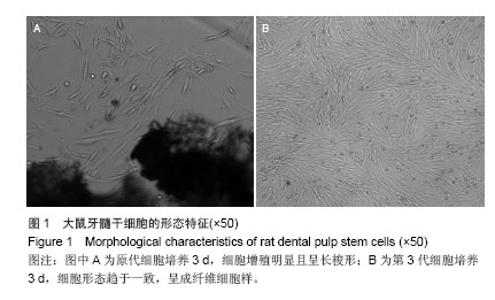
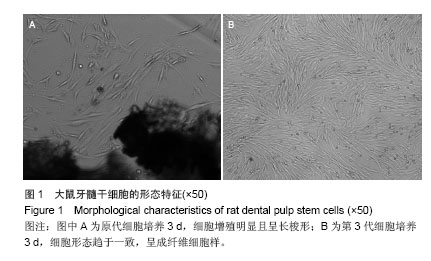
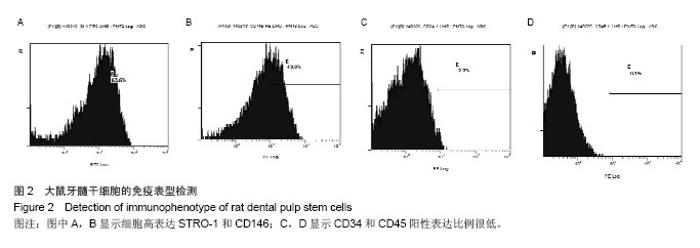
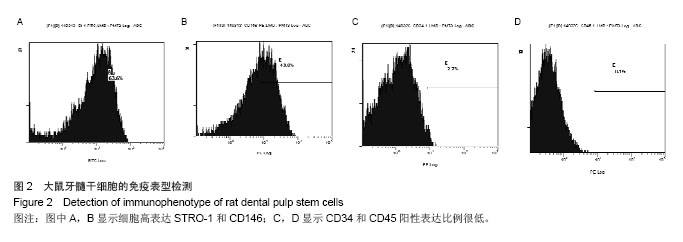
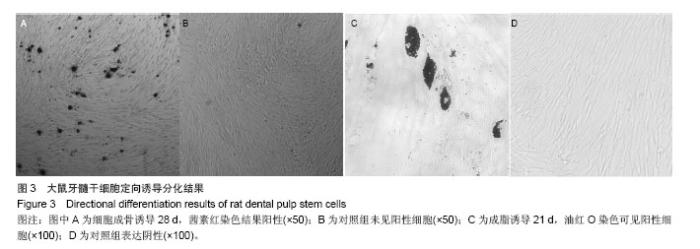
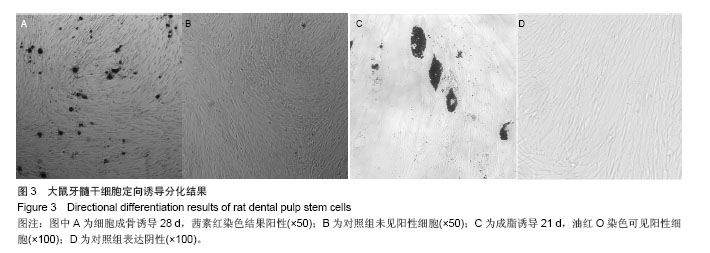
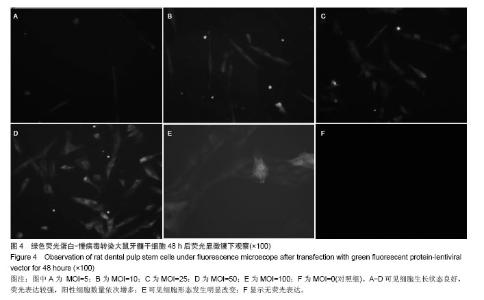
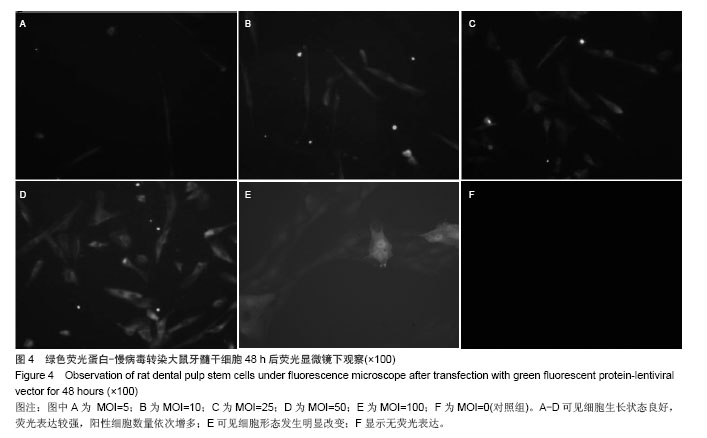
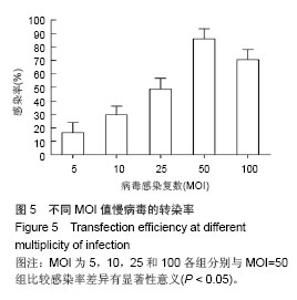
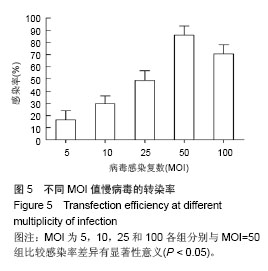
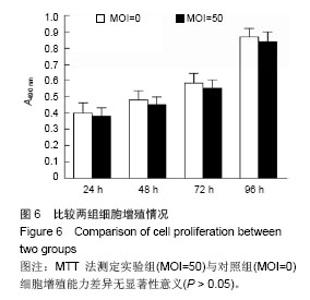
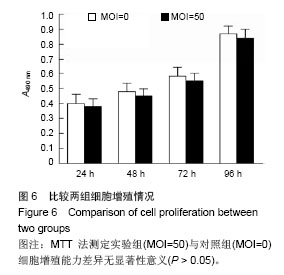
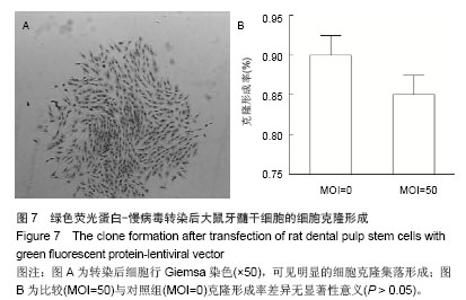
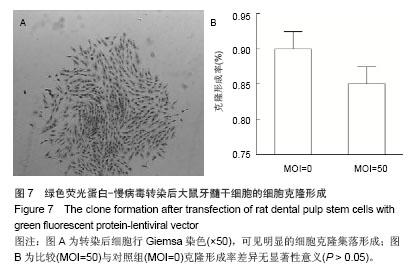
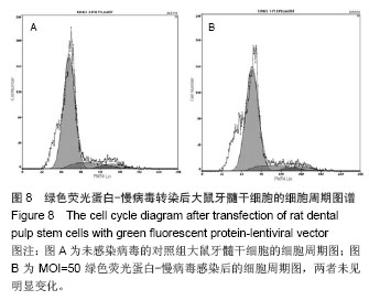
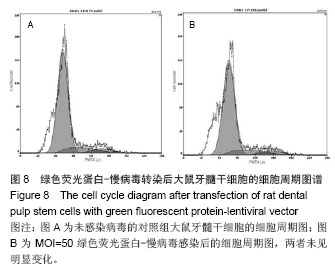
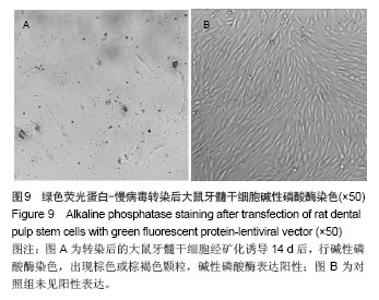
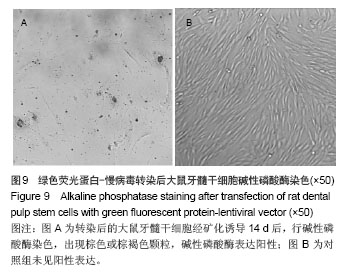
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (45): 7299-7305.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.45.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transfection of stem cells derived from rat dental pulp with green fluorescent protein infection by lentiviral vector
Zhang Rui-han, Liu Jia, Nie Shan-shan, Wang Xuan, Li Bo-qi, Sun Da-lei, Refukati Dilimaolati, Liu Yi-shan
- Department of Prevention and Health Care of Children’s Teeth, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2014-11-05Published:2014-11-05 -
