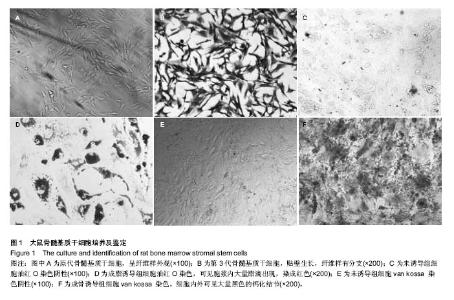
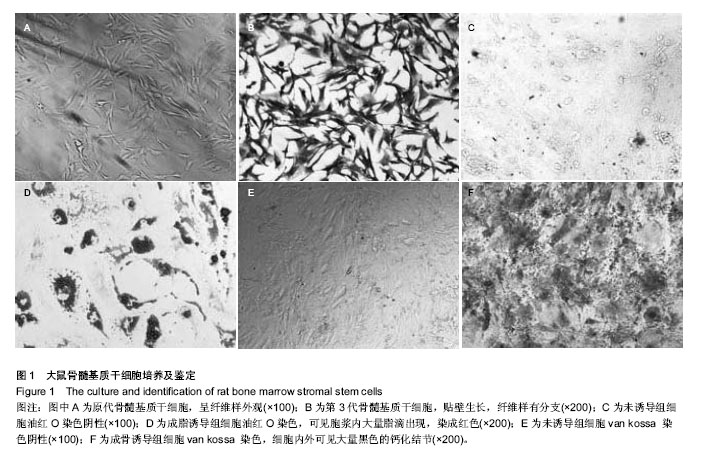
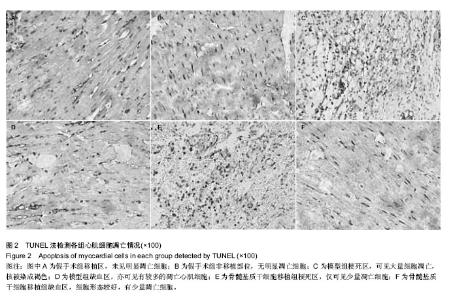
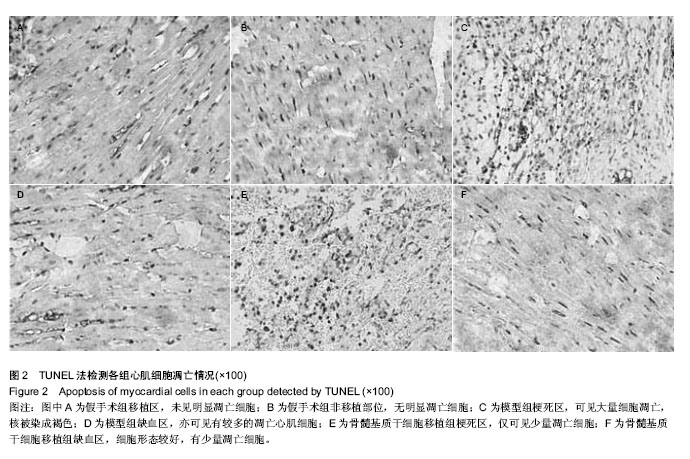
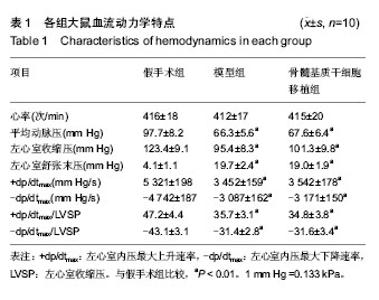
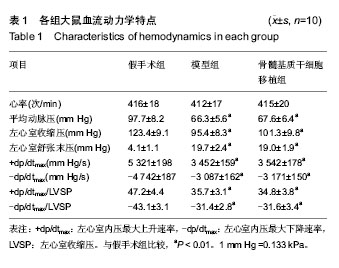
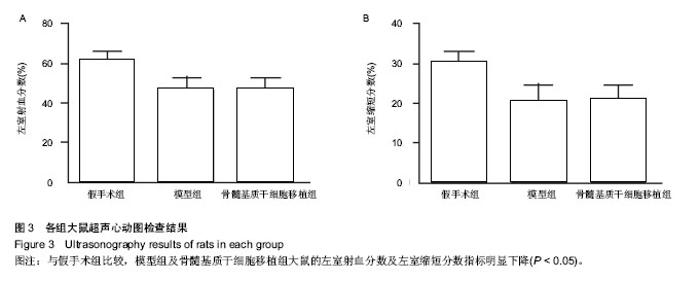
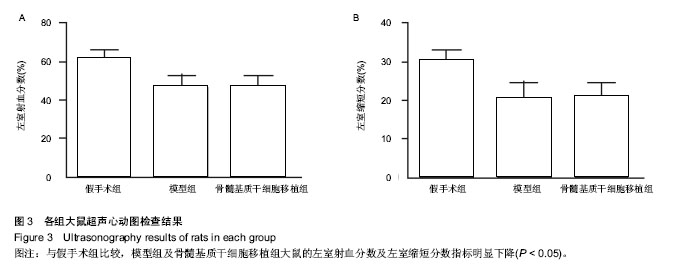
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (1): 108-113.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.01.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transplantation of bone marrow stromal stem cells into the ischemic myocardium reduces myocardial apoptosis but cannot improve cardiac function
Jiang Shuai1, Dong Shi-cai1, Wei Dong-xing2
- 1Department of Cardiology, Jinzhou Center Hospital, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Jinzhou Center Hospital, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2014-11-21Online:2015-01-01Published:2015-01-01 -
Contact:Wei Dong-xing, Department of Orthopedics, Jinzhou Center Hospital, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Jiang Shuai, Attending physician, Department of Cardiology, Jinzhou Center Hospital, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Shuai, Dong Shi-cai, Wei Dong-xing. Transplantation of bone marrow stromal stem cells into the ischemic myocardium reduces myocardial apoptosis but cannot improve cardiac function[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(1): 108-113.
share this article
| [1] Piro FR, di Gioia CR, Gallo P, et al. Is apoptosis a diagnostic marker of acute myocardial infarction.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000;124(6):827-831. [2] Joggerst SJ, Hatzopoulos AK.Stem cell therapy for cardiac repair: benefits and barriers.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009;11: e20. [3] Abdel-Latif A, Bolli R, Tleyjeh IM,et al.Adult bone marrow- derived cells for cardiac repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(10):989-997. [4] Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt prevent remodeling and restore performance of infarcted hearts.Nat Med. 2003;9(9): 1195-1201. [5] Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M,et al.Apoptosis in human acute myocardial infarction.Circulation. 1997;95(2):320-323. [6] 边素艳,盖鲁粤,叶平,等.SPK1 基因转染对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的影响[J].军医进修学院学报,2010,31(3):261-264. [7] Bian SY,Gai LY,Ye P,et al. Sphingosine kinase-1 protects transplanted mesenchymal stem cells and improves the performance of the infarcted heart. Gene Ther Mol Biol.2009; 13:274-283. [8] Noiseux N, Gnecchi M, Lopez-Ilasaca M,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing Akt dramatically repair infarcted myocardium and improve cardiac function despite infrequent cellular fusion or differentiation.Mol Ther. 2006; 14(6): 840-850. [9] 文毅,边素艳,王红叶.