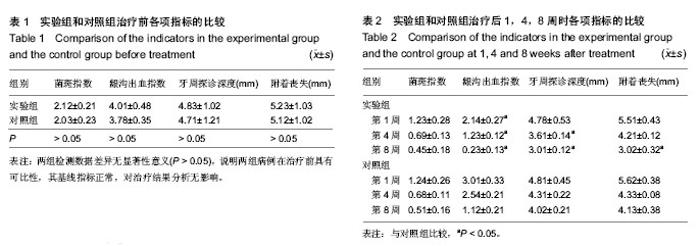
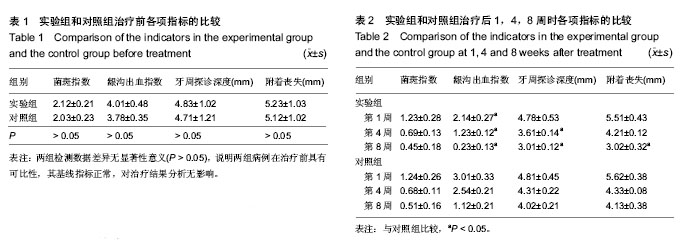
| [1] 杜平中.透明质酸的功能,制备及其在医学中的应用[J].上海医药, 2012,33(15):46-51.
[2] 宋磊,王腾飞.透明质酸的研究现状综述[J].山东轻工业学院学报, 2012,26(2):15-18.
[3] 孟繁桐,谭成玉,刘富俊,等.透明质酸特性及其制备和应用概述[J].精细与专业化学品,2012,20(5):17-22.
[4] 赵京玉,柴家科.外源性透明质酸对创面愈合影响的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2011,6(1):107-110.
[5] 杨敏,饶友义,宁红.透明质酸在外科领域的临床应用[J].中国药业,2014,23(14):102-104.
[6] 李允允,法永红.透明质酸在口腔领域中的应用进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2013,40(3):344-346.
[7] Xu Y, Höfling K, Fimmers R, et al.Clinical and microbiological effects of topical subgingival application of hyaluronic acid gel adjunctive to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis.JPeriodontol. 2004;75(8):1114-1148.
[8] Xu Y,Frentzen M,Jerve- Storm PM.Clinical study of hyaluronic acid in the treatment of chronic periodontitis.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi.2004;22(1):32-34.
[9] Mesa FL, Aneiros J, Cabrera A, et al.Antiproliferative effect of topic hyaluronic acid gel. Study in gingival biopsies of patients with periodontal disease.Histol Histopathol. 2002;17(3):747753.
[10] Smith AJ,Wade W,Addy M,et al.The relationship between microbial factors and gingival crevicular fluid glycosaminoglycans in human adult periodontitis.Arch Oral Biol.1997;42(1):89-92.
[11] Waddington RJ,Langley MS,Guida L,et al.Relationship of sulphated glycosaminoglycans in human gingival crevicular fluid with active periodontal disease.Periodontal Res. 1996; 31(3):168-170.
[12] 吴亚菲,黄姣,徐屹,等.Gengige凝胶在菌斑性牙龈炎治疗中的作用[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2005,21(4):540-542.
[13] 章彦彦,杨旭,陈才展,等.观察Gengigel凝胶对Ⅱ度根分叉病变的疗效[J].口腔医学研究,2013,6(3):321-328.
[14] Sagar A. Full mouth versus quadrant treatment in chronic periodontitis.Prim Dent J.2014;3(3):66-69.
[15] Mlachkova AM,Popova CL.Efficiency of nonsurgical periodontal therapy in moderate chronic periodontitis.Folia Med (Plovdiv).2014;56(2):109-115.
[16] Zhao Y,Yin Y,Tao L,et al.Er:YAG laser versus scaling and root planing as alternative or adjuvant for chronic periodontitis treatment: a systematic review. JClin Periodontol. 2014;41(11): 1069-1079.
[17] Fawzy El-Sayed KM, Dahaba MA,Aboul-Ela S,et al.Local application of hyaluronan gel in conjunction with periodontal surgery: a randomized controlled trial.JClin Oral Investig. 2012;16(4):1229-1236.