Contact:Liu Yi-shan, Master, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Department of Prevention and Health Care of Children’s Teeth, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Rui-han, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Prevention and Health Care of Children’s Teeth, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2011211A067
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Rui-han, Liu Jia, Nie Shan-shan, Wang Xuan, Li Bo-qi, Sun Da-lei, Refukati Dilimaolati, Liu Yi-shan. Transfection of stem cells derived from rat dental pulp with green fluorescent protein infection by lentiviral vector[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(45): 7299-7305.
share this article
| [1]Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J,et al.Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[2]Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W,et al.Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells.J Dent Res. 2002;81(8): 531-535.
[3]Zhang J, Jiang D, Zhang J,et al.Synthesis of dental enamel-like hydroxyapatite through solution mediated solid-state conversion.Langmuir. 2010;26(5):2989-2994.
[4]Zheng Y, Wang XY, Wang YM,et al.Dentin regeneration using deciduous pulp stem/progenitor cells.J Dent Res. 2012;91(7): 676-682.
[5]Brazelton TR, Blau HM.Optimizing techniques for tracking transplanted stem cells in vivo.Stem Cells. 2005;23(9): 1251-1265.
[6]Chudakov DM, Matz MV, Lukyanov S,et al.Fluorescent proteins and their applications in imaging living cells and tissues.Physiol Rev. 2010;90(3):1103-1163.
