Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (7): 1099-1103.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.07.021
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ulcerative colitis and epigenetic modification
Huang Yan1, 2, Dou Chuan-zi1, 2, Liu Hui-rong1, 2, Wu Lu-yi2, Lu Yuan2, Wang Xiao-mei1, 2, Hu Hong-yi2,Wu Huan-gan1, 2
- 1Shanghai Research Institute of Acupuncture and Meridan, Shanghai 200030, China; 2Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
-
Online:2015-02-12Published:2015-02-12 -
Contact:Wu Huan-gan, M.D., Professor, Shanghai Research Institute of Acupuncture and Meridan, Shanghai 200030, China; Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China -
About author:Huang Yan, M.D., Attending physician, Shanghai Research Institute of Acupuncture and Meridan, Shanghai 200030, China; Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China -
Supported by:the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program), No. 2015CB554500; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81303033; the Young Talent Project in the Health System of Shanghai, No. XYQ2011068
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Yan, Dou Chuan-zi, Liu Hui-rong, Wu Lu-yi, Lu Yuan, Wang Xiao-mei, Hu Hong-yi. Ulcerative colitis and epigenetic modification[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(7): 1099-1103.
share this article
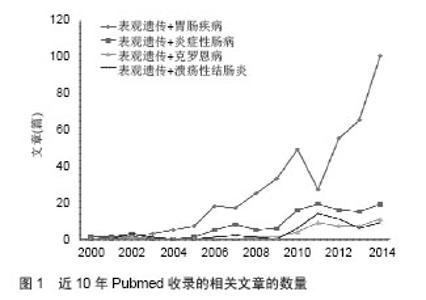
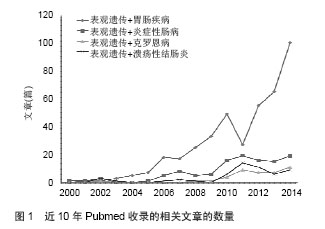
