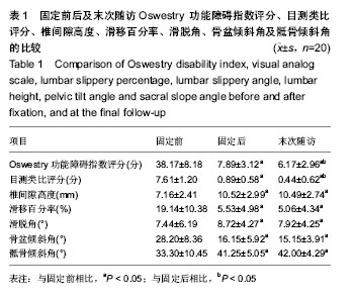
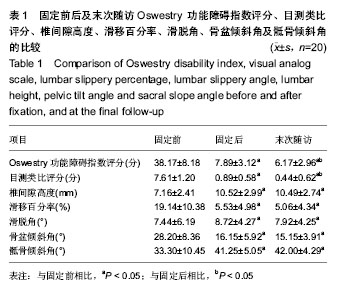
| [1] Wiltse LL, Newman PH, Macnab I. Classification of spondyloisis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;6(117):23-29.
[2] 西永明,贾连顺.退行性腰椎滑脱外科治疗中的相关问题[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(1):65-67.
[3] Kalichman L, Kim DH, Li L, et al. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: prevalence and association with low back pain in the adult community-based population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(2):199-205.
[4] Herkowitz HN. Spine update. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1995;20(9):1084- 1090.
[5] Rubery PT. Degenerative spondylolisthesis. Curr Opin Orthop. 2001;12(3):183-188.
[6] 杜心如,张一模,赵玲秀.腰椎椎弓根螺钉人字嵴顶点进钉方法的放射解剖学研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2000,15(3):206.
[7] Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, et al. Adding posterior lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1997;22(2):210-220.
[8] 吴国保,李健,郑德富.退变性腰椎滑脱症的临床治疗[J].临床骨科杂志,2005,8(2):152-153.
[9] 王静成,戴松茂,董仁章,等.腰椎滑脱的外科治疗初探[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,1997,7(2):87-88.
[10] Lehman RA, Kuklo TR, Belmont PJ, et al. Advantage of pedicle screw fixation directed into the apex of the sacral promontory over bicortical fixation:a biomechanical analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(8):806-811.
[11] 张忠民,金大地,陈建庭.重度腰椎滑脱脊柱序列功能重建[J].中华骨科杂志,2008,28(4):302-306.
[12] Ray CD. Threaded titanium cages for lumbar interbody fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(6):667-680.
[13] 王新伟,赵杰,陈德玉.椎间融合器治疗腰椎滑脱中的即刻复位效应[J].第二军医大学学报,2000,7(21):S13-S14.
[14] Klemme WR, Owens BD, Dhawan A, et al. Lumbar sagittal contour after posterior interbody fusion:threaded devices alone versus versus vertical cages plus posterior instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(5):534-537.
[15] Labelle H, Roussouly P, Chopin D, et al. Spino-pelvic alignment after surgical correction for developmental spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(9):1170-1176.
[16] Hresko MT, Hirschfeld R, Buerk AA, et al. The effect of reduction and instrumentation of spondylolisthesis on spinopelvic sagittal alignment. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009;29(2): 157-162.
[17] Park SJ, Lee CS, Chung SS, et al. Postoperative changes in pelvic parameters and sagittal balance in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis. Neurosurgery. 2011;68(2 Suppl Operative): 355-363.
[18] Jackson RP, Peterson MD, McManus AC, et al. Compensatory spinopelvic balance over the hip axis and better reliability in measuring lordosis to the pelvic radius onstanding lateral radiographs of adult volunteers and patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(16):1750-1767.
[19] Martin CR, Gruszczynski AT, Braunsfurth HA, et al. The surgical management of degenerative lumbar spodylolishthesis: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(16):1791-1798.
[20] Fernandez FM, Sala P, Ramirez H, et al. A prospective randomized study of unilateral versus bilateral instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(4):395-401.
[21] Guo Z, Chen Z, Qi Q, et al. The treatment of severe lumbar dysplastic spondylolisthesis.Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014; 52(11):845-850.
[22] Lan J, Tang X, Xu Y, et al. Surgical treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis with multi-segment lumbar spinal stenosis. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;28(8): 960-964.
[23] Gao Z, Wang M, Zhu W, et al. Tuberculosis of ultralong segmental thoracic and lumbar vertebrae treated by posterior fixation and cleaning of the infection center through a cross-window. Spine J. 2015;15(1):71-78.
[24] Zhang QS, Lü GH, Wang XB, et al. The significance of removing ruptured intervertebral discs for interbody fusion in treating thoracic or lumbar type B and C spinal injuries through a one-stage posterior approach. PLoS One. 2014; 9(5):e97275.
[25] Lequin MB, Verbaan D, Bouma GJ. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with stand-alone Trabecular Metal cages for repeatedly recurrent lumbar disc herniation and back pain. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(6):617-622.
[26] Yu X, Zhu L, Su Q. Lumbar spine stability after combined application of interspinous fastener and modified posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a biomechanical study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(5):623-629.
[27] Jin YM, Yang D, Shao HY, et al. Single midline posterior approach for 360 degree decompression and internal fixation with interbody bone graft fusion for severe thoracolumbar spinal fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2013;26(11):901-906.
[28] Hart RA, Domes CM, Goodwin B, et al. High-grade spondylolisthesis treated using a modified Bohlman technique: results among multiple surgeons. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014; 20(5):523-530.
[29] Tegos S, Charitidis C, Korovessis PG. Hybrid circumferential fixation for degenerative lumbosacral spine disease: posterior lumbar interbody fusion plus universal clamp rod-band instrumentation: a novel technique for lumbosacral fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(7):E441-E449.
[30] Whang PG, Sasso RC, Patel VV, et al. Comparison of axial and anterior interbody fusions of the L5-S1 segment: a retrospective cohort analysis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013; 26(8):437-443.
[31] Wang X, Pang X, Wu P, et al. One-stage anterior debridement, bone grafting and posterior instrumentation vs. single posterior debridement, bone grafting, and instrumentation for the treatment of thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(4):830-837. |