[7]Bauer G, Dao MA, Case SS,et al.In vivo biosafety model to assess the risk of adverse events from retroviral and lentiviral vectors.Mol Ther. 2008;16(7):1308-1315.
[8]别利克孜•卡德尔,刘奕杉,王璇,等.改良酶消化法分离培养人乳牙牙髓干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(10):1793-1800.
[9]Arthur A, Shi S, Zannettino AC,et al.Implanted adult human dental pulp stem cells induce endogenous axon guidance.Stem Cells. 2009 Sep;27(9):2229-2237.
[10]刘怡,王松灵.口腔特有的成体干细胞的研究进展[J]. 国外医学:口腔医学分册,2006,33(2):110-113.
[11]Ballini A, De Frenza G, Cantore S,et al.In vitro stem cell cultures from human dental pulp and periodontal ligament: new prospects in dentistry.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2007;20(1):9-16.
[12]Karaöz E, Do?an BN, Aksoy A,et al.Isolation and in vitro characterisation of dental pulp stem cells from natal teeth. Histochem Cell Biol. 2010;133(1):95-112.
[13]Leiker M, Suzuki G, Iyer VS,et al.Assessment of a nuclear affinity labeling method for tracking implanted mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Transplant. 2008;17(8):911-922.
[14]Kato Y, Sawata SY, Inoue A.A lentiviral vector encoding two fluorescent proteins enables imaging of adenoviral infection via adenovirus-encoded miRNAs in single living cells.J Biochem. 2010;147(1):63-71.
[15]Yang HN, Park JS, Na K,et al.The use of green fluorescence gene (GFP)-modified rabbit mesenchymal stem cells (rMSCs) co-cultured with chondrocytes in hydrogel constructs to reveal the chondrogenesis of MSCs.Biomaterials. 2009;30(31):6374-6385.
