间存在异质性,采用随机效应模型,荟萃结果显示:平均值标准差MD=-314.96,95%CI(-448.76,-181.16),菱形位于无效线左侧,Z,P < 0.000 1。结果说明氨甲环酸与对照组间差异有显著性意义,氨甲环酸组总失血量明显少于对照组,见图2。=4.61 2.2.2 置换后失血量 本文研究共有8篇文献明确术后失血量,氨甲环酸组与对照组失血总量分别为314 mL和 354 mL,见图3;两组间存在异质性,采用随机效应模型,荟萃结果显示:平均值标准差MD=-417.72,95%CI 为(-508.87,-326.56),菱形位于无效线左侧,Z=8.98,P < 0.00 0 1。结果说明氨甲环酸与对照组间差异有显著性意义,氨甲环酸组术后失血量明显少于对照组,见图3。"
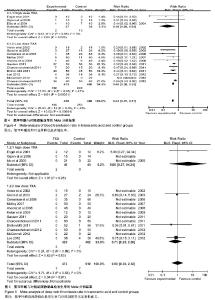
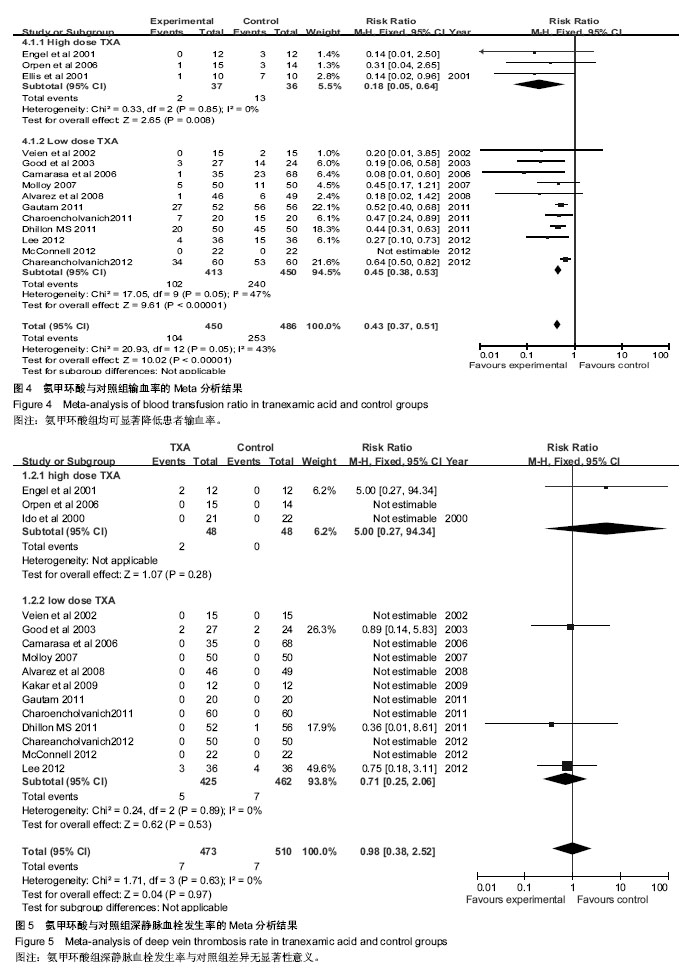
2.2.3 置换后输血率 本文共有14篇研究提出术后输血率,氨甲环酸与对照组总数分别为450和486例,两组间存在异质性,采用固定效应模型,荟萃结果显示:RR=0.43,95%CI(0.37,0.51),菱形位于无效线左侧,Z=10.02,P < 0.000 1。结果说明氨甲环酸组术后输血率明显少于对照组,同时根据剂量分为高低剂量两个亚组,差异均有显著性意义,氨甲环酸组均可显著降低患者输血率,见图4。 2.2.4 置换后深静脉血栓发生率 本文研究有15篇文献提到术后深静脉血栓发生率,两组间同质性较好,采用固定效应模型,荟萃所得结果显示:RR=0.98,95%CI(0.38,2.52),Z=0.04,P=0.97。结果说明氨甲环酸组与对照组间差异无显著性意义,氨甲环酸组深静脉血栓发生率与对照组差异无显著性意义,同时根据剂量分为高低剂量两个亚组,差异也无显著性意义,见图5。"
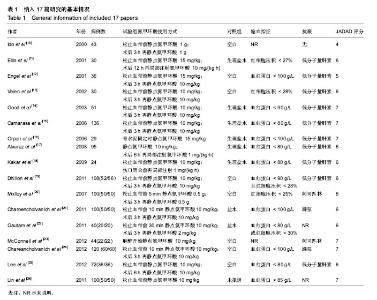
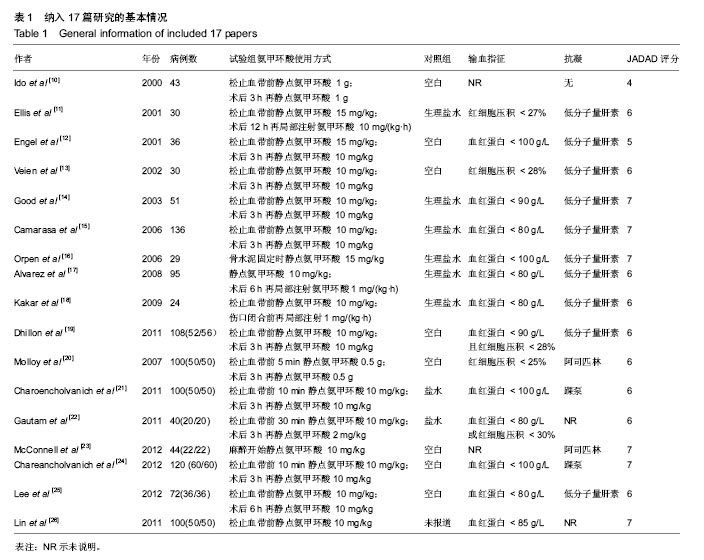
| [1] 赵旻暐,李子剑,张克. 氨甲环酸在人工全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,8(2):236-239. [2] Barwell J, Anderson G, Hassan A, et al. The effects of early tourniquet release during total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized double-blind study. J Bone Joint Surg [Br].1997;79:265-268. [3] Kumar A. Perioperative management of anemia: limits of blood transfusion and alternatives to it. Cleve Clin J Med. 2009; 76:112-118. [4] Lemaire R. Strategies for blood management in orthopaedic and trauma surgery. J Bone Joint Surg [Br].2008;90: 1128-1136. [5] Hill GE, Frawley WH, Griffith KE, et al. Allogeneic blood transfusion increases the risk of postoperative bacterial infection: a meta-analysis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;54(5):908-914. [6] Rajesparan K, Biant LC, Ahmad M, et al. The effect of an intravenous bolus of tranexamic acid on blood loss in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br]. 2009;91:776-783. [7] Sukeik M, Alshryda S, Haddad FS,et al.Systematic review and meta -analysis of the use of tranexa mic acid in total hip replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011;93(1):39-46. [8] 方志辉,杨华清,李兵奎,等. 氨甲环酸应用于膝关节置换术随机对照安慰剂试验的Meta分析[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2012,6(24):8173-8179. [9] Panteli M, Papakostidis C, Dahabreh Z, et al. Topical tranexamic acidintotal knee replacement: Asystematic reviewandmeta-analysis. Knee. 2013;20(5):300-309. [10] Ido K, Neo M, Asada Y, et al. Reduction of blood loss using tranexamic acid in total knee and hip arthroplasties. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2000;120:518-520 [11] Ellis MH, Fredman B, Zohar E, et al. The effect of tourniquet application, tranexamic acid, and desmopressin on the procoagulant and fibrinolytic systems during total knee replacement. J Clin Anesth. 2001;13:509-513. [12] Engel JM, Hohaus T, Ruwoldt R, et al. Regional hemostatic status and blood requirements after total knee arthroplasty with and without tranexamic acid or apro-tinin. Anesth Analg. 