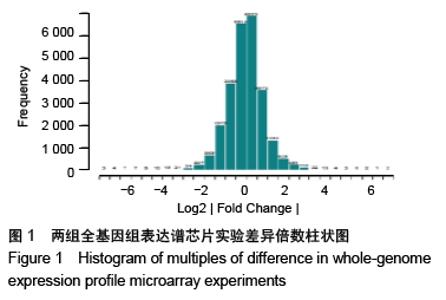
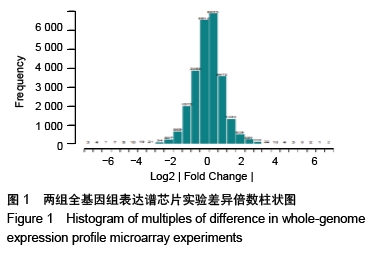
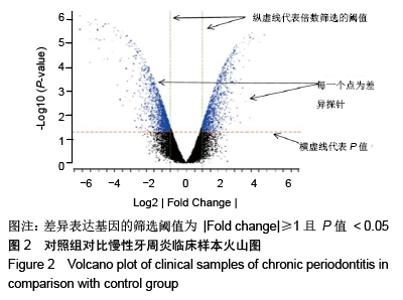
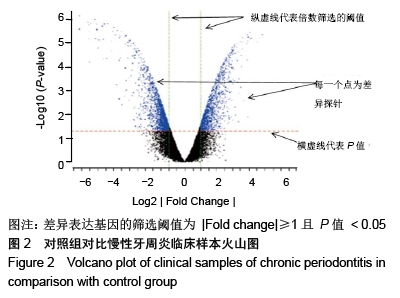
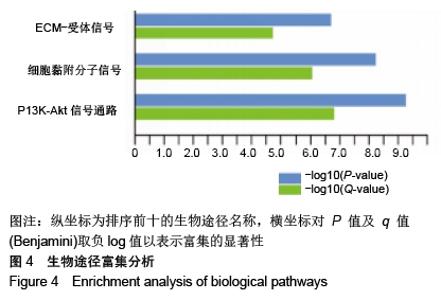
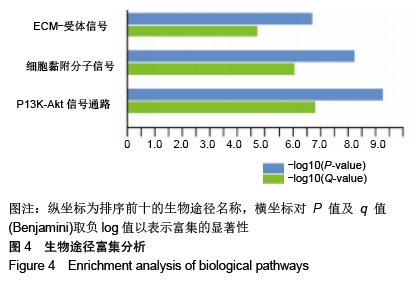
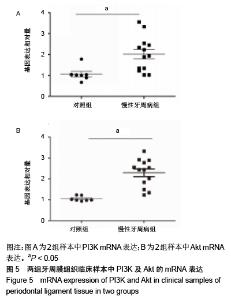
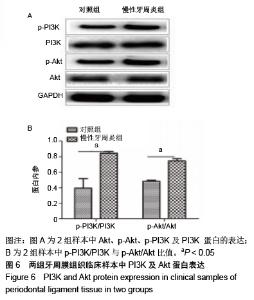
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (23): 3615-3620.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2723
Previous Articles Next Articles
Screening chronic periodontitis-related genes using whole-genome expression profiling
Wu Hui1, Xu Nuo2, Wang Qian3, Shi Chun3, Jiang Long2
- 1Department of Stomatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570102, Hainan Province, China; 2Zhongshan College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China; 3School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2019-12-02Revised:2019-12-04Accepted:2020-01-10Online:2020-08-18Published:2020-04-26 -
Contact:Jiang Long, Lecturer, Zhongshan College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wu Hui, Master, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570102, Hainan Province, China Xu Nuo, Master, Associate professor, Attending physician, Zhongshan College of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116000, Liaoning Province, China Wu Hui and Xu Nuo contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 20180550563
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Hui, Xu Nuo, Wang Qian, Shi Chun, Jiang Long. Screening chronic periodontitis-related genes using whole-genome expression profiling[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3615-3620.
