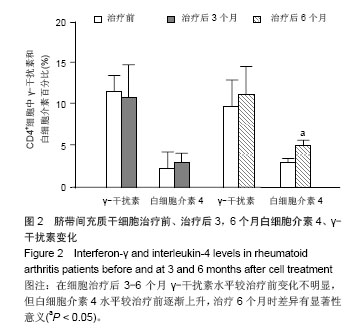
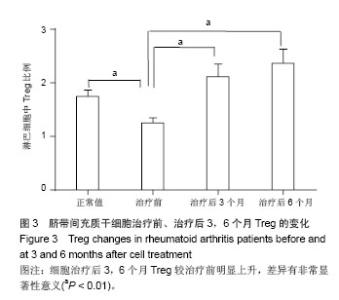
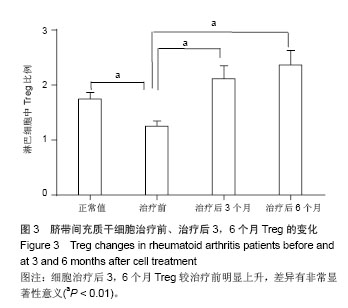
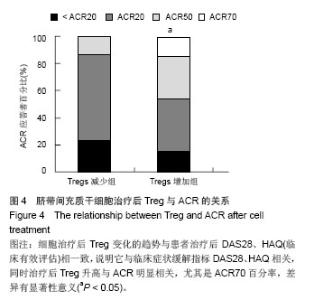
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (45): 7279-7284.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.45.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Variation of Th1/Th2 and Terg in rheumatoid arthritis patients undergoing umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation
Wang Li-ming1, Wang Li-hua2, Li Ming1, Bai Wen1, Zhong Zhan-qiang1, Shi Jun1, Zhou Jian-jun1, Huang Shi-gao1, Li Na2, Ji Hai-jie2, Liu Yong-jun2, Wu Ming-yuan2
- 1the 323rd Hospital of PLA, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Heze Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine Research Center, Tianjin 300381, China