2.1 溃疡性结肠炎的易感基因 最新一项以非西方人群炎症性肠病与环境危险因素相关性研究,提示吸烟与溃疡性结肠炎的发生呈正相关,接受母乳喂养与儿童溃疡性结肠炎的发生呈现负相关性,爱活动与久坐不动的妇女相比溃疡性结肠炎的发病率降低[4]。全基因组关联研究的研究发现有163个基因易感位点与炎症性肠病发病相关,其中有110个同时与克罗恩病和溃疡性结肠炎发病相关,仅23个位点是溃疡性结肠炎特异性的[5]。溃疡性结肠炎的发病与Th17细胞及白细胞介素12/白细胞介素23 相关通路密切相关,其中白细胞介素23受体、IL12B、JAK2和 STAT3均为遗传易感性位点,白细胞介素10的功能不全也是主要的致病机制[6-7]。 人类白细胞抗原变异也是溃疡性结肠炎特异性易感基因,主要有与肠上皮的屏障功能密切相关的[8]。其他易感基因包括TNF相关受体TNFRSF14、TNFRSF9,和白细胞介素相关受体白细胞介素1受体2、IL8Ra/RB及白细胞介素7受体等[6]。 溃疡性结肠炎相关的全基因组关联研究研究还发现了自噬在发病机制中扮演重要角色。虽然前期的全基因组关联研究提示自噬基因ATG16L1、IRGM和LRRK2 和内质网应激基因ORMDL3与溃疡性结肠炎相关[9],但是另一个研究中却发现在自噬改变在克罗恩病的患者中较多,而这些基因在溃疡性结肠炎患者中并没有相关性[10]。 CTLA4与溃疡性结肠炎的发生也密切相关,是人体内一种控制免疫功能的基因,研发的CTLA4-Ig被应用到溃疡性结肠炎的临床治疗,但这种生物疗法并没有像想象中的那样发挥疗效[11]。另外,多个基因表现出显著的甲基化差异性,几个出现在溃疡性结肠炎和克罗恩病的包括THRAP2、FANCC、GBGT1、DOK2、TNFSF4、TNFSF12和FUT7[12]。由此可见,全基因组关联研究提示溃疡性结肠炎与肠上皮屏障功能、机体免疫炎症状态、内质网应激及自噬等因素密切相关。 2.2 表观遗传修饰 表观遗传学补充了“中心法则”忽略的两个问题,一是哪些因素决定了基因的正常转录和翻译;另外,核酸并不是存储遗传信息的唯一载体。表观遗传学是本身不改变基因的序列,但是可以通过基因修饰,蛋白质与蛋白质、DNA和其他分子的相互作用,而影响和调节遗传的基因的功能和特性,并且通过细胞分裂和增殖周期影响遗传的一门新兴学科,也是生命科学中一个普遍而又十分重要的新的研究领域。表观遗传学研究的具体内容包括:①基因选择性转录表达的调控(DNA甲基化,基因印记,DNA甲基化与转座子的稳定性,染色质重塑,伪基因)。②基因转录后的调控(非编码RNA,microRNA,反义RNA,内含子)。③蛋白质的翻译后修饰(组蛋白的甲基化和乙酰化,组蛋白的其他修饰,非组蛋白的共价修饰)。但这些改变是可逆的,即环境及药物可以作用其中的关键酶改变基因的功能,这为疾病的治疗提供了可能。 真核细胞中的基因组DNA在细胞核里是以染色质形式存在的,染色质的基本结构是核小体,重复的核小体结构加上连接的DNA,通过组蛋白及其他非组蛋白蛋白进一步的折叠、压缩形成高度有序的染色质结构。影响基因转录活性而不涉及DNA序列改变的基因表达调控方式称为表观遗传调控,其分子基础有两个方面:即针对DNA本身的修饰和对组蛋白的修饰。研究发现基因沉默或表达在染色质结构上有一定的规律,如DNA甲基化(DNAme)总能在沉默染色质上发现:组蛋白的乙酰化促进基因转录,而去乙酰化抑制基因转录:组蛋白特定氨基酸残基的甲基化可促进基因转录或抑制基因转录[13]。表观遗传修饰常常不是孤立的,而是以共价修饰的方式相互作用的。 DNA的甲基化与组蛋白的乙酰化修饰常常互相影响,是一个复杂的调控体系表观遗传学与遗传学不同,具有可逆性的特点,可以介导基因组和环境之间的相互作用,为基因与环境搭建桥梁。近年来发现的微小RNA(miRNA)在基因的转录后调控中发挥着重要作用。近10余年来,表观遗传在胃肠疾病中的作用机制研究与应用越来越多,在PubMed网站上搜到的相关文献结果表明,近两年相关研究快速增长(见图1)。其中,表观遗传应用在炎症性肠病的研究在近几年中也快速增长,在溃疡性结肠炎发病原因中遗传因素只占其中的一部分,疾病的演变过程中基因与环境的相互作用越来越受到重视。 "
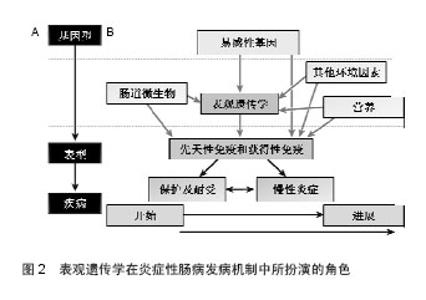
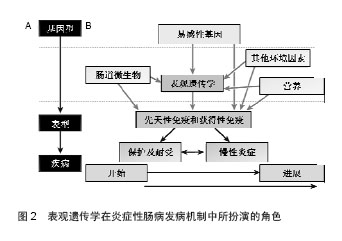
