Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (1): 30-36.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.01.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with peptide hydrogel and chondrogenic factors for repair of articular cartilage defects in rabbits
Wang Yan1, 2, Li De-hua1
- 1Department of Anatomy, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China
2Department of Imaging, Fushu Center Hospital, Fushu 113000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Revised:2014-11-26Online:2015-01-01Published:2015-01-01 -
Contact:Li De-hua, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Anatomy, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Yan, Studying for master’s degree, Associate chief physician, Department of Anatomy, Liaoning Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China; Department of Imaging, Fushu Center Hospital, Fushu 113000, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yan, Li De-hua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with peptide hydrogel and chondrogenic factors for repair of articular cartilage defects in rabbits[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(1): 30-36.
share this article
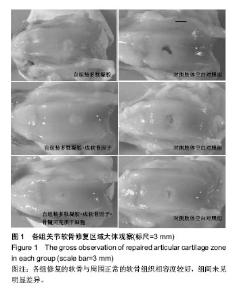
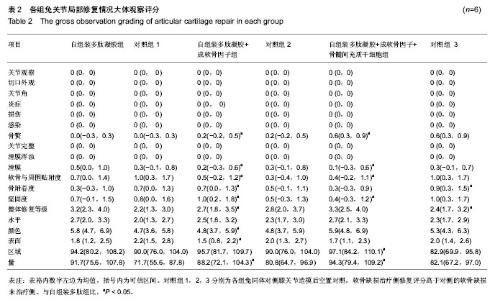
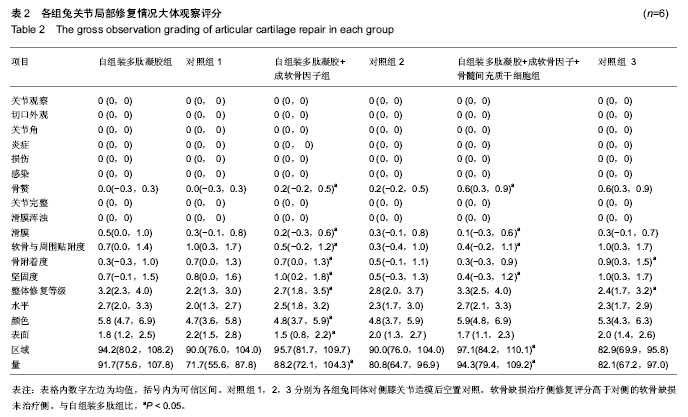
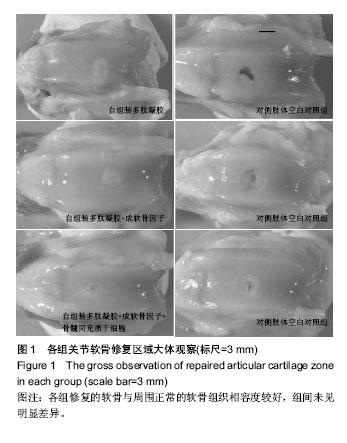
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用新西兰白兔18只,分为3组,实验过程动物无脱落,24只动物全部进入结果分析。 2.2 各组兔股骨影像学分析结果 影像学检测各组动物在治疗前未发现有任何骨局部硬结出现。治疗后自组装多肽凝胶组未见有明显骨赘出现,而自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子显现有轻微骨赘形成。自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子+ 骨髓间充质干细胞组可见明显骨赘形成,各组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.3 各组兔关节局部大体观察结果 关节修复区未见炎症反应,表明局部无免疫抑制反应发生。各组修复的软骨与周围正常的软骨组织相容度较好,组间差异无显著性意义(P ≥ 0.05)。 从整合度上分析,修复的组织接近周围正常组织,组间比较差异无显著性意义(P ≥ 0.05)。自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子+骨髓间充质干细胞组显示有轻度的骨赘形成,比单纯自组装多肽凝胶组评分高(P < 0.05)。自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子+骨髓间充质干细胞组较未处理组对于软骨下骨有更好的贴附作用(P < 0.05)。总之,治疗组软骨修复的量都大于对侧的空白对照组(P < 0.05),并且修复的效果也优于对侧的未处理组(P < 0.05)。各组软骨缺损治疗侧都要优于他们各自的对侧未治疗侧(P < 0.05)。软骨缺损治疗侧修复评分高于对侧的软骨缺损未治疗侧(P < 0.05)。见图1,表2。"
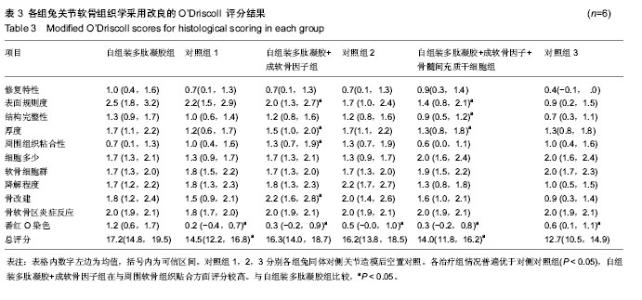
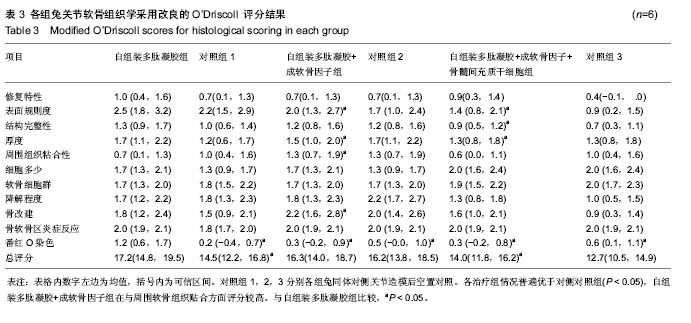
