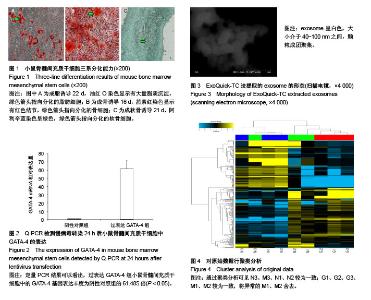
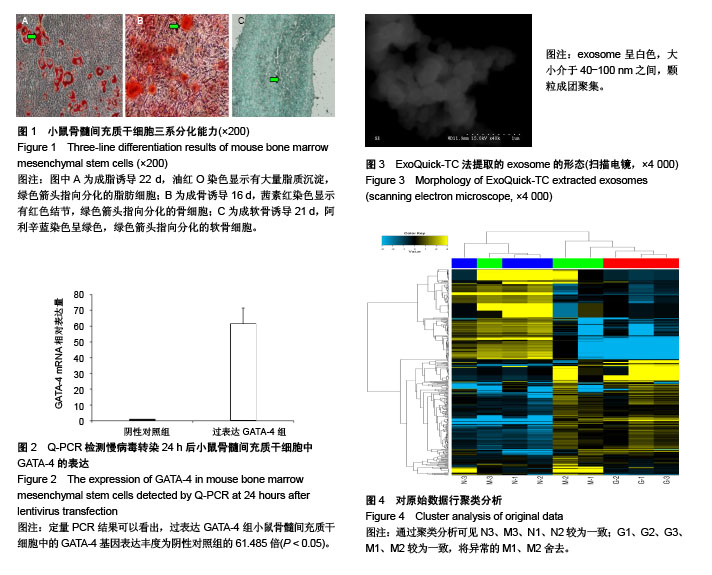
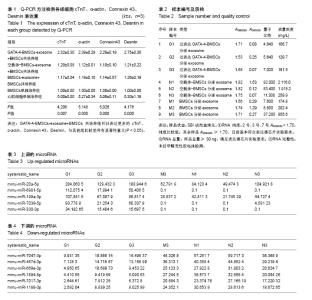
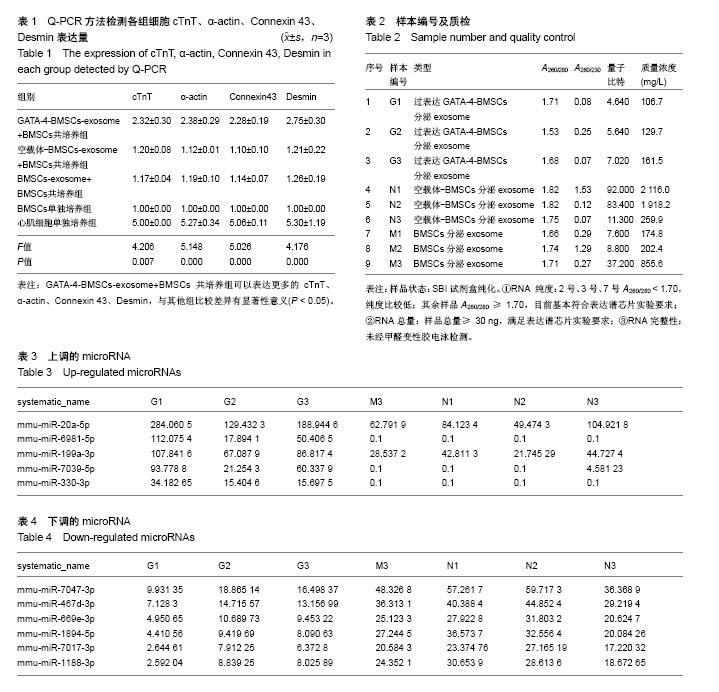
| [1] The top 10 causes of death. June 2011. at http:// www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/index.html.[2] Shah N, Soon K, Wong C, et al. Screening for asymptomatic coronary heart disease in the young 'at risk' population: Who and how. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2014;6: 60-65.[3] Fang L, Deng Z, Shatseva T, et al. MicroRNA miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting integrin-β8. Oncogene. 2011;30(7):806-821.[4] Lim LP, Lau NC, Weinstein EG, et al. The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes Dev. 2003;17(8):991-1008.[5] Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Meyer J, et al. New microRNAs from mouse and human. RNA. 2003;9(2): 175-179.[6] Kim S, Lee UJ, Kim MN, et al. MicroRNA miR-199a* regulates the MET proto-oncogene and the downstream extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2). J Biol Chem. 2008;283(26):18158-18166.[7] Shatseva T, Lee DY, Deng Z, et al. MicroRNA miR-199a-3p regulates cell proliferation and survival by targeting caveolin-2. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 16):2826-2836.[8] Wang Z, Ma X, Cai Q, et al. MiR-199a-3p promotes gastric cancer progression by targeting ZHX1. FEBS Lett. 2014; 588(23):4504-4512.[9] Vergaro G, Del Franco A, Giannoni A, et al. Galectin-3 and myocardial fibrosis in nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 2015;184:96-100. [10] Mackinnon AC, Gibbons MA, Farnworth SL, et al. Regulation of transforming growth factor-β1-driven lung fibrosis by galectin-3. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012; 185(5):537-546. [11] Lino Cardenas CL, Henaoui IS, Courcot E, et al. miR-199a-5p Is upregulated during fibrogenic response to tissue injury and mediates TGFbeta-induced lung fibroblast activation by targeting caveolin-1. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(2): e1003291.[12] Lee CG, Kim YW, Kim EH, et al. Farnesoid X receptor protects hepatocytes from injury by repressing miR-199a-3p, which increases levels of LKB1. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(5):1206-1217.[13] Weng J, Wang C, Zhong W, et al. Activation of CD137 Signaling Promotes Angiogenesis in Atherosclerosis via Modulating Endothelial Smad1/5-NFATc1 Pathway. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(3): e004756.[14] Port JD, Walker LA, Polk J, et al. Temporal expression of miRNAs and mRNAs in a mouse model of myocardial infarction. Physiol Genomics. 2011;43(19):1087-1095. |