2001;92:775-780. [13] Veien M, Sørensen JV, Madsen F, et al. Tranexamic acid given intraop-eratively reduces blood loss after total knee replacement: a randomized, controlled study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002;46:1206-1211. [14] Good L, Peterson E, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth. 2003;90:596-599. [15] Camarasa MA, Ollé G, Serra-Prat M, et al. Efficacy of aminocaproic, tranexamic acids in the control of bleeding during total knee replacement: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96:576-582. [16] Orpen NM, Little C, Walker G, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces early post-operative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised con-trolled trial of 29 patients. Knee. 2006;13:106-110. [17] Alvarez JC, Santiveri FX, Ramos I, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces blood transfu-sion in total knee arthroplasty even when a blood conservation program is applied. Transfusion. 2008; 48:519-525. [18] Kakar PN, Gupta N, Govil P, et al. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in con-trol of bleeding following TKR: a randomized clinical trial. Indian J Anaesth. 2009;53: 667-671. [19] Dhillon MS, Bali K, Prabhakar S. Tranexamic acid for control of blood loss in bilateral total knee replacement in a single stage. Indian J Orthop. 2011;45:148-152. [20] Molloy DO, Archbold HA, Ogonda L, et al. Comparison of topical fibrin spray and tranexamic acid on blood loss after total knee replacement: a prospective, randomised controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(3):306-309. [21] Charoencholvanich K, Siriwattanasakul P. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and blood transfusion after TKA: a prospec-tive randomized controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469 (10):2874-2880. [22] Gautam PL, Katyal S, Yamin M, et al. Effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss and transfusion requirement in total knee re-placement in the Indian population: a case series. Indian J Anaesth. 2011;55(6):590-593. [23] McConnell JS, Shewale S, Munro NA, et al. Reducing blood loss in primary knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial of tranexamic acid and fibrin spray. Knee. 2012; 19 (4):295-298. [24] Chareancholvanich K, Siriwattanasakul P, Narkbunnam R, et al. Temporary clamping of drain combined with tranexamic acid reduce blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:124. [25] Lee SH, Cho KY, Khurana S, et al. Less blood loss under concomitant administration of tranexamic acid and indirect factor Xa inhibitor following total knee arthroplasty: a prospective ran-domized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012. [26] Lin PC, Hsu CH, Chen WS, et al. Does tranexamic acid save blood in minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469:1995-2002. [27] Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty:correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee. 2000;7(3): 151-155. [28] 高福强,李子剑,刘延青,等.