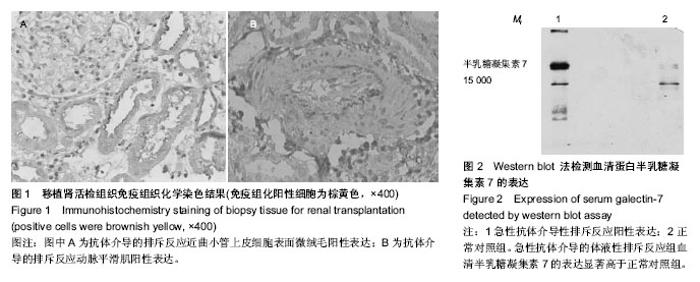
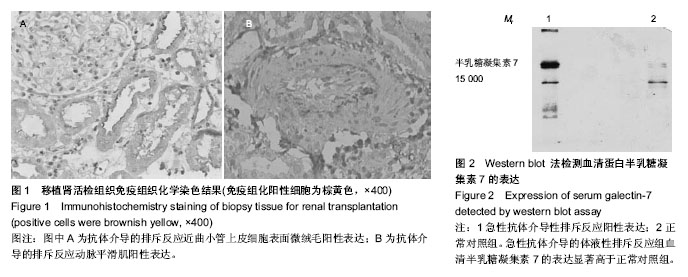
| [1] 韩永,郭晖,蔡明,等.移植肾活检:病理及组织学的早期诊断价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(5):785-790.
[2] Suryawanshi A, Cao Z, Thitiprasert T, et al. Galectin-1-mediated suppression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced corneal immunopathology.J Immunol. 2013;190(12):6397-6409.
[3] Perone MJ, Bertera S, Shufesky WJ,et al. Suppression of autoimmune diabetes by soluble galectin-1. J Immunol. 2009; 182(5):2641-2653.
[4] Ye Y, Yan S, Jiang G,et al. Galectin-1 prolongs survival of mouse liver allografts from Flt3L-pretreated donors. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(3):569-579.
[5] Chen X, Song CH, Liu ZQ, et al. Intestinal epithelial cells express galectin-9 in patients with food allergy that plays a critical role in sustaining allergic status in mouse intestine. Allergy. 2011;66(8):1038-1046.
[6] 雒真龙,周鸿敏,黄霞,等.Galectin-7 在人和鼠同种异体心脏移植物中的表达及其意义[J].实用医学杂志,2013, 29(10): 1567-1569.
[7] Koller H, Steurer W, Mark W, et al. Clearance of C4d deposition after successful treatment of acute humoral rejection in follow-up biopsies: a report of three cases. Transpl Int. 2004;17(4):177-181.
[8] Hokama A, Mizoguchi E, Mizoguchi A.Roles of galectins in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14(33):5133-5137.
[9] Troncoso MF, Elola MT, Croci DO, et al. Integrating structure and function of 'tandem-repeat' galectins. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2012;4:864-887.
[10] Vijayakumar S, Peng H, Schwartz GJ.Galectin-3 mediates oligomerization of secreted hensin using its carbohydrate- recognition domain. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013; 305(1):F90-99.
[11] Takeuchi T, Tamura M, Nishiyama K, et al.Mammalian galectins bind galactoseβ1-4fucose disaccharide, a unique structural component of protostomial N-type glycoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2013;436(3):509-513.
[12] Vizzini A, Parrinello D, Sanfratello MA, et al.Inducible galectins are expressed in the inflamed pharynx of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012; 32(1):101-109.
[13] Magnaldo T, Bernerd F, Darmon M. Galectin-7, a human 14-kDa S-lectin, specifically expressed in keratinocytes and sensitive to retinoic acid. Dev Biol. 1995;168(2):259-271.
[14] Nio J, Kon Y, Iwanaga T. Differential cellular expression of galectin family mRNAs in the epithelial cells of the mouse digestive tract. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005;53(11): 1323-1334.
[15] Young PP, Modur V, Teleron AA, et al. Enrichment of genes in the aortic intima that are associated with stratified epithelium: implications of underlying biomechanical and barrier properties of the arterial intima. Circulation. 2005;111(18): 2382-2390.
[16] 韩永,黄海燕,许晓光,等.移植肾穿刺组织病理学检查及临床分析[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志[J].2010,24(12):1173-1178.
[17] 石炳毅.应进一步提高肾脏移植排斥反应的无创诊断水平[J].中华医学杂志,2011, 91(48):3385-3387.
[18] 郭晖.抗体介导的排斥反应病理学研究概要[J].中华移植杂志, 2012,6(2):138-143.
[19] Tyan DB, Li VA, Czer L, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin supprcssion of HLA alloant ibody in highly sensit ized transplant candidat es and transplant at ion w ith a hist oincompat ible organ. Trans plantat ion.1994;57(4):553-562.
[20] Montgomery RA, Zachary AA, Racusen LC, et al. Plasmepheresis and intravenous immune globulin p rovides effective rescue therapy for refractory humoral rejection and allows kidneys to be succeddfully transp lanted into cross2match2positive recip ients. Transp lantion. 2000;70(6): 887-895.
[21] Casadei D, Rial M, Argento J, et al. Preliminary results from a randomized and prospective study of high-dose immunoglobulin versus monoclonal antibody in the rescue of steroid-resistant rejections. Transplant Proc.1998;30(5):2164.
[22] John R, Konvalinka A, Tobar A, et al. Determinants of long-term graft outcome in transplant glomerulopathy. Transplantation.2010;90(7):757-764.
[23] 邹万忠.发展和提高我国的肾活检病理检查水平[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2005,21(6):303-305.
[24] 向雪宝.肾移植围手术期目标导向性液体治疗进展[J].器官移植, 2014,5(3):191-193.
[25] John R, Konvalinka A, Tobar A, et al. Determinants of long-term graft outcome in transplant glomerulopathy. Transplantation. 2010;90(7):757-764. |