| [1]胡晓静,黄国荧.新生儿先天性心脏病病筛查的研究进展[J].国际儿科学杂志,2014,41(2):120-123.
[2]王佼,杨世伟,朱善良.基因拷贝数变异与先天性心脏病的研究进展[J].国际儿科学杂志,2014,41(2):113-116.
[3]Huber SM, Oncochannels. Cell Calcium. 2013;53:241-255.
[4]Rook MB, Evers MM, Vos MA, et al. Biology of cardiac sodium channel Navl.5 expression. Cardiovasc Res. 2012;93:12-23.
[5]Shy D, Gillet L, Abriel H. Cardiac sodium channel NaV 1.5 distribution in myocytes via interacting proteins:the multiple pool model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1833:886-894.
[6]Klaver EC, Versluijs GM, Wilders R. Cardiac ion channel mutations in the sudden infant deaths yndrome. Int J Cardiol. 2011;152:162-170.
[7]Otagiri T, Kijima K, Osawa M, et al. Cardiac ion channel gene mutations in sudden infant deaths yndrome. Pediatr Res. 2008;64:482-487.
[8]Lei M, Coddard C, Liu J, et al. Sinus node dysfunction following targeted disruption of the cardiac sodium channel gene, SCN5A.J Physiol. 2005;567(2):387-400.
[9]Zeng J, Lin Y, Yan A, et al. Establishment of a molecular diagnostic system for spinal muscular atrophy experience from a clinical laboratory in china. J Mol Diagn. 2011;13(1):41-47.
[10]Liu WL, Li F, He ZX, et al. Molecular analysis of the SMN gene mutations in spinal muscular atrophy patients in China. Genet Mol Res. 2013;12(3):3598-3604.
[11]Tfelt-Hansen J, Winkel BG, Gmmet M, et al. Inherited cardiac diseases caused by mutations in the Navl.5 sodium channel. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21(1):107-115.
[12]Parisi P, Oliva A, Coll Vidal M, et al. Coexistence of epilepsy and Brugada syndrome in a family with SCN5A mutation. Epilepsy Res. 2013;105(3):415-418.
[13]Winkler S, Dahneri L, Hindricks G, et al. New familial heterozygous c 4066_4068delTT 2 bp deletion of The SCN5A gene causing Brugada syndrome. Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(8): 1224-1227 .
[14]Butters TD, Aslanidi 0V, Inada S, et al.Mechanistic links between Na+ channel (SCN5A) mutations and imDaired cardiac pacemaking in sick sinus syndrome. Circ Res. 2010;107(1):126-137.
[15]Makiyama T, Akao M, Shizuta S, et al. A novel SCN5A gain-of-function mutation M1875T associated with familial atrial fibrillation. J Am Coil Cardiol. 2008;52(16):1326-1334.
[16]Gui J, Wang T, Trump D, et al. Mutation-specific effects of Polymorphism H558R in SCN5A-related sick sinus syndrome. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2010;21(5):564-573.
[17]仇晓亮,刘文玲,胡大一,等.国人确诊及疑似Brugada综合征患者SCN5A基因变异筛查[J].中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志, 2009, 23(3):204-208.
[18]Yang P, Kanki H, Drolet B, et al. Allelic variants in long-QT disease genes in patients with drug-associated torsades depointes. Circulation. 2002;105(16):1943-1948.
[19]Chen LY, Ballew JD, Herron KJ, et al. A common polymorphism in SCN5A is associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;81(1):3541.
[20]Maekawa K, Saito Y, Ozawa S, et al. Genetic polymorphisms and haplotypes of the human cardiac sodium channel alpha subunit gene (SCN5A) in Japanese and their association with arrhythmia. Ann Hum Genet. 2005;69(Pt 4):413-428.
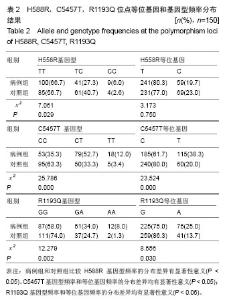
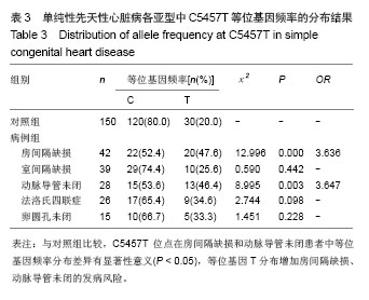
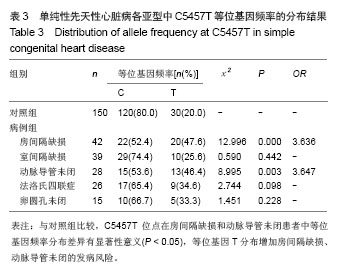
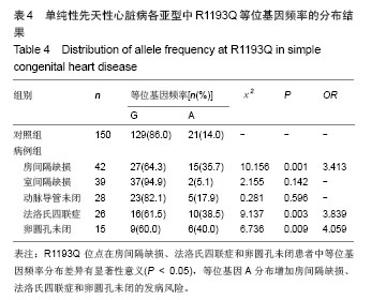
[21]周峰,张坤水,薛天羽,等.中国南方汉族人群SCN5A基因H558R、R1193Q、C5457T及3666+69G﹥C多态性与青壮年猝死综合征的相关性研究[J].国际内科学杂志,2008,35(11):632-636 .
[22]Gouas L, Nicaud V, Berthet M, et al. Association of KCNQI, KCNEI, KCNH2 and SCN5A polymorphisms with QTc interval length in a healthy population. Eur J Hum Genet. 2005; 13(11): 1213-1222.
[23]Wattanasirichaigoon D, Vesely MR, Duggal P, et al. Sodium channel abnormalities are infrequent in patient with long QT syndrome: identification of two novel SCN5A mutations. Am J Med Genet. 1999:86:470-476.
[24]Maekawa K, Saito Y, Ozawa S, et al. Genetic polymorphisms and haplotypes of the human cardiac soudium channel alpha subunit gene (SCN5A) in Japanese ahd association with arrhythmia. Ann Hum Genet. 2005;69:413-428.
[25]Chen JZ, Xie XD, Wang XX, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the SCN5A gene in Han Chinese and their relation with Brngada syndrome. Chin Med J (Engl). 2004;117: 652-656.
[26]Chen LY, Ballew JD, et al. A common polymorphism in SCN5A is associated with lone atrial fibrillation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;81(1):35-41.
[27]Wang Q, Chen S, Chen Q, et al. The common SCN5A mutation R1193Q causes LQTS-type electrophysiological alterations of the cardiac sodium channel. J Med Genet. 2004; 41(5):e66.
[28]Matsusue A, Kashiwagi M, Hara K, et al. An autopsycase of sudden unexpected nocturnal death syndrome with R1193Q polymorphism in the SCN5A gene. Leg Med. 2012;4:9.
[29]Takahata T, Yasui FN, Sasaki S, et al. Nucleotide changes in the translated region of SCN5A from Japanese patients with Brugada syndrome and control subjects. Life Sci. 2003;72(21): 2391-2399.
[30]Chen YT, Hwang HW, Niu DM, et al. R1193Q of SCN5A,a Brugada and long QT mutation, is a common polymorphism in Han Chinese. J Med Genet. 2005;42:e7. |