初次全膝关节置换术后肢体肿胀程度与隐性失血量的相关性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011, 19(3): 199-202. [29] Zhang H, Chen J, Chen F, et al. The effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss and use of blood products in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(9):1742-1752. [30] Ishida K, Tsumura N, Kitagawa A, et al. Intra -articular injection of tranexamic acid reduces not only blood loss but also knee joint swelling after total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2011;35(11):1639-1645. [31] Camarasa MA, Olle G, Serra -Prat M, et al. Efficacy of aminocaproic,tranexamic acids inthe control of bleeding during total knee replacement: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Anaesth. 2006;96(5):576-582. [32] Orpen NM, Little C, Walker G, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces earlypost -operative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial of 29 patients. Knee. 2006;13(2):106-110. [33] Roy SP,Tanki UF,Dutta A,et al.Efficacy of intra-articular Tranexamic acid in blood loss reduction following primary unil ateral total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(12): 2494-2501. [34] Wong J, Abrishami A, El Beheiry H, et al. Topical application of tranexamic acid reduces postoperative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: arandomized,controlledtrial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(15):2503-2513. [35] Alshryda S, Mason J, Vaghela M, et al. Topical (intra-articular) tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates following total knee replacement: a randomized controlled trial (TRANX-K). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(21): 1961-1968. [36] Orpen NM, Little C, Walker G, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces early post-operative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomised controlled trial of 29 patients. Knee. 2006;13(2):106-110. [37] 王思群,黄钢勇,夏军,等.全膝关节置换术后膝关节位置对术后失血的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2011,5(2): 19-21. [38] 岳辰,马俊,杨沛青,等.氨甲环酸减少同期双侧全髋置换围术期失血有效性及安全性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(10):865-869. [39] Endo Y, Nishimura S, Miura A. Deep-vein thrombosis induced by tranexamic acid in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. JAMA.1988;259(24):3561-3562. [40] 尹勇,马广文,黄斐,等.氨甲环酸减少全髋关节置换失血量的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究.2014,18(17):2752-2757. [41] Benoni G, Lethagen S, Fredin H.The effect of tranexamicacidon local and plasma fibrinolysis during total knee arthroplasty. Thromb Res. 1997;85:195-206. [42] Yang ZG, Chen WP, Wu LD. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94: 1153-1159. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||