2.4 各组兔关节软骨组织学检查结果 通过滑膜苏木精-伊红检查显示,各治疗组有轻度的内膜增生和中度的血管化和内膜纤维化,但是各组之间差异无显著性意义(P ≥0.05)。关节软骨的苏木精-伊红染色评分显示,治疗组较对侧关节对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。自组装多肽凝胶和自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子组累计的评分高于自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子+骨髓间充质干细胞组(P < 0.05)。单纯自组装多肽凝胶组的最终组织学评分是最高的。其他组都有纤维软骨和非软骨细胞出现。自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子+骨髓间充质干细胞组表面修复平整度较差,可见一些裂缝存在(P < 0.01,表3),还有一些组织降解的表现。细胞数目也较自组装多肽凝胶和自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子组有所减少(P < 0.05,表3)。自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子组软骨下骨重建情况优于自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子+骨髓间充质干细胞组(P < 0.05)。但是各组均在正常水平以下。治疗组情况普遍优于对侧未治疗组(P < 0.05),自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子组在与周围软骨组织贴合方面评分较高,但组间比较差异无显著性意义(P ≥ 0.05)。见表3。"
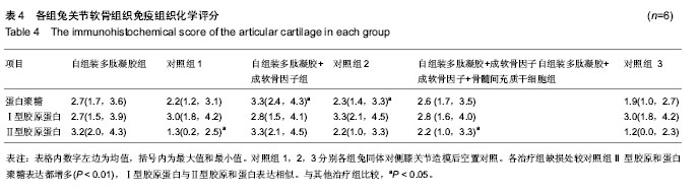
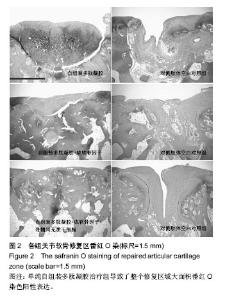
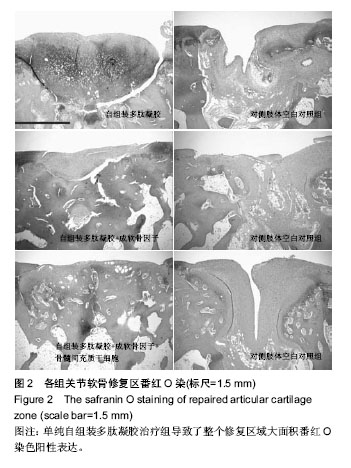
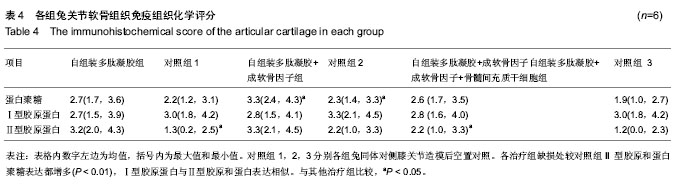
2.6 各组兔关节软骨组织免疫组织化学结果 自组装多肽凝胶治疗组显示,Ⅱ型胶原染色较对侧的缺损未处理组明显增加(P < 0.05);尽管自组装多肽凝胶治疗组蛋白多糖免疫染色获得了较高的分数,但是其与对侧关节对照组之间差异无显著性意义(P ≥ 0.05)。这与从番红染色的结果正好相反。自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子治疗组发现修复的组织内部蛋白聚糖成分较对侧的未处理组增多(P < 0.05)。此外,虽然自组装多肽凝胶+成软骨因子治疗组型胶原免疫组化染色评分最高,但和其对侧的未处理组相比差异无显著性意义(P≥0.05)。对比所有的缺损,治疗组缺损处较未处理组Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖表达都增多(P < 0.01)。Ⅰ型胶原蛋白也在所有治疗组的缺损处发现和Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白表达相似。这与大体组织观察的评分结果相一致,见表4。 总之,在修复的组织区域,Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白在组织内部表达的明显,而Ⅱ型胶原蛋白在表面表达的多一些。蛋白聚糖的表达比较成均匀分布,但是只在组织内部出现较强的阳性反应。"
| [1] Getgood A, Brooks R, Fortier L, et al. Articular cartilage tissue engineering. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2009; 91-B:565-576. [2] Hoemann C, Sun J, McKee M, et al.Chitosan-glycerol phosphate/blood implants elicit hyaline cartilage repair integrated with porous subchondral bone in microdrilled rabbit defects. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.2007; 15:78-89. [3] Jaklenec A, Hinckfuss A, Bilgen B, et al. Sequential release of bioactive IGF-I and TGF-β1 from PLGA microsphere-based scaffolds.Biomaterials. 2008;29:1518-1525. [4] Nixon A, Fortier L, Williams J, et al. Enhanced repair of extensive articular defects by insulin-like growth factor-I-laden fibrin composites. J Orthop Res. 1999; 17:475-487. [5] Hwang NS, Elisseeff JP. Application of Stem Cells for Articular Cartilage Regeneration. J Knee Surg. 2009; 22:60-71. [6] Re'em T, Witte F, Willbold E, et al. Simultaneous regeneration of articular cartilage and subchondral bone induced by spatially presented TGF-beta and BMP-4 in a bilayer affinity binding system.Acta Biomater. 2012 ;8(9):3283-3293. [7] Frisbie D, Bowman S, Colhoun H, et al. Evaluation of autologous chondrocyte transplantation via a collagen membrane in equine articular defects-results at 12 and 18 months. