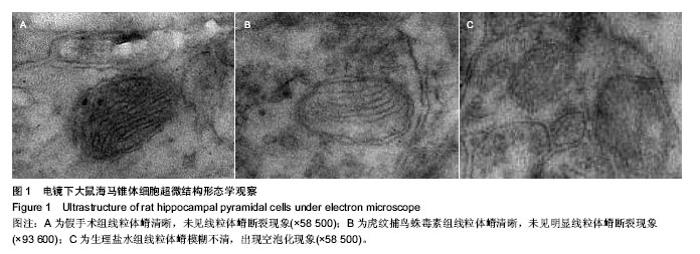
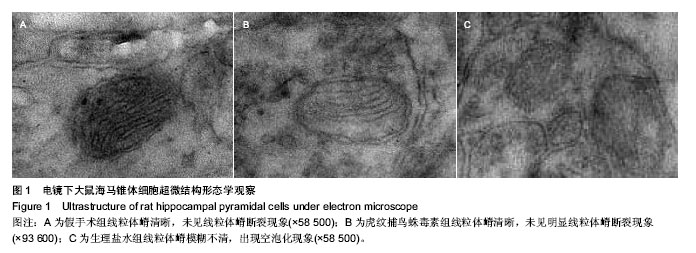
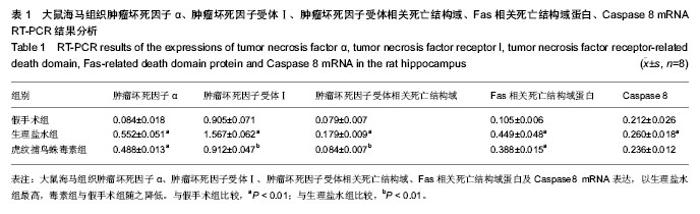
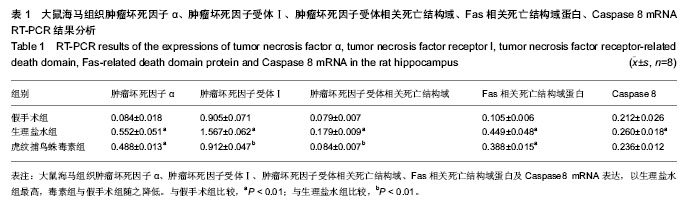
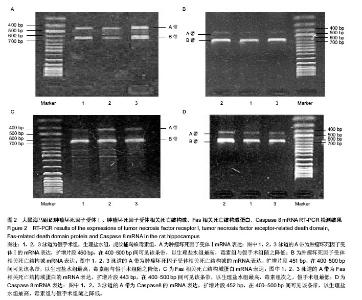
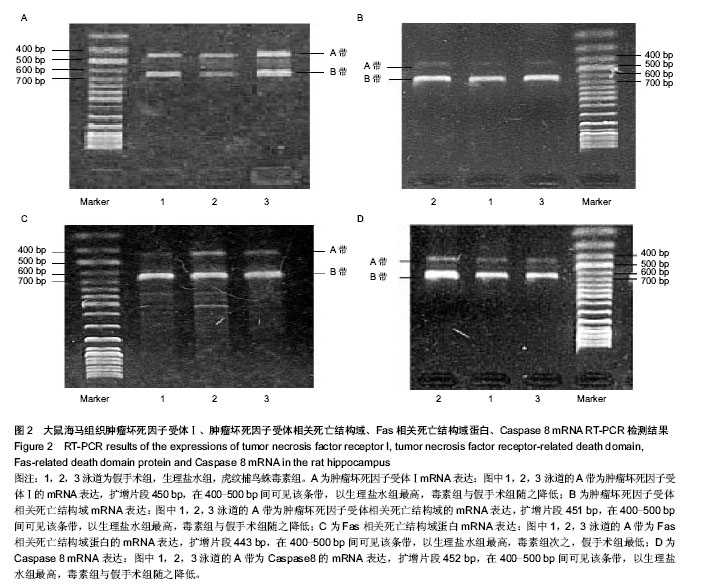
| [1] Lipton P.Ischemic Cell Death in Brain Neurons. Physiol Rev. 1999;79(4):1431-568.