2.3 表观遗传修饰的改变与溃疡性结肠炎疾病的发生、发展密切相关 表观遗传学相关基因表达的变化与结肠黏膜免疫和防御反应密切相关,提示了溃疡性结肠炎的表观遗传变化和炎症之间的关系,有助于寻找潜在的发病原因。表观遗传随着老年化发生改变,从基因型到表型的改变是一系列环境的因素引起的。所以,表观遗传学在溃疡性结肠炎疾病及其他疾病的发病机制中扮演一个关键的角色,影响基因和环境因素(比如肠道微生物环境)之间相互作用[3](见图2)。 2.3.1 DNAme DNA甲基化在溃疡性结肠炎疾病发生、发展中作用是研究最早的一个表观遗传修饰机制,DNA甲基化研究得最清楚、也是最重要的表观遗传修饰形式。通常,DNAme被认为与基因沉默相关联,而去甲基化与使基因活化,表达增强相关联。内外环境可导致机体DNAme,不仅影响基因的转录,还可能影响染色体结构的稳定性。基因组DNA低甲基化通过一系列的途径导致大肠癌的进展,这些途径包括染色体失稳定性,印迹缺失,促癌基因激活和微卫星的失稳定性。CpG岛高甲基化的发生不是随机的。 基因特异性甲基化模式可作为大肠癌与年龄相关的肠道疾病的风险的生物标志物。特定基因的甲基化已经显示出通过一些诱导的基因沉默和染色体的不稳定的途径,包括抑癌基因失活、染色质浓缩和抑制DNA修复机制。 关于溃疡性结肠炎的功能性甲基化图谱在2012年被公布,EWAS结果提示了61个与溃疡性结肠炎疾病相关的DNAme位点,其中一部分甲基化位点是新发现的,在以前尚未报道,新发现的位点中有几个是与炎症发生的过程相关的,如CFI、SPINK4及THY(也称CD90),DNAme增高伴随着MT1H基因表达水平的降低,TK1基因表达水平的增高;而DNAme降低伴随着CFI、HKDC1、SPINK4、THY1等基因表达水平的增高,FLNA、PTN基因表达水平的降低。这个发现有助于揭示疾病发生发展中未被阐明的疾病风险因素相关的分子机制[14]。另有研究表明,溃疡性结肠炎患者被发现ESR-1和N-33基因的启动子区域发生了甲基化,尤其是N-33基因处于高甲基化状态,这可能促进了溃疡性结肠炎患者结直肠组织老化或者是端粒缩短[15]。 2.3.2 组蛋白修饰 组蛋白转录后修饰是另一种研究较多的表观遗传学机制,通常发生在精氨酸、赖氨酸、丝氨酸及苏氨酸的末端残基上,目前研究确认的组蛋白修饰方式有67中,主要包括乙酰化、甲基化、泛素化等,凸显出表观遗传机制的高度复杂性[16]。其中,H3和H4赖氨酸末端残基乙酰化是被研究较为明确的,与基因活化呈正相关,但具体作用机制尚未清楚。组蛋白赖氨酸乙酰化常发生在DNA甲基化降低的密度较小的染色质结构(常染色质)上,此处的基因相对于异染色质其表达水平通常激活。组蛋白乙酰化与去乙酰化状态主要受组蛋白乙酰转移酶(histoneacetylases,HATs)和组蛋白去乙酰化酶(histonedeacetylases,HDACs)相互作用调控。组蛋白乙酰化通过改变核小体内与DNA链相连的组蛋白二级结构使转录因子更易与基因启动子结合,而组蛋白去乙酰化则使转录因子难以与启动子区域结合,以此来激活或抑制基因转录,从而对基因表达进行调节。HATs和HDACs之间的动态平衡控制着染色质的结构和基因的表达,组蛋白乙酰化状态的失衡与许多疾病的发生密切相关。组蛋白乙酰化及去乙酰化修饰是最重要的方式,是基因表达调控最主要的驱动力。 2013年发现,在大肠上皮细胞条件性敲除HDAC3基因后结直肠出现了明显的表型,结直肠明显缩短,这种去乙酰化酶缺失后体内H3K9乙酰化水平增多,而溃疡性结肠炎模型小鼠体质量下降,苏木精-伊红染色提示有结直肠明显的炎症损害,说明了HDAC3在溃疡性结肠炎疾病中具有重要的作用[17]。 黑莓通过纠正抑癌基因启动子区域高甲基化,从而抑制了DSS诱导的结直肠的溃疡,结肠组织HDAC1、HDAC2和MBD2(甲基化结合区域2)表达水平均出现下 调[18]。HDAC抑制剂被应用于溃疡性结肠炎的治疗,结果提示HDAC抑制剂具有明显的抑制结肠炎症,修复溃疡损伤的作用,其机制不是简单的组蛋白去乙酰化和乙酰 化[19]。 丁酸盐是机体内也存在的一种内源性HDACs抑制剂,通常通过增加体内的组蛋白乙酰化而激活NOD2表达[20]。组蛋白乙酰化还可以促进肠道内的碱性磷酸酶分泌,促进β防御素的产生,对肠道微生态具有重要作用以维持内环境稳态[20]。 