间充质干细胞移植早期对心肌细胞凋亡及左心室功能的影响[J].军医进修学院学报,2012,33(9):953-956. [10] Gnecchi M, He H, Noiseux N,et al.Evidence supporting paracrine hypothesis for Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac protection and functional improvement. FASEB J. 2006;20(6):661-669. [11] 常影,李树岩,董明慧.骨髓间充质干细胞联合VEGF基因移植对AMI心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国临床研究,2012,25(5): 420-423. [12] 曾彬,林国生,张艳,等.血红素氧合酶-1修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞心肌移植对梗死后心肌细胞凋亡及左心室功能的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25(9):1681-1685. [13] Hua F, Cornejo MG, Cardone MH,et al.Effects of Bcl-2 levels on Fas signaling-induced caspase-3 activation: molecular genetic tests of computational model predictions.J Immunol. 2005;175(2):985-995. [14] Zachary I.Signaling mechanisms mediating vascular protective actions of vascular endothelial growth factor.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;280(6):C1375-1386. [15] Tang YL, Zhao Q, Qin X,et al.Paracrine action enhances the effects of autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on vascular regeneration in rat model of myocardial infarction. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80(1):229-236. [16] Markel TA, Crisostomo PR, Wang M,et al.TNFR1 signaling resistance associated with female stem cell cytokine production is independent of TNFR2-mediated pathways.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;295(4):R1124- 1130. [17] Plumas J, Chaperot L, Richard MJ,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells induce apoptosis of activated T cells.Leukemia. 2005; 19(9):1597-1604. [18] Markel TA, Wang Y, Herrmann JL,et al.VEGF is critical for stem cell-mediated cardioprotection and a crucial paracrine factor for defining the age threshold in adult and neonatal stem cell function.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008; 295(6):H2308-2314. [19] 王欢,邓丽群,王亚利,等.骨髓间充质干细胞通过旁分泌作用治疗大鼠心肌梗死[J].中华移植杂志:电子版,2013,7(2):94-98. [20] 郭俊芳,张赢予,莫亚宏,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞对体外损伤心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].江苏大学学报:医学版,2009,19(3):225-229. [21] Ito S, Barrett AJ, Dutra A,et al.Long term maintenance of myeloid leukemic stem cells cultured with unrelated human mesenchymal stromal cells.Stem Cell Res. 2014;14(1): 95-104. [22] Jeong HS, Lee HK, Tark KC,et al.Effect of endogenous bone marrow derived stem cells induced by AMD-3100 on expanded ischemic flap.J Korean Med Sci. 2014;29 Suppl 3:S237-248. [23] Li M, Guo K, Ikehara S.Intractable diseases treated with intra-bone marrow-bone marrow transplantation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2014;2:48. [24] Pereira WC, Khushnooma I, Madkaikar M,et al.Reproducible methodology for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord and its potential for cardiomyocyte generation.