[16]Cho SR, Kim YR, Kang HS,et al.Functional recovery after the transplantation of neurally differentiated mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone barrow in a rat model of spinal cord injury.Cell Transplant. 2009;18(12):1359-1368.
[17]武京国,谢方南,马慧雨,等. EGFP和CM-Dil示踪骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程骨的体内研究[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(3): 406-409.
[18]吴沛桥,巴晓革,胡海,等. 绿色荧光蛋白GFP的研究进展及应用[J].生物医学工程研究,2009,28(1):83-86.
[19]Lasek AW, Azouaou N.Virus-delivered RNA interference in mouse brain to study addiction-related behaviors.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;602:283-298.
[20]Tannemaat MR, Verhaagen J, Malessy M.The application of viral vectors to enhance regeneration after peripheral nerve repair.Neurol Res. 2008;30(10):1039-1046.
[21]Heilbronn R, Weger S.Viral vectors for gene transfer: current status of gene therapeutics.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2010; (197): 143-170.
[22]Burns TC, Ortiz-González XR, Gutiérrez-Pérez M,et al.Thymidine analogs are transferred from prelabeled donor to host cells in the central nervous system after transplantation: a word of caution.Stem Cells. 2006;24(4): 1121-1127.
[23]Nowakowski A, Andrzejewska A, Janowski M,et al.Genetic engineering of stem cells for enhanced therapy.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2013;73(1):1-18.
[24]Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G,et al.Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression.Science. 1994;263(5148): 802-805.
[25]王巍巍,张金元.携带增强绿色荧光蛋白的慢病毒载体感染人脂肪源性干细胞的有效性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(36):6695-6698.
[26]郭红延,吴补领,郭希民,等.大鼠牙髓干细胞的培养和鉴定[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2004,14(5):242-245.
[27]Engelhardt M, Kumar R, Albanell J,et al.Telomerase regulation, cell cycle, and telomere stability in primitive hematopoietic cells.Blood. 1997;90(1):182-193.
[28]Coppe C, Zhang Y, Den Besten PK.Characterization of primary dental pulp cells in vitro.Pediatr Dent. 2009;31(7): 467-471.
[29]Shimizu S, Kitada M, Ishikawa H,et al.Peripheral nerve regeneration by the in vitro differentiated-human bone marrow stromal cells with Schwann cell property.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;359(4):915-920.
[30]Kaneko T, Arayatrakoollikit U, Yamanaka Y,et al. Immunohistochemical and gene expression analysis of stem-cell-associated markers in rat dental pulp.Cell Tissue Res. 2013;351(3):425-432.
[31]李宏松,徐晨,邹俊.慢病毒负载GFP转染兔脂肪干细胞的效率及毒性评价[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2013,33(4):439-444.
[32]Cuenca-López MD, Zamora-Navas P, García-Herrera JM,et al.Adult stem cells applied to tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2008; 54(1):40-51.
[33]Huang GT, Gronthos S, Shi S.Mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental tissues vs. those from other sources: their biology and role in regenerative medicine.J Dent Res. 2009;88(9):792-806.
[34]Murray PE, Matthews JB, Sloan AJ,et al.Analysis of incisor pulp cell populations in Wistar rats of different ages.Arch Oral Biol. 2002;47(10):709-715.
[35]Uchida N, He D, Friera AM,et al. The unexpected G0/G1 cell cycle status of mobilized hematopoietic stem cells from peripheral blood.Blood. 1997;89(2):465-472.
[36]章静波,宗书东,马文丽.干细胞[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社,2003:137-141.
[37]贺慧霞.牙髓干细胞分离鉴定及其制备组织工程化牙本质牙髓复合体的实验研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2005.
[38]王志刚,刘兴容.牙髓干细胞及其表面特异标志物[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2010,37(1):56-58. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||