2.3.3 非编码RNA(ncRNA)所介导的基因沉默 ncRNA是表观遗传另一个机制的重要发现,其特点是从基因组上转录而来,但不翻译成蛋白,在RNA层面就有各自的生物学功能,参与信号转导、细胞繁殖、分化及凋亡。ncRNA包括tRNAs、rRNAs、snoRNAs、miRNAs、siRNAs、snRNAs、exRNAs和 piRNAs。这些分子影响mRNA翻译过程,通过DNA-ncRNA或ncRNA-蛋白的相互作用诱导其降解或调节基因表达[21]。 全基因组关联研究还发现8个miRNA分子在溃疡性结肠炎中显著上调,3个显著下调,其中在溃疡性结肠炎患者中miR-192明显下调,该微小RNA具有降低炎症细胞趋化的作用[22]。MiRNA在炎症性肠病中的作用研究提示,miRNAs参与转录因子核因子κB途径,比如miR-146、miR-122、miR-132、miR-126等;参与肠上皮屏障功能,如miR-21、miR-150和miR-200等;参与自噬活性,如miR-30、miR-130、miR-106、miR-93和miR-196等[23]。 Dicer1是miRNA发展成熟过程中的关键酶,Dicer1基因敲除后,小鼠肠上皮细胞分化功能受损,防御功能减弱,肠上皮有中性类细胞大量浸润,淋巴细胞发生迁移,说明了微小RNA在溃疡性结肠炎中具有重要的调节作用[24]。MiRNA-155可能通过激活了核因子κB途径,调控了FOXO3a基因的沉默。动物研究中发现miR-19a作用靶点是肿瘤坏死因子α,参与溃疡性结肠炎的病理过程[25]。在儿童溃疡性结肠炎活动期患者中,miR-124调控了STAT3的表达,miR-124表达水平下调的同时STAT3表达上调,在儿童溃疡性结肠炎病理过程中促进炎症的作用[26]。"
| [1]Ng SC, Tang W, Ching JY, et al. Incidence and Phenotype of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Based on Results From the Asia-Pacific Crohn's and Colitis Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology.2013;145(1):158-165.
[2]王玉芳,欧阳钦.3100例溃疡性结肠炎住院病例回顾分析[J].中华消化杂志,2006,26(6):368-372.
[3]Ventham NT,Kennedy NA, Nimmo ER, et al. Beyond Gene Discovery in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: The Emerging Role of Epigenetics. Gastroenterology.2013;145(2):293-308.
[4]Ng SC, Tang W, Leong RW, et al. Environmental risk factors in inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based case-control study in Asia-Pacific. Gut. 2014;gutjnl-2014- 307410.
[5]Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature.2012;491(7422):119-124.
[6]Anderson CA,Boucher G,Lees CW, et al. Meta-analysis identifies 29 additional ulcerative colitis risk loci, increasing the number of confirmed associations to 47. Nat Genet.2011; 43(3):246-252.