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008;2(7):394-399. [25] Tarte K, Gaillard J, Lataillade JJ,et al.Clinical-grade production of human mesenchymal stromal cells: occurrence of aneuploidy without transformation.Blood. 2010;115(8): 1549-1553. [26] Jin J, Zhao Y, Tan X,et al.An improved transplantation strategy for mouse mesenchymal stem cells in an acute myocardial infarction model.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21005. [27] Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W,et al.Heart disease and stroke statistics--2006 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee.Circulation. 2006;113(6):e85-151. [28] 王莹.静脉移植骨髓间充质干细胞对心肌梗死大鼠心脏的保护作用[D].西安:第四军医大学,2007. [29] 余其贵,王永,吴继雄. 自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植心肌梗死区后细胞因子分泌和血管新生及心肌细胞凋亡的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(16):3001-3005. [30] Van Kerckhoven R, van Veghel R, Saxena PR,et al. Pharmacological therapy can increase capillary density in post-infarction remodeled rat hearts.Cardiovasc Res. 2004; 61(3):620-629. [31] Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, et al. Universal definition of myocardial infarction.Eur Heart J. 2007;28(20):2525-2538. [32] Perez-Ilzarbe M, Agbulut O, Pelacho B,et al.Characterization of the paracrine effects of human skeletal myoblasts transplanted in infarcted myocardium.Eur J Heart Fail. 2008; 10(11):1065-1072. [33] Hansson EM, Lindsay ME, Chien KR.Regeneration next: toward heart stem cell therapeutics.Cell Stem Cell. 2009; 5(4):364-377. [34] Hofmann M, Wollert KC, Meyer GP,et al.Monitoring of bone marrow cell homing into the infarcted human myocardium. Circulation. 2005;111(17):2198-2202. [35] Barbash IM, Chouraqui P, Baron J,et al.Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infarcted myocardium: feasibility, cell migration, and body distribution.Circulation. 2003;108(7):863-868. [36] Tang YL, Zhao Q, Zhang YC,et al.Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation induce VEGF and neovascularization in ischemic myocardium.Regul Pept. 2004;117(1):3-10. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [4] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [5] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [7] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [8] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [9] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [10] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [11] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [12] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [13] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||