Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (33): 5310-5316.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.33.011
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interleukin-10 and conjugative plasmid of Salmonella mediate bacterial biofilm formation
Que Feng-xia, Liu Zhen, Wang Ting, Yan Jing, Li Yuan-yuan, Wu Shu-yan, Huang Rui
- Department of Pathogen Biology, Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2014-08-13Published:2014-08-13 -
Contact:Wu Shu-yan, Department of Pathogen Biology, Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Que Feng-xia, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Pathogen Biology, Medical College of Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. BK2011286
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Que Feng-xia, Liu Zhen, Wang Ting, Yan Jing, Li Yuan-yuan, Wu Shu-yan, Huang Rui. Interleukin-10 and conjugative plasmid of Salmonella mediate bacterial biofilm formation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(33): 5310-5316.
share this article
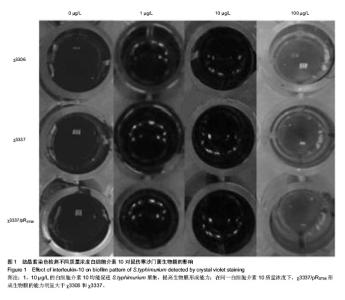
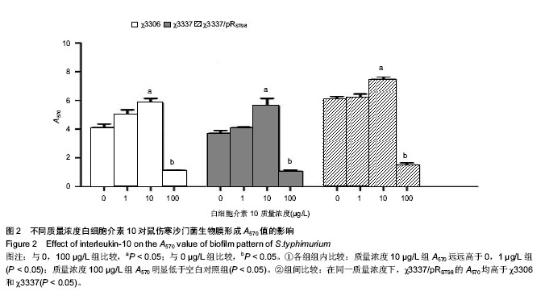
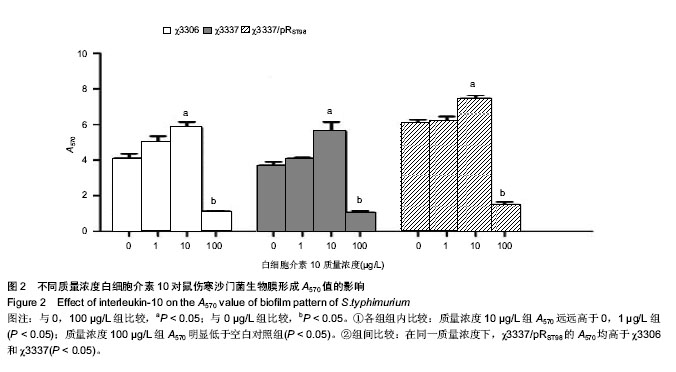
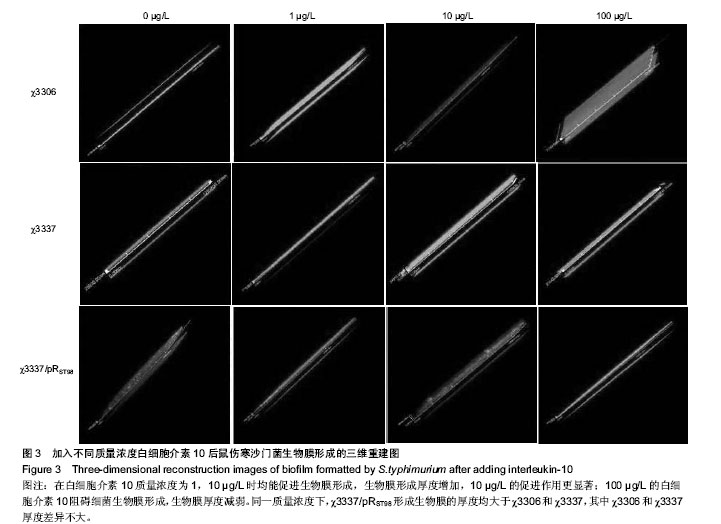