[7]Brand S. Crohn's disease: Th1, Th17 or both? The change of a paradigm: new immunological and genetic insights implicate Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease. Gut.2009; 58(8):1152-1167.
[8]Juyal G, Negi S, Sood A, et al. Genome-wide association scan in north Indians reveals three novel HLA-independent risk loci for ulcerative colitis. Gut., 2014,16.pii: gutjnl-2013- 306625.
[9]Palomino-Morales RJ, Oliver J, Gómez-García M, et al. Association of ATG16L1 and IRGM genes polymorphisms with inflammatory bowel disease: a meta-analysis approach. Genes Immun.2009;10(4):356-364.
[10]Hoefkens E, Nys K, John JM, et al.Genetic association and functional role of Crohn disease risk alleles involved in microbial sensing, autophagy, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Autophagy.2013:9 (12):2046-2055.
[11]Mayer L, Kaser A, Blumberg RS. Dead on arrival: understanding the failure of CTLA4-immunoglobulin therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(1):13-17.
[12]Cooke J, Zhang H, Greger L,et al. Mucosal genome-wide methylation changes in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis.2012;18(11):2128-2137.
[13]黄艳,卢圣锋,何苏云,等.组蛋白乙酰化与缺血性心肌病[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(8):2285-2288.
[14]Häsler R, Feng Z, Bäckdahl L, et al. A functional methylome map of ulcerative colitis. Genome Res.2012;22(11):2130-2137.
[15]Arasaradnam RP, Khoo K, Bradburn M, et al. DNA methylation of ESR-1 and N-33 in colorectal mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). Epigenetics. 2010;5(5): 422-426.
[16]Tan M, Luo H, Lee S, et al. Identification of 67 Histone Marks and Histone Lysine Crotonylation as a New Type of Histone Modification. Cell.2011;146(6):1016-1028.
[17]Alenghat T, Osborne LC, Saenz SA, et al. Histone deacetylase 3 coordinates commensal-bacteria-dependent intestinal homeostasis. Nature.2013;504(7478):153-157.
[18]Wang LS, Kuo CT, Stoner K, et al. Dietary black raspberries modulate DNA methylation in dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced ulcerative colitis. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(12): 2842-2850.
[19]Glauben R,Sonnenberg E,Zeitz M,et al.HDAC inhibitors in models of inflammation-related tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2009;280(2):154-159.
[20]Lees CW, Barrett JC, Parkes M, et al. New IBD genetics: common pathways with other diseases. Gut.2011;60(12): 1739-1753.
[21]Nie L, Wu HJ, Hsu JM, et al. Long non-coding RNAs: versatile master regulators of gene expression and crucial players in cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2012;4(2):127-150.
[22]Wu F, Zikusoka M, Trindade A, et al. MicroRNAs are differentially expressed in ulcerative colitis and alter expression of macrophage inflammatory peptide-2 alpha. Gastroenterology.2008;135(5):1624-1635.
[23]Chen WX, Ren LH, Shi RH. Implication of miRNAs for inflammatory bowel disease treatment: Systematic review. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol.2014;5(2):63-70.
[24]McKenna LB,Schug J,Vourekas A,et al.MicroRNAs control intestinal epithelial differentiation, architecture, and barrier function. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(5):1654-1664.
[25]周鹏志,陈斌,胡品津,等.miR-19a对溃疡性结肠炎的作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(9):1325-1328.
[26]Koukos G,Polytarchou C,Kaplan JL,et al.MicroRNA-124 regulates STAT3 expression and is down-regulated in colon tissues of pediatric patients with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology.2013;145(4):842-852.
[27]Takaishi H, Kanai T, Nakazawa A, et al. Anti-high mobility group box 1 and box 2 non-histone chromosomal proteins (HMGB1/HMGB2) antibodies and anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies (ASCA):accuracy in differentially diagnosing UC and CD and correlation with inflammatory bowel disease phenotype. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47(9):969-977.
