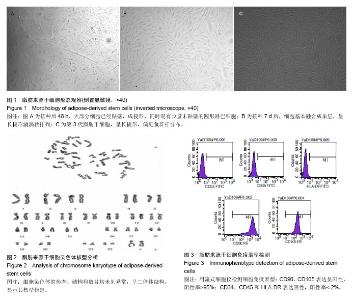
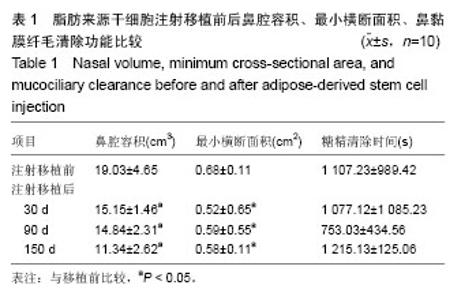
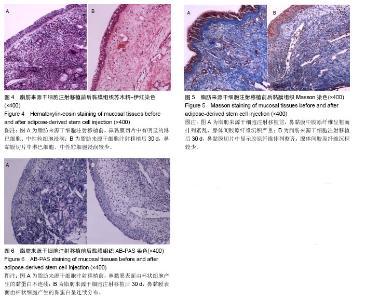
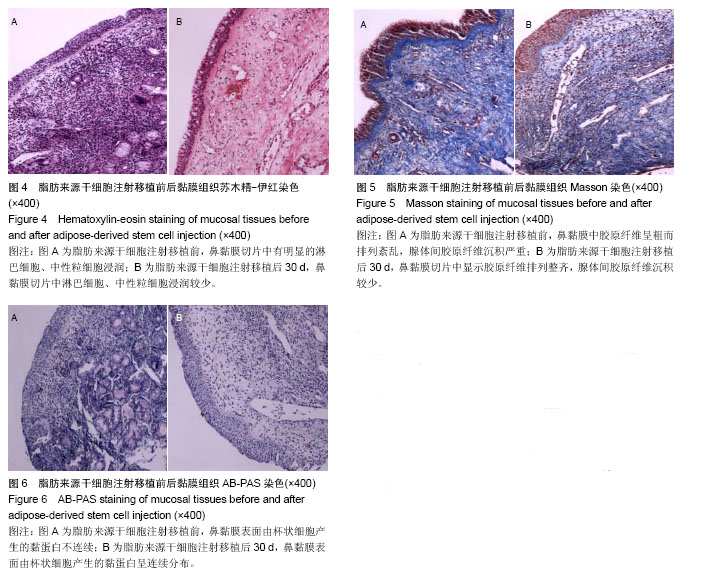
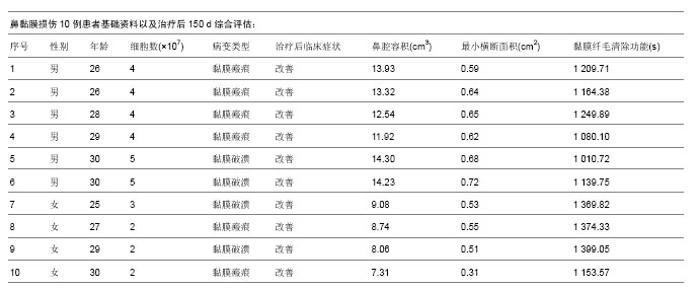
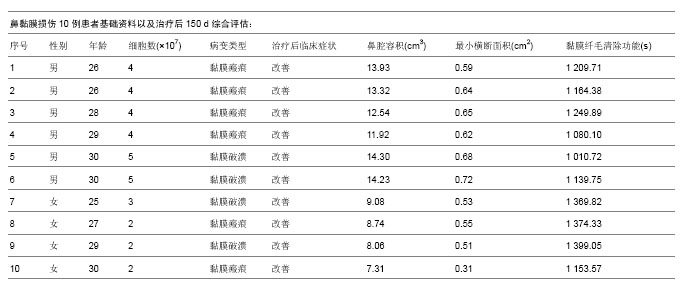
| [1] 韩锦华,王彤,臧洪瑞,等.难治性鼻窦炎黏膜和骨质重构的组织病理学研究[J].中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,2011,18(8):448-450.
[2] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H,et al.Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.
[3] Gimble JM, Katz AJ, Bunnell BA.Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine.Circ Res. 2007;100(9):1249-1260.
[4] Fraser JK, Wulur I, Alfonso Z,et al.Fat tissue: an underappreciated source of stem cells for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2006;24(4):150-154.
[5] Baglioni S, Francalanci M, Squecco R, et al. Characterization of human adult stem-cell populations isolated from visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue.FASEB J. 2009;23(10): 3494-3505.