[2] 王薇,赵冬,刘静,等.中国35~64岁人群血压水平与10年心血管病发病危险的前瞻性研究[J].中华内科杂志,2004,43(10): 730-734.
[3] Takehashi T, Moniyama A. Different type of calcium channels mediate central synaptic transmission. Nature (London).1993; 366:156-158.
[4] Peng K, Chen XD, Liang SP,et al. The effect of Huwentoxin-I on Ca2+ channels in differentiated NG108-15 cells, a patch-clamp study. Toxicon. 2001;39(4):491-498.
[5] Jiaqin C, Yongquen Z, Jie D, et al. Antinociceptive effects of intrathecally administered huwentoxin-I, a selective N-type calcium channel blocker, in the formalin test in conscious rats. Toxicon.2005;45:15-20.
[6] Jiaqin C, Weihua C, Meichun D, et al. Huwentoxin-I: antinociceptive effects and its comparison with -conotoxin-MVIIA on acute visceral pain in rats. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 2005;21(1): 24-29.
[7] Valentino K, Newcomb R,Gadbois T, et al. A selective N-type calcium channel antagonist protects against neuronal loss after global cerebral ischemia. neurobiology.1993;90: 7894-7897.
[8] Smith MT, Cabot PT, Ross FB, et al. The novel N-type calcium channel blocker, AM336, produces potent dose-dependent antinociception after intrathecal dosing in rats and inhibits substance P release in rat spinal cord slices. Pain.2002; 96:119-127.
[9] Yaksh TL, Rudy A. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav.1976;17:175-185.
[10] Pulsinelli WA, Brierley JB. A new model of bilateral hemispheric ischemic in the unanesthetized rat. Stroke. 1979;10(3):267-272.
[11] Frederick C, Hui L, Alastair M, et al. Continuing Postischemic Neuronal Death in CA1 Influence of Ischemia Duration and Cytoprotective Doses of NBQX and SNX-111 in Rats. Stroke. 1999;30:662-668.
[12] 袁春华.两种虎纹捕鸟蛛毒素的结构与功能研究[J].长沙:湖南师范大学:生物化学与分子生物学,2003.
[13] 毛海峰,陈嘉勤,周鸿燕,等.SD大鼠全全脑缺血结合蛛网膜下腔置管模型的构建[J].湖南师范大学学报医学版,2005,2(1):46-49.
[14] 毛海峰,陈嘉勤,周鸿燕,等.HWTX-I对全脑缺血大鼠脑组织自由基及海马神经元损伤的保护作用研究[J].北京体育大学学报, 2007,30(3):351-353.
[15] 吴坤,赵艳,于卫平.细胞凋亡的研究进展[J].国外医学:遗传学分册,2001,24(3):134-138.
[16] Liu Z, Jiao QF, You C, et al. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on cytochrome C, Bcl-2 and bax expression after experimental traumatic brain injury in rats.Chin J Traumatol.2006;9(3): 168-174.
[17] Fall CP, Bennett JP Jr. Visualization of cyclosporin A and Ca2+-sensitive cyclical mitochondrial depolarizations in cell culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1410(1):77-84.
[18] Chan PH. Mitochondria and neuronal death/survival signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Res.2004;29(11): 1943-1949.
[19] Yan N, Shi Y. Mechanisms of apoptosis through structural biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.2005;21:35-56.
[20] 吴刚,薛荣亮.死亡受体介导的信号转导与脑缺血再灌注损伤[J].国外医学:麻醉学与复苏分册,2004,25(1):11-15.
[21] Berti R, Williams AJ, Moffett JR, et al. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory gene expression associated with ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22(9);1068-1079.
[22] Wang CX. Shuaib A. Involvement of inflammatory cytokines in central nervous system injury. Prog Neurobiol.2002,67(2): 161-172.
[23] Malink T, Bailey F, Zhang IG, et al. Nitric oxide measured by a porˉphyrinic microsensor in rat brain after transient middle flow. Metab.1993;13:335-338.
[24] Rothstein JD, Bristol LA, Hosler B, et al. Chronic inhibition of superoxide dismutase produces apoptosis: a role for reactive oxygen species in program-medneuronal death. Neuron.1995; 14:303-315. |