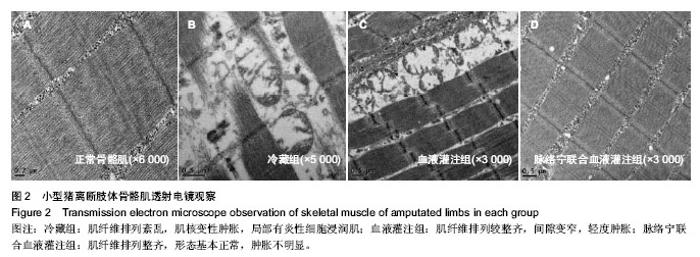
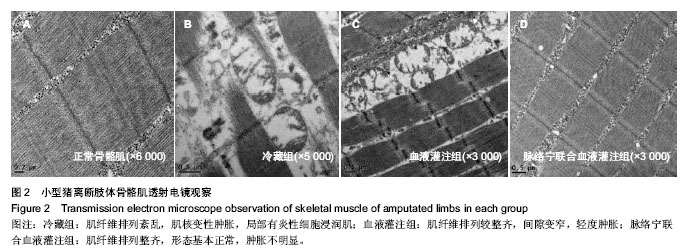
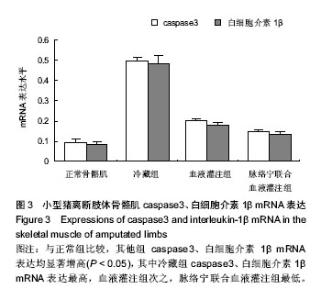
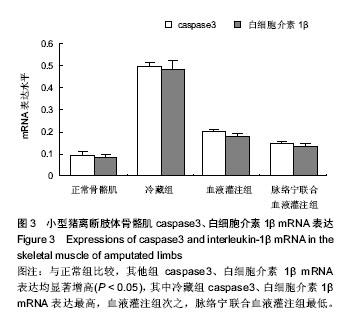
| [1] Mowlavi A, Neumeister MW, Wilhelmi BJ, et al. Local hypothermia during early reperfusion protects skeletal muscle from ischemia- reperfusion injury. Plast Reconstr Surg.2003; 111(1):242-250.
[2] 洪念国,田中伟,李涛, 等.断肢再植缺血再灌注损伤的保护机制[J].河南科技大学学报:医学版,2006,24:(3):171-172.
[3] Wagh M, Pantazi G, Romeo R, et al. Cold storage of rat skeletal muscle free flaps and pre-ischemic perfusion with modified UW solution. Microsurgery.2000;20(7):343- 349.
[4] Bastiaanse J, Nanhekhan LV, Slaaf DW, et al. Preservation of rat cremaster muscle microcirculation after prolonged cold storage and transplantation. Surg Res.2006;131(1): 41-48.
[5] Tsuchida T, KatoT, Yamaga M, et al. Effect of perfusion during ischemia on skeletal muscle. J Surg Res.2001;101(2): 238-241.
[6] Kurt B, Kurt Y, Karsliogu Y, et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on energy production and xanthine oxidase levels in striated muscle tissue of healthy rats.Clin Neurosci.2008;15(4): 445-450.
[7] Zemmel NJ, Amis LR, Sheppard FR, et al. A temporal analysis of the effects of pressurized oxygen (HBO) on the pH of amputated muscle tissue. Ann Plast Surg.1998; 40(6): 624-629.
[8] Vidigal J, José Fagundes D, De Jesus Simoes M, et al. Effect of different periods of hyperbaric oxygen on ischemia- reperfusion injury of rat skeletal muscle. Microsurgery. 2007; 27(4):252-257.
[9] 王江宁,童致虹,张铁慧,等.暂时性异位断足寄养再回植术[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2003,17(1):46-49.
[10] Wang JN, Wang SY, Wang ZJ, et al. Temporary ectopic implantation for salvage of amputated lower extremities: case reports. Microsurgery. 2005;25(5):385-389.
[11] Wang JN, Tong ZH, Zhang TH, et al. Salvage of amputated upper extremities with temporary ectopic implantation followed by replantation at a second stage. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2006;22(1):15-20.
[12] 王江宁,尹叶锋,高磊,等.不同温度对体外模拟体内生理环境寄养断肢系统的影响研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013, 27(1): 65-69.
[13] 王江宁,尹叶锋,高磊,等.不同氧体积分数气体对体外模拟体内生理环境寄养断肢系统血氧分压的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(5):855-858.
[14] Müller S, Constantinescu MA, Kiermeir DM, et al. Ischemia/ reperfusion injury of porcine limbs after extracorporeal perfusion. J Surg Res.2013;181(1):170-182.
[15] Li X, Cooley BC, Gould JS. Ex vivo perfusion with anticoagulated blood decreases ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Hand Surg Am.1993;18(4):629-634.
[16] 段永壮,钟世镇,王增涛,等.依达拉奉对深低温保存大鼠断肢再植后缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(8):1416-1418.
[17] Chin KY, Hart AM.Temporary catheter first perfusion during hand replantation with prolonged warm ischemia. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012;65(5):675-677.
[18] 王岱君,王金平,田华.脉络宁注射液对肢体缺血再灌注损伤一氧化氮及一氧化氮合酶的影响[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2005, 12(1):43-46.
[19] 王岱君,王金平,鞠学红,等.脉络宁对兔肢体缺血再灌注损伤的防护作用[J].中华创伤杂志,2004;20(4):234-237.
[20] 李军凯,杨高潮,黄河.脉络宁对大鼠肢体缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2012;10(10):1232- 1233.
[21] 韦正超,金文涛,张峻峰.四肢血管损伤的手术治疗[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(3):191-192.
[22] 吴桂英,廖忠莉,李宁,等.氧中毒发生及其防治研究进展[J].重庆医学,2009,38(8):907-909.
[23] 李宁,黄怀.高压氧临床治疗学[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社,2007:299-301.
[24] Albadawi H, Oklu R, Cormier NR, et al. Hind limb ischemia- reperfusion injury in diet-induced obese mice.J Surg Res. 2014;1(17):1-9.
[25] Zang LY, Cosma G, Gardner H, et al. Scavenging of superoxide anion radical by chaparral. Mol Cell Biochem. 1999;196(2):157 -161.
[26] 顾亚夫,赖尧基,倪正,等.脉络宁治疗三种血栓病的疗效观察及其机理探讨[J].中西医结合杂志,1987,7(12):718-721.
[27] 王岱君,田华.脉络宁对肢体缺血/再灌注兔骨骼肌iNOS mRNA及eNOS mRNA表达的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2014,30(3): 439-441.
[28] 梁倩倩,田华,庄宝祥,等.脉络宁对兔肢体缺血/再灌注损伤过程中SOD及MPO的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2012,28(6): 885-886.
[29] 李军凯.脉络宁对大鼠肢体缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].太原:山西医科大学,2013.
[30] 王岱君,田华,王金平.脉络宁注射液对缺血/再灌注骨骼肌丙二醛及谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的影响[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2009,16(3):175-176.
[31] 吴婷,张军,储继红,等.谈恒山脉络宁注射液药理及药代学研究进展[J].江苏中医药,2011,43(9):93-94.
[32] 李文星,刘建国,周顺延,等.丁素银脉络宁联合微波治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变30例疗效观察[J].疑难病杂志,2008,7(9): 548-549.
[33] 万政佐.脉络宁复合液治疗大鼠激素性股骨头坏死机理的实验研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院:中西医结合临床,2008. |