[6] Zavan B, Michelotto L, Lancerotto L,et al.Neural potential of a stem cell population in the adipose and cutaneous tissues. Neurol Res. 2010;32(1):47-54.
[7] 闫俊灵,狄国虎,丁红,等.脂肪干细胞介导的自体脂肪移植隆胸[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(5): 878-885.
[8] 汤苏阳,李彦,闫俊灵,等.体外扩增的自体脂肪干细胞介导自体脂肪移植的临床研究[J].中国医药生物技术,2013,8(6):433-438.
[9] 李梁,贾德进,闫俊灵,等.体外扩增自体脂肪干细胞对空鼻综合征患者黏膜功能重建的临床研究[J].解放军医学,2014,39(10): 815-818.
[10] 国家药典委员会.中华人民共和国药典(2010年版)三部[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2010:95-98.
[11] Aly LA, El-Menoufy H, Sadeq HS,et al.Efficiency of systemic versus intralesional bone marrow-derived stem cells in regeneration of oral mucosa after induction of formocresol induced ulcers in dogs.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2014;11(2): 212-221.
[12] 代涛.干细胞科技与产业发展报告[M].北京:科学出版社,2012.
[13] Hanson SE, Kim J, Johnson BH,et al. Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from human vocal fold fibroblasts. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(3):546-551.
[14] Vaananen HK. Mesenchymal stem cells. Ann Med. 2005;37: 469-79.
[15] Falanga V, Iwamoto S, Chartier M,et al.Autologous bone marrow-derived cultured mesenchymal stem cells delivered in a fibrin spray accelerate healing in murine and human cutaneous wounds.Tissue Eng. 2007;13(6):1299-1312.
[16] Li D,Yang C,Qu R, et al. Cognitive improvement following transvenous adipose-derived mesenchmal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of traumatic Brain injury. Neural Regeneration Research.2011;6(10):111-112.
[17] Zuk PA.The adipose-derived stem cell: looking back and looking ahead.Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21(11):1783-1387.
[18] González MA, Gonzalez-Rey E, Rico L,et al.Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental colitis by inhibiting inflammatory and autoimmune responses.Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):978-989.
[19] Batra PS, Kern RC, Tripathi A,et al.Outcome analysis of endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with nasal polyps and asthma.Laryngoscope. 2003;113(10):1703-1706.
[20] 黄选兆,汪吉宝.实用耳鼻咽喉科学[M].北京:人民出版社,1998: 116.
[21] 贺广湘,孙虹,曾庆善,等.慢性鼻窦炎鼻内窥镜手术前后鼻粘膜观察[J].中华耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2001,36(5):326-329.
[22] Chhabra N, Houser SM.The diagnosis and management of empty nose syndrome.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2009;42(2): 311-330.
[23] 吕萍,喻元凤,甘卫刚,等.伴耳鼻咽喉疾病焦虑抑郁症的诊治体会(附20例报告)[J]. 川北医学院学报,2013,28(1):45-47.
[24] Braunstahl GJ, Fokkens WJ, Overbeek SE,et al.Mucosal and systemic inflammatory changes in allergic rhinitis and asthma: a comparison between upper and lower airways.Clin Exp Allergy. 2003;33(5):579-587.
[25] Chanez P, Vignola AM, Vic P, et al.Comparison between nasal and bronchial inflammation in asthmatic and control subjects.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159(2):588-595.
[26] Molet SM, Hamid QA, Hamilos DL.IL-11 and IL-17 expression in nasal polyps: relationship to collagen deposition and suppression by intranasal fluticasone propionate. Laryngoscope. 2003;113(10):1803-1812.
[27] Wang QP, Escudier E, Roudot-Thoraval F, et al. Myofibroblast accumulation induced by transforming growth factor-beta is involved in the pathogenesis of nasal polyps.Laryngoscope. 1997;107(7):926-931.
[28] Grässel S, Bauer RJ.Collagen XVI in health and disease. Matrix Biol. 2013;32(2):64-73.
[29] Bassiouni A, Naidoo Y, Wormald PJ.Does mucosal remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis result in irreversible mucosal disease. Laryngoscope. 2012;122(1):225-229.
[30] Saitoh T, Kusunoki T, Yao T,et al.Role of interleukin-17A in the eosinophil accumulation and mucosal remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps associated with asthma.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010;151(1):8-16.
[31] Ponikau JU, Sherris DA, Kephart GM,et al.Features of airway remodeling and eosinophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis: is the histopathology similar to asthma?J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;112(5):877-882. |