share this article
| [1] FENG X, LIU J. Association between IL-1A (-889C/T) polymorphism and susceptibility of chronic periodontitis: a meta-analysis. Gene. 2020;729:144227. [2] MOONEN CG, BUURMA KG, FARUQUE MR, et al. Periodontal therapy increases neutrophil extracellular trap degradation.Innate Immun. 2019:1753425919889392. [3] NARIMIYA T, KANZAKI H, YAMAGUCHI Y, et al. Nrf2 activation in osteoblasts suppresses osteoclastogenesis via inhibiting IL-6 expression. Bone Rep. 2019;11:100228. [4] SCHULZ S, SCHLITT A, HOFMANN B, et al. Periodontal pathogens and its role in cardiovascular outcome. J Clin Periodontol. 2020;47(2):173-181. [5] NARDI C, CALISTRI L, PIETRAGALLA M, et al. Electronic processing of digital panoramic radiography for the detection of apical periodontitis. Radiol Med. 2020;125(2):145-154. [6] PAN W, WANG Q, CHEN Q. The cytokine network involved in the host immune response to periodontitis. Int J Oral Sci. 2019;11(3):30. [7] DUTZAN N, ABUSLEME L. T Helper 17 Cells as Pathogenic Drivers of Periodontitis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019; 1197: 107-117. [8] KHOURY RD, PRADO RFD, MATOS FS, et al. The influence of adrenergic blockade in rats with apical periodontitis under chronic stress conditions. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;110:104590. [9] MINTY M, CANCEIL T, SERINO M, et al. Oral microbiota-induced periodontitis: a new risk factor of metabolic diseases. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2019;20(4): 449-459. [10] ZHANG Z, YUAN W, DENG J, et al. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) regulates neutrophils infiltration and periodontal tissue destruction in an experimental periodontitis. Mol Immunol. 2019;117: 110-121. [11] ASA'AD F, MONJE A, LARSSON L. Role of epigenetics in alveolar bone resorption and regeneration around periodontal and peri-implant tissues. Eur J Oral Sci. 2019;127(6): 477-493. [12] VELIDANDLA S, BODDURU R, BIRRA V, et al. Distribution of Periodontal Pockets Among Smokers and Nonsmokers in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis: A Cross-sectional Study. Cureus. 2019;11(9): e5586. [13] WAGNER MC, CAVAGNI J, GAIO EJ, et al. Effect of red wine and its major components on periodontitis and systemic inflammation in rats. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2019;21(4): 139-147. [14] WANG Y, LI Y, SHAO P, et al. IL1beta inhibits differentiation of cementoblasts via microRNA-325-3p. J Cell Biochem. 2020; 121(3):2606-2617. [15] ZHONG W, PENG Y, YUE E, et al. Gingival crevicular fluid levels of SLIT3 are increased in periodontal disease. Oral Dis. 2020;26(1):182-192. [16] HARGADON KM. Whole Genome Expression Microarray Analysis of Highly Versus Poorly Tumorigenic Murine Melanoma Cell Lines Provides Insights into Factors That Regulate Tumor Growth, Metastasis, and Immunogenicity. Front Immunol. 2015;6:452. [17] WEI Y, CHEN L, XU H, et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunctions Regulated Radioresistance through Mitochondria-to-Nucleus Retrograde Signaling Pathway of NF-kappaB/PI3K/AKT2/ mTOR. Radiat Res. 2018;190(2): 204-215. [18] XU X, FENG L, LIU Y, et al. Differential gene expression profiling of gastric intraepithelial neoplasia and early-stage adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2014; 20(47): 17883-17893. [19] FREIRE JMO, CHAVES HV, TEIXEIRA AH, et al. Protective effect of Platymiscium floribundum Vog. in tree extract on periodontitis inflammation in rats. PLoS One. 2019;14(11): e0223800. [20] GUSTAFSSONN, AHLQVIST J, NASLUND U, et al. Associations among Periodontitis, Calcified Carotid Artery Atheromas, and Risk of Myocardial Infarction. J Dent Res. 2019: 22034519885362. [21] LI H, ZHONG X, LI W, et al. Effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on experimental periodontitis and AhR/NF-kappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in a mouse model. J Appl Oral Sci. 2019; 27: e20180713. [22] MAJZOUB J, BAROOTCHI S, TAVELLI L, et al. Guided tissue regeneration combined with bone allograft in infrabony defects: Clinical outcomes and assessment of prognostic factors. J Periodontol. 2019 Nov 4. doi: 10.1002/JPER.19-0336. [23] SHI T, JIN Y, MIAO Y, et al. IL-10 secreting B cells regulate periodontal immune response during periodontitis. Odontology. 2019 Nov 7. doi: 10.1007/s10266-019-00470-2. [24] JOEHANES R, ZHANG X, HUAN T, et al. Integrated genome-wide analysis of expression quantitative trait loci aids interpretation of genomic association studies. Genome Biol. 2017 18(1):16. [25] CHO H, CHOU HH. Thermodynamically optimal whole-genome tiling microarray design and validation. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9:305. [26] ARTHUR L M, TURNBULL A K, WEBBER V L, et al. Molecular changes in lobular breast cancers in response to endocrine therapy. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(19): 5371-5376. [27] DESCHAMPS-LENHARDT S, MARTIN-CABEZAS R, HANNEDOUCHE T, et al. Association between periodontitis and chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Dis. 2019;25(2):385-402. [28] BAUS-DOMINGUEZ M, GOMEZ-DIAZ R, TORRES-LAGARES D, et al. Differential Expression of Inflammation-Related Genes in Down Syndrome Patients with or without Periodontal Disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2019; 2019: 4567106. [29] BOYAPATI R, SWARNA C, DEVULAPALLI N, et al. Unveiling the Link between Prostatitis and Periodontitis. Contemp Clin Dent. 2018;9(4):524-529. [30] MARTON I J, HORVATH J, LABISCSAK P, et al. Salivary IL-6 mRNA is a Robust Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Clin Med. 2019; 8(11). Pii: E1958. [31] NIAZI FH, KOPPOLU P, TANVIR SB, et al. Clinical efficacy of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis among HIV seropositive patients: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2019: 101608. [32] BISHOP JA, GAGAN J, BAUMHOER D, et al. Sclerosing Polycystic "Adenosis" of Salivary Glands: A Neoplasm Characterized by PI3K Pathway Alterations More Correctly Named Sclerosing Polycystic Adenoma. Head Neck Pathol. 