[18] 李凯,吕少一,周建业,等.不同浓度透明质酸水凝胶的细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(16):2927-2934.
[19] 中华人民共和国国务院颁发.《医疗机构管理条例》.1994-09-01.
[20] 曹采方.牙周病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001:87,90,94.
[21] 闫晨,李昀生,冯炜.牙周翻瓣术与二次牙周龈下刮治临床疗效对照研究[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2007,32(7):56-60.
[22] Xu X,ha AK,Harrington DA,et al. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels: from a Natural Polysaccharide to Complex Networks.Soft Matter.2012;8(12):3280-3294.
[23] Chen X,Thibeault SL.Response of fibroblasts to transforming growth factor-β1 on two-dimensional and in three-dimensional hyaluronan hydrogels.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(23-24): 2528-2538.
[24] Mohand-Kaci F,Assoul N,Martelly I,et al.Optimized hyaluronic acid-hydrogel design and culture conditions for preservation of mesenchymal stem cell properties.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013;19(4):288-298.
[25] Medaiah S,Srinivas M,Melath A,et al.Chlorhexidine chip in the treatment of chronic periodontitis - a clinical study.J Clin Diagn Res.2014;8(6):ZC22-25.
[26] Dias Gonçalves TE,Feres M,Zimmermann GS,et al.Effects of Scaling and Root Planing on Clinical Response and Serum Levels of Adipocytokines in Obese Patients With Chronic Periodontitis.J Periodontol.2014;14:1-12.
[27] Yaghini J,Shahabooei M,Aslani A,et al.Efficacy of a local-drug delivery gel containing extracts of Quercus brantii and Coriandrum sativum as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in moderate chronic periodontitis patients. J Res Pharm Pract. 2014;3(2):67-71.
[28] Petelin M,Perki? K,Seme K,et al.Effect of repeated adjunctive antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on subgingival periodontal pathogens in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. Lasers Med Sci.2014.[Epub ahead of print]
[29] 罗丽,张纲,祝金香,等.模拟高原缺氧环境对家兔慢性牙周炎龈下菌群种类分布的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2012,3(6):267-272.
[30] 江燕军,李昀生.白细胞介素17与牙周炎关系的研究进展[J].医学综述,2012,18(2):195-197.
[31] Eick S,Renatus A,Heinicke M,et al. Hyaluronic Acid as an adjunct after scaling and root planing: a prospective randomized clinical trial.J Periodontol. 2013;84(7):941-949.
[32] 谭荣,胡冬梅,胡坤娥.透明质酸治疗复发性口腔溃疡的临床疗效观察[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(10):420-421.
[33] 谭荣,江燕军,刘剑.壳聚糖抗菌膜用于治疗口腔黏膜创伤的临床疗效观察[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂,2014,12(6):66-68.
[34] Bevilacqua L, Eriani J, Serroni I, et al.Effectiveness of adjunctive subgingival administration of amino acids and sodium hyaluronate gel on clinical and immunological parameters in the treatment of chronic periodontitis.Ann Stomatol (Roma). 2012;3(2):75-81.
[35] Gontiya G,Galgali SR.Effect of hyaluronan on periodontitis: A clinical and histological study.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2012;16(2):184-192.
[36] 闫晨,李昀生,李武德,等.四种治疗牙本质过敏方法的临床效果研究[J].北京口腔医学,2007,20(1):17-22.
[37] Pilloni A,Annibali S,Dominici F,et al.Evaluation of the efficacy of an hyaluronic acid-based biogel on periodontal clinical parameters. A randomized-controlled clinical pilot study.Ann Stomatol (Roma).2011;2(3-4):3-9.
[38] Johannsen A,Tellefsen M,Wikesjö U,et al.Local delivery of hyaluronan as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis.J Periodontol. 2009; 80(9): 1493-1497.
[39] 王丽霞,赵寰,蒋波,等.人牙周膜细胞在透明质酸/胶原支架上的粘附与生长[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(2):220-223.
[40] 李向利,曹浪,沈双青,等.腔治捷在治疗Ⅱ型糖尿病伴发牙周炎中的作用[J].武警后勤学院学报:医学版,2014,23(7):583-588. |