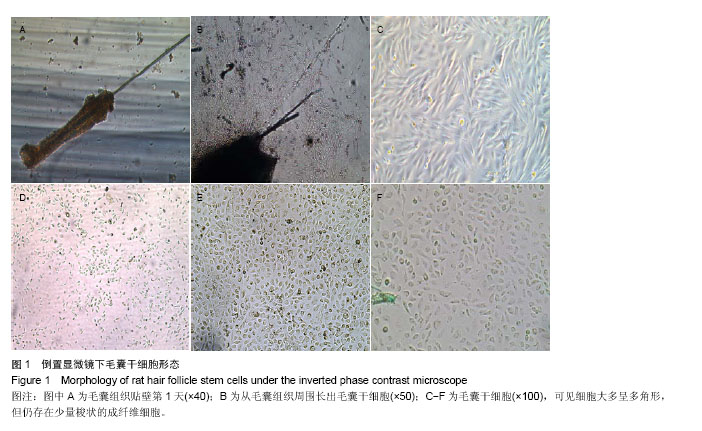
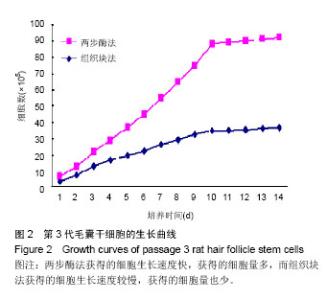
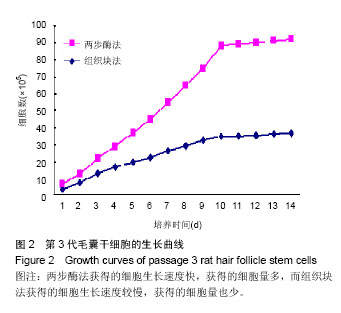
| [1] Drewa T, Joachimiak R, Kaznica A,et al.Hair stem cells for bladder regeneration in rats: preliminary results.Transplant Proc. 2009;41(10):4345-4351.
[2] Drewa T, Joachimiak R, Kaznica A,et al.Primary cultures from rat vibrissae as a potential cell source for in vitro construction of urinary bladder wall grafts.Transplant Proc. 2009;41(5): 1932-1935.
[3] Cotsarelis G, Sun TT, Lavker RM.Label-retaining cells reside in the bulge area of pilosebaceous unit: implications for follicular stem cells, hair cycle, and skin carcinogenesis.Cell. 1990;61(7):1329-1337.
[4] Rochat A, Kobayashi K, Barrandon Y.Location of stem cells of human hair follicles by clonal analysis.Cell. 1994;76(6): 1063-1073.
[5] Morasso MI, Tomic-Canic M.Epidermal stem cells: the cradle of epidermal determination, differentiation and wound healing.Biol Cell. 2005;97(3):173-183.
[6] Paus R, Foitzik K.In search of the "hair cycle clock": a guided tour.Differentiation. 2004;72(9-10):489-511.
[7] Najafzadeh N, Nobakht M, Pourheydar B, et al. Rat hair follicle stem cells differentiate and promote recovery following spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(36): 3365-3372.
[8] 李睿书,王石泉.毛囊干细胞[J].细胞生物学杂志,2007, 29(4): 457-462.
[9] Ohyama M, Terunuma A, Tock CL,et al.Characterization and isolation of stem cell-enriched human hair follicle bulge cells.J Clin Invest. 2006;116(1):249-260.
[10] Ni TX, Zhang KZ, Liu XJ, et al. miR-21 promotes the differentiation of hair follicle-derived neural crest stem cells into Schwann cells.Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(8):828-836.
[11] Jones PH, Watt FM.Separation of human epidermal stem cells from transit amplifying cells on the basis of differences in integrin function and expression.Cell. 1993;73(4):713-724.
[12] 张群,杨光辉,丛笑倩,等.差速贴壁法分选人毛囊干细胞的实验研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2006,23(6):755-757.
[13] 杨青,李秀兰,张杨,等.表皮干细胞与毛囊干细胞生物学特性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(27):5034-5038.
[14] Lee SE, Sada A, Zhang M,et al.High Runx1 levels promote a reversible, more-differentiated cell state in hair-follicle stem cells during quiescence.Cell Rep. 2014;6(3):499-513.
[15] 王祝迁,木拉提•热夏提,李佳,等.大鼠触须毛囊干细胞的分离培养和鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27): 5031-5034.
[16] 邓立欢,杨斌.毛囊干细胞双向分化的分子调控机制[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2010,6(2):111-113,117.
[17] Bongiovanni L, Di Diodoro F, Della Salda L,et al.On the role of survivin as a stem cell biomarker of canine hair follicle and related tumours.Vet Dermatol. 2014;25(2):138-141, e39-40.
[18] Wang Y, Liu J, Tan X, et al.Induced pluripotent stem cells from human hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9(4):451-460.
[19] 彭彧,王玉杰,李佳,等.不同体积分数富血小板血浆与大鼠毛囊干细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(45):8501-8505.
[20] 王平,杜明军,解海博,等.毛囊干细胞结合电纺纳米丝素纤维构建组织工程尿道膜片的体外研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2014,10(2):69-72.
[21] 杨珂,姜自林,杨恬,等.大鼠毛囊干细胞的体外分离培养及增强型绿色荧光蛋白示踪[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(8):1481-1484.
[22] Lien WH, Polak L, Lin M,et al.In vivo transcriptional governance of hair follicle stem cells by canonical Wnt regulators.Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(2):179-190.
[23] 张群,杨光辉,丛笑倩,等.毛囊干细胞表皮膜片修复裸鼠皮肤缺损的实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2009,5(2):79-82.
[24] 杨鹏高,方勇.毛囊干细胞的研究及应用进展[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2008,24(1):71-73.
[25] Wang Y, Liu J, Tan X, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells from human hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cell Rev. 2013;9(4):451-460.
[26] Folgueras AR, Guo X, Pasolli HA, et al.Architectural niche organization by LHX2 is linked to hair follicle stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(3):314-327.
[27] 王祝迁,木拉提•热夏提,李佳,等.大鼠触须毛囊干细胞的分离培养和鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27): 5031-5034.
[28] 许志成,李宏,张群.体外诱导毛囊干细胞成血管平滑肌细胞的实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2012,8(4):181-184.
[29] Bongiovanni L, Di Diodoro F, Della Salda L,et al.On the role of survivin as a stem cell biomarker of canine hair follicle and related tumours.Vet Dermatol. 2014;25(2):138-141, e39-40.
[30] Li S, Park H, Trempus CS,et al.A keratin 15 containing stem cell population from the hair follicle contributes to squamous papilloma development in the mouse.Mol Carcinog. 2013; 52(10):751-759.
[31] 张志强,王玉杰,李佳,等.大鼠毛囊干细胞的成骨及成脂诱导[J].医学研究生学报,2014,27(4):340-343.
[32] 胡孝辉,方勇.毛囊干细胞及其增殖分化研究进展[J].中华烧伤杂志,2009,25(2):156-158.
[33] Waghmare SK, Tumbar T.Adult hair follicle stem cells do not retain the older DNA strands in vivo during normal tissue homeostasis.Chromosome Res. 2013;21(3):203-212. |