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.2008; 16:667-679. [8] Elisseeff J, McIntosh W, Fu K, et al. Controlled-release of IGF-1 and TGF-β1 in a photopolymerizing hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. J Orthop Res. 2001; 19: 1098-1104. [9] Kim K, Lam J, Lu S, et al. Osteochondral tissue regeneration using a bilayered composite hydrogel with modulating dual growth factor release kinetics in a rabbit model.J Control Release.2013;168(2):166-178. [10] Aulin C, Jensen-Waern M, Ekman S, et al.Cartilage repair of experimentally 11 induced osteochondral defects in New Zealand White rabbits.Lab Anim. 2013;47(1):58-65. [11] Lee CS, Watkins E, Burnsed OA, et al. Tailoring adipose stem cell trophic factor production with differentiation medium components to regenerate chondral defects.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(11-12):1451-1464. [12] Davis ME, Hsieh PCH, Takahashi T, et al. Local myocardial insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) delivery with biotinylated peptide nanofibers improves cell therapy for myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2006; 103:8155-8160. [13] Ahearne M, Liu Y, Kelly DJ.Combining freshly isolated chondroprogenitor cells from the infrapatellar fat pad with a growth factor delivery hydrogel as a putative single stage therapy for articular cartilage repair.Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(5-6):930-939. [14] Unterman SA, Gibson M, Lee JH, et al.Hyaluronic acid-binding scaffold for articular cartilage repair.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(23-24):2497-506. [15] Kopesky P, Vanderploeg E, Kisiday J, et al.Controlled delivery of TGF-b1 by self-assembling peptide hydrogels induces chondrogenesis of bone marrow stromal cells and modulates Smad2/3 signaling. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(1-2):83-92. [16] Park K-H, Park W, Na K. Synthetic matrix containing glucocorticoid and growth factor for chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells. J Biosci Bioeng. 2009; 108: 168-173. [17] Schmidt M, Chen E, Lynch S. A review of the effects of insulin-like growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor on in vivo cartilage healing and repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14:403-412. [18] Hunziker E.Growth-factor-induced healing of partial-thickness defects in adult articular cartilage.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001; 9:22-32. [19] Noth U, Steinert AF, Tuan RS. Technology Insight: adult mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis therapy.Nat Rev Rheumatol.2008; 4:371-380. [20] Ikeda R, Fujioka H, Nagura I, et al. The effect of porosity and mechanical property of a synthetic polymer scaffold on repair of osteochondral defects. Int Orthop. 