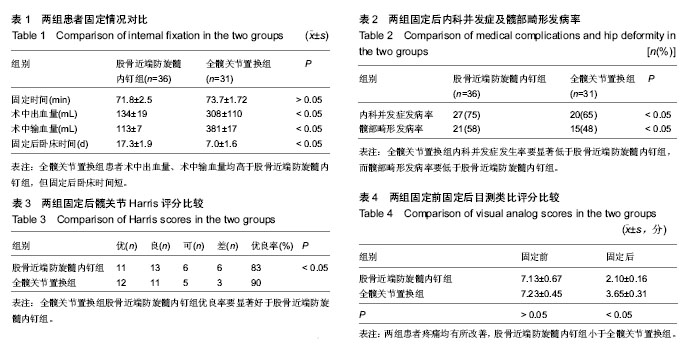
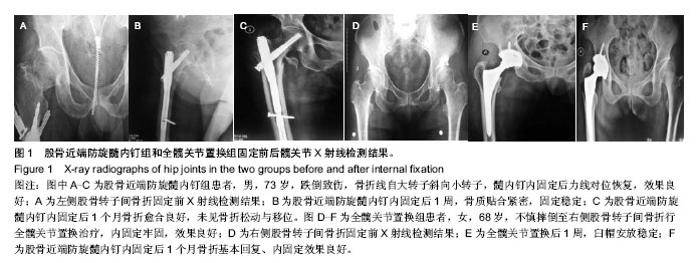
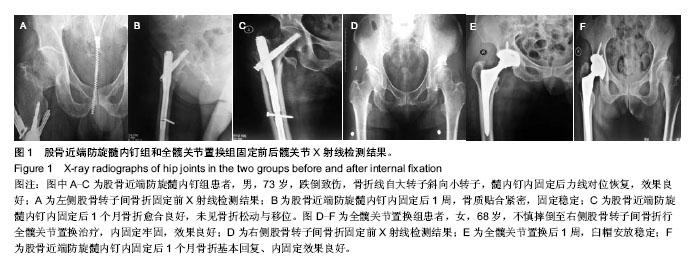
| [1] 孔长庚,张寿.股骨粗隆间骨折的治疗进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(4):379-381.
[2] Erhart S, Kammerlander C, El-Attal R, et al. Is augmentation a possible salvage procedure after lateral migration of the proximal femur nail antirotation? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(11):1577-1581.
[3] Schill S. Ankle arthrodesis with interposition graft as a salvage procedure after failed total ankle replacement. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2007;19(5-6):547-560.
[4] Liu JJ, Shan LC, Deng BY, et al. Reason and treatment of failure of proximal femoral nail antirotation internal fixation for femoral intertrochanteric fractures of senile patients. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(3):5949-56.
[5] 郭晓亮,卫小春,王小虎.股骨转子间骨折髓内固定物治疗的优劣评说[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(26):4904-4911.
[6] 刘海春,陈允震,杨子来,等.股骨粗隆间粉碎性骨折不同内固定疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(1):18.
[7] 方超,谢加兵,徐祝军,等.亚洲型防旋股骨近端髓内钉微创修复股骨转子间骨折:可为高龄患者首选[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(22):3469-3474.
[8] 刘国强,李坚,徐刚.双极人工股骨头置换治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(2):191-192.
[9] 戴兵,孟祥德,骆洪涛,等.PFNA内固定与关节置换治疗高龄骨质疏松患者股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效评价[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2010,16(4):282-285.
[10] Abdelkhalek M, Ali AM, Abdelwahab M. Cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty with a cerclage cable technique for unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures in elderly patients. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(4):443-448.
[11] Bonnaire F, Lein T, Bula P. Trochanteric femoral fractures: anatomy, biomechanics and choice of implants. Unfallchirurg. 2011;114(6):491-500.
[12] Lechler P, Frink M, Gulati A, et al. The influence of hip rotation on femoral offset in plain radiographs. Acta Orthop. 2014; 85(4):389-395.
[13] Kayali C, Altay T, Kement Z, et al. A rare complication after intertrochanteric fracture treated with proximal femoral nail: femoral neck insufficiency fracture. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23 Suppl 2:S241-245.
[14] Sidhu AS, Singh AP, Singh AP, et al. Total hip replacement as primary treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. Int Orthop. 2010;34:789-792.
[15] Kokoroghiannis C, Aktselis I, Deligeorgis A, et al. Evolving concepts of stability and intramedullary fixation of intertrochanteric fractures-a review. Injury. 2013;44(6): 877-878.
[16] Tang P, Hu F, Shen J, et al.Proximal femoral nail anti rotation versus hemiarthroplasty:a study for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2012;43(6):876-881.
[17] Attar S, Manning D, Spangehl M. Conversion of cephalomedullary nail fixation to hip arthroplasty: technical points and pitfalls. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2014;43(10): 472-475.
[18] Tyagi V, Yang JH, Oh KJ. A computed tomography-based analysis of proximal femoral geometry for lateral impingement with two types of proximal femoral nail anterotation in subtrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2010;41(8):857-861.
[19] D'Arrigo C, Perugia D, Carcangiu A, et al. Hip arthroplasty for failed treatment of proximal femoral fractures. Int Orthop. 2010; 34(7):939-942.
[20] 贺建军.半髋关节置换与防旋型股骨近端髓内钉治疗老年人不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折疗效比较[J].中国基层医药,2014,7(20): 1044-1045.
[21] 熊健,佘远举,许永涛.半髋关节置换与防旋型股骨近端髓内钉治疗高龄不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折效果比较[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2014,23(10):1106-1108.
[22] 庞向华,欧兆强,欧阳建江.半髋关节置换与防旋型股骨近端髓内钉治疗高龄不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效对比[J].重庆医学, 2013,42(10):1086-1088.
[23] Feng Y, Fang X, Shi Z, et al. Effects of PFNA exposure on expres-sion of junction-associated molecules and secretory function in ratSertoli cells. Rep Toxicol. 2010;30(3):429-437.
[24] 王亚平,路通.人工髋关节置换与股骨近端髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(52):8961-8966.
[25] Park-Wyllie LY, Mamdani MM, Juurlink DN, et al. Bisphosphonate use and the risk of subtrochanteric or fern oral shaft fractures in older women. JAMA. 2011;305(8): 783-789.
[26] Lee PC, Hsieh PH, Chou YC, et al. Dynamic hip screws for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patientsencouraging results with a cement augmentation technique. J Trauma. 2010,68(4):954-964.
[27] Sidhu AS, Singh AP, Singh AP, et al. Total hip replacement as primary treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. Int Orthop. 2010;34(6):789-792.
[28] Grimsrud C, Monzon RJ, Richman J, et al. Cemented hip arthroplasty with a novel cerclage cable technique for unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(3):337-343. |