[28]Dhir M,Montgomery EA,Glöckner SC,et al.Epigenetic regulation of WNT signaling pathway genes in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) associated neoplasia. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12(10):1745-1753. |
| [1] | Zhang Shuang, Tan Rui, Wang Chunxiao, Wu Fengyu, Guo Hongyu. MicroRNAs for assessing the motion control of human skeletal muscles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2755-2760. |
| [2] | Ren Chunmei, Liu Yufang, Xu Nuo, Shao Miaomiao, He Jianya, Li Xiaojie. Non-coding RNAs in human dental pulp stem cells: regulations and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1130-1137. |
| [3] | Han Mingli, Lü Pengwei, Qian Xueke, Yang Xue, Yang Yunqing, Gu Yuanting. MicroRNA-10b regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 mRNA and protein expression in breast cancer MCF-7 cell line [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1349-1353. |
| [4] | Yang Jinfeng, Ma Sanhui. Association between polymorphism of aggregate protein metabolic pathway gene and severity of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 4939-4944. |
| [5] | Gao Hongqiang, Liu Jing, Li Zhiqiang, Wang Hailei, Zhao Xiongqi, Zhang Shengning, Ran Jianghua, Li Li . Ulinastatin improves rat liver metabolism after reduced-size liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 435-440. |
| [6] | Deng Guiying1, 2, Zeng Gaofeng3, Cen Zhongxi1, Gao Yunbing1, Cao Baichuan1, Huang Jianhua1, Zong Shaohui1 . Effect of miRNA-136-5p on inflammatory factors in rat models of acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2397-2402. |
| [7] | Gong Hewei, Liu Chengwei, Liang Bingsheng, Li Gang. Lentiviral vector-mediated overexpression of miRNA-1 in L6 myoblasts: cell proliferation, differentiation and histone deacetylase expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2075-2080. |
| [8] | Qi Minjun, Wu Xiaopeng, Zhou Zhongxing, Jiang Xiaodong. miR-142-3p effect on the stemness of bladder cancer stem cells via regulation of S1PR3 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2028-2034. |
| [9] | Deng Qiang1, Zhang Ya-lou2, Zhou Yangjunjie1, Ma Chuang1, Sheng Wei-bin1. Differential expression of microRNAs related to apoptosis in human osteoblasts induced by sodium fluoride [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(8): 1149-1154. |
| [10] | Liu Rui1, He Jia2, Liu Xiufang2, Feng Xiaoqiu1, Gu Zhanxin2, Kang Shanping1. Gene chipset analysis in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease intervened by polyene phosphatidylcholine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5833-5839. |
| [11] | He Pin, Guo Fu-qiang. miR-124 facilitates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells by inhibiting the Notch pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5344-5349. |
| [12] | Yang Kai-yun, Sun Pei-pei, Wu Wen-liang, Liu Hai-chun. Interactions of Notch signaling pathway and miR-21 in peripheral nerve repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(32): 5139-5144. |
| [13] | Wang Wen-zhao, Su Yan-lin, Li Hong-fei, Shen Lin, Chen Jia-nan, Pan Xin-da, Jia Tang-hong. miR-21a-5p knockdown promotes the locomotor function recovery of mouse models of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(32): 5180-5185. |
| [14] | He Xin-zhi, Lu Guan-ming, Pu Jian, Wei Zhong-heng, Ma Yan-fei, Chen Yong-cheng, Qin Qiang, Huang Qian-fang, Luo Zhi-zhai. miR-93 effects on the proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of tumor stem cells in thyroid papillary carcinoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(25): 3987-3992. |
| [15] | He Ji-gang, Han Jin-xiu, Yan Dan, Li Bei-bei, Sa Ya-lian, Xie Qiao-li. A molecular study on myocardial repair via exosomes secreted from GATA-4-overexpressed bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(21): 3292-3298. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||