2019 Oct 11. doi: 10.1007/s12105-019-01088-0. [33] CHENG M, HUANG W, CAI W, et al. Growth hormone receptor promotes osteosarcoma cell growth and metastases. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10(1):127-134. [34] DONG C, WANG X, LI N, et al. microRNA-mediated GAS1 downregulation promotes the proliferation of synovial fibroblasts by PI3K-Akt signaling in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(6):4273-4286. [35] IHLE CL, PROVERA MD, STRAIGN DM, et al. Distinct tumor microenvironments of lytic and blastic bone metastases in prostate cancer patients. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1): 293. [36] IRELLI A, SIRUFO M M, SCIPIONI T, et al. mTOR Links Tumor Immunity and Bone Metabolism: What are the Clinical Implications? Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23). pii: E5841. [37] SHEIKH-ZEINEDDINI N, SAFAROGHLI-AZAR A, SALARI S, et al. C-Myc inhibition sensitizes pre-B ALL cells to the anti-tumor effect of vincristine by altering apoptosis and autophagy: Proposing a probable mechanism of action for 10058-F4. Eur J Pharmacol.2019:172821. [38] WANG Z, ZHAO Y, PHIPPS-GREEN A, et al. Differential DNA methylation of networked signaling, transcriptional, innate and adaptive immunity, and osteoclastogenesis genes and pathways in gout. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Nov 18. doi: 10.1002/art.41173. [39] WATRAS A, WUJCZYK M, ROECKEN M, et al. Investigation of Pyrophosphates KYP2O7Co-Doped with Lanthanide Ions Useful for Theranostics. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019; 9(11) . pii: E1597. [40] WU S, ZHAO F, ZHAO J, et al. Dioscin improves postmenopausal osteoporosis through inducing bone formation and inhibiting apoptosis in ovariectomized rats. Biosci Trends. 2019;13(5): 394-401. [41] WU TC, CHEN JS, WANG CH, et al. Activation of heme oxygenase-1 by Ginkgo biloba extract differentially modulates endothelial and smooth muscle-like progenitor cells for vascular repair. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):17316. [42] XU W, LI J, TIAN H, et al. MicroRNA1865p mediates osteoblastic differentiation and cell viability by targeting CXCL13 in nontraumatic osteonecrosis. Mol Med Rep. 2019; 20(5): 4594-4602. [43] ZHANG Y, CAO X, LI P, et al. LncRNA NKILA integrates RXFP1/AKT and NF-kappaB signalling to regulate osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2020; 24(1):521-529. |
| [1] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [2] | Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie. Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665. |
| [3] | Chen Xinling, Wang Shenglan. Cell autophagy, pathway, regulation and its multiple correlations with pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 311-316. |
| [4] | Fei Jing, Zheng Hongdi, Yu Liya, Li Leiji. Involvement of GDNF/PI3K/AKT pathway in promoting facial nerve regeneration using electroacupuncture in a rabbit model of facial nerve crush injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1094-1100. |
| [5] | Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Mechanism of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway regulating osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 408-415. |
| [6] | Yuan Guoqiang, Qin Yongsheng, Peng Peng. High-intensity interval training for treating pathological cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3708-3715. |
| [7] | Shi Dongmei, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and bone destruction: problems and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3716-3722. |
| [8] | Fu Yunyu, Qiu Xiaotang, Yang Wenkui, Mo Shian, Wu Xiaocui, Wu Yingping. Berberine alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 230-235. |
| [9] | Yin Lingni, Chen Dexuan. The role of PI3K/Akt pathway in hypoxia-induced cell proliferation and endothelial cell differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3004-3009. |
| [10] | Cao Yang, Hu Ping, Tian Min, Wei Fang, Gu Qing, Lü Hongbin. Effects of 6-phosphofructokinase-2/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3 on tubule formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2217-2222. |
| [11] | Xu Canhong, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Role of osteogenic signaling pathway in non-traumatic femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2235-2242. |
| [12] | Liu Yan, Guan Yongge, Song Yang. Guishen Pill water extract intervenes with the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and expression levels of PI3K and AKT in Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 1983-1988. |
| [13] | Tao Hai, Guo Weichun. Regulation of osteosarcoma and stem cell-related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2102-2107. |
| [14] | Zhang Fuhua, Fan Wenjuan, Hua Xinyu, Chen Xudong. Compound brain peptide ganglioside can improve intrauterine hypoxia-induced neonatal brain injury and promote synapse regeneration in a mouse model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1689-1694. |
| [15] | He Yunfei, Wang Shuang, Ma Jun, Yu Lei, Wen Jiankun, Ye Xiaojian. P38/Akt pathway regulates the oriented differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in nanofiber annulus fibrosus scaffolds with different spatial structures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1540-1546. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||