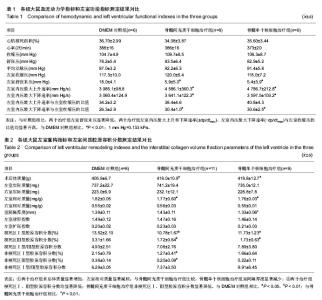
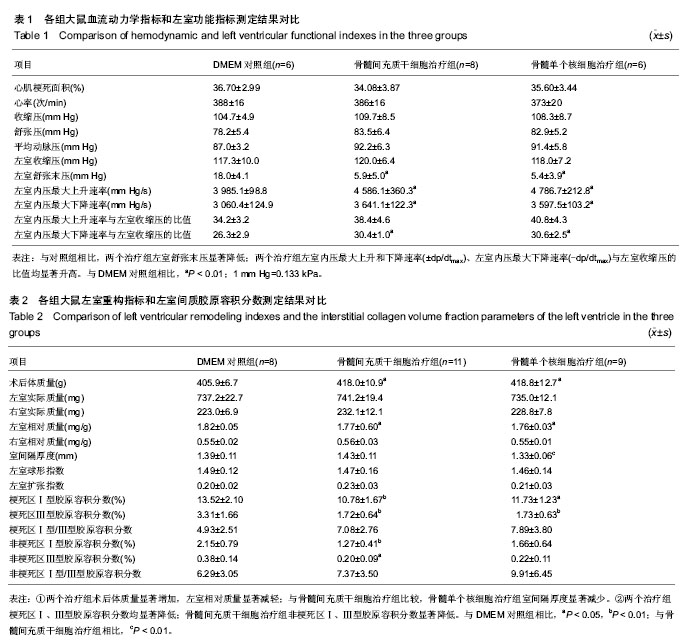
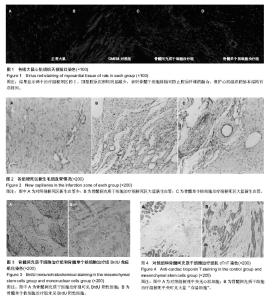
| [1] |
Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan.
Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-.
|
| [2] |
Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang.
Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan.
Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345.
|
| [4] |
Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng.
Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255.
|
| [5] |
Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao.
Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990.
|
| [6] |
Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing.
Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995.
|
| [7] |
Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei.
Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001.
|
| [8] |
Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui.
Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007.
|
| [9] |
Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang.
Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013.
|
| [10] |
Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin.
Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018.
|
| [11] |
Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong.
Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025.
|
| [12] |
Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang.
Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031.
|
| [13] |
Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di.
Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036.
|
| [14] |
Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin.
Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049.
|
| [15] |
Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan.
Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080.
|