2009; 33:821-828. [21] Holland TA,Bodde EW,Cuijpers VM et al. Degradable hydrogel scaffolds for in vivo delivery of single and dual growth factors in cartilage repair.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007; 15:187-197. [22] Fortier LA, Mohammed HO, Lust G, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I enhances cell-based repair of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84-B:276-288. [23] Davidson EN, van der Kraan P, van den Berg W. TGF-b and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15:597-604. [24] Diao H, Wang J, Shen C, et al. Improved cartilage regeneration utilizing mesenchymal stem cells in TGF-β1 gene-activated scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part A.2009; 15: 2687-2698. [25] Guo X,Park H, Young S,et al. Repair of osteochondral defects with biodegradeable hydrogel composites encapsulating marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a rabbit model. Acta Biomaterialia. 2010; 6:39-47. [26] Mi Z, Ghivizzani S, Lechman E, et al. Adverse effects of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of human TGF-β1 into rabbit knees. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003; 5:R132-R139. [27] Fan H, Hu Y, Qin L, et al. Porous gelatin-chondroitin- hyaluronate tri-copolymer scaffold containing microspheres loaded with TGF-β1 induces differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vivo for enhancing cartilage repair. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006; 77:785-794. [28] Miller RE, Grodzinsky AJ, Barrett MF,et al. Effects of the combination of microfracture and self-assembling Peptide filling on the repair of a clinically relevant trochlear defect in an equine model.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(19): 1601-1609. [29] Chen P, Zhu S, Wang Y, et al. The amelioration of cartilage degeneration by ADAMTS-5 inhibitor delivered in a hyaluronic acid hydrogel.Biomaterials. 2014;35(9):2827-2836. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [4] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [5] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [7] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [8] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [9] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [10] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [11] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [12] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [13] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||