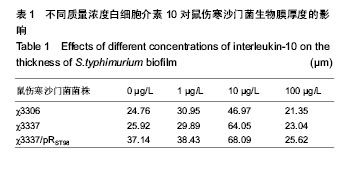
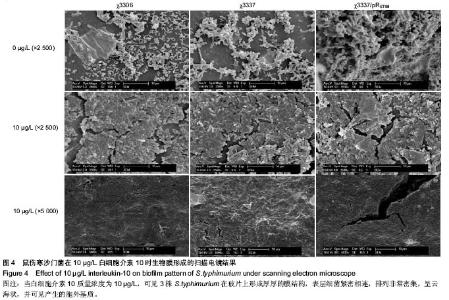
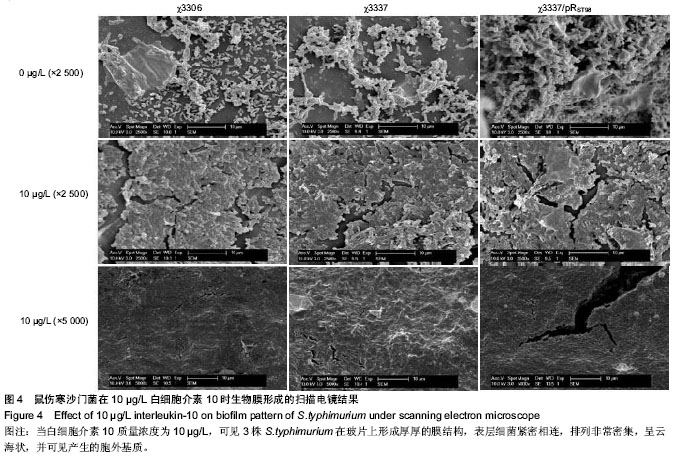
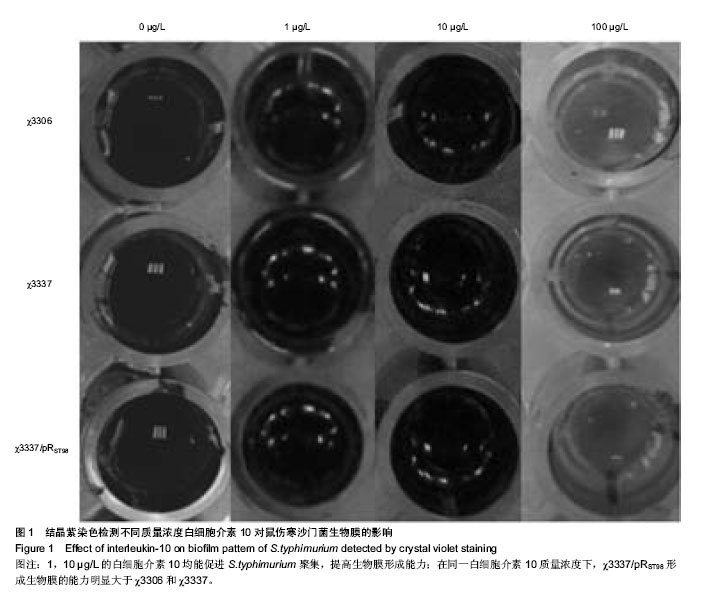
2.1 结晶紫染色半定量法检测白细胞介素10对细菌生物膜的影响 结晶紫染色结果显示,与空白对照组相比,质量浓度为1,10 µg/L的白细胞介素10在96孔板内均能促进S.typhimurium聚集,提高生物膜形成能力。特别是白细胞介素10质量浓度为10 µg/L时,S.typhimurium结晶紫染色更深,生物膜形成能力显著增加。当白细胞介素10质量浓度为100 µg/L时,与空白对照组相比生物膜形成能力受到抑制。在同一白细胞介素10质量浓度下,χ3337/pRST98形成生物膜的能力明显大于χ3306和χ3337(图1)。半定量结果显示,与空白对照组相比,3组S.typhimurium在白细胞介素10质量浓度为10 µg/L时,A570远远高于空白对照组和质量浓度为1 µg/L组(P < 0.05);当白细胞介素10的质量浓度为100 µg/L时,A570明显低于空白对照组(P < 0.05),提示该质量浓度抑制生物膜形成。在白细胞介素10三个质量浓度下,χ3337/pRST98的A570均高于χ3306和χ3337 (P < 0.05),见图2。"
| [1]Wojcik OP,Kjelso C,Kuhn KG,et al.Salmonella typhimurium outbreak associated with smoked pork tenderloin in Denmark, January to March 2011. Scand J Infect Dis.2012;44(12): 903-908. [2]Lafuente S,Bellido JB,Moraga FA,et al.Salmonella paratyphi B and Salmonella litchfield outbreaks associated with pet turtle exposure in Spain. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2013; 31(1):32-35. [3]Crump JA,Mintz ED.Global trends in typhoid and paratyphoid Fever.Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(2):241-246. [4]Gole VC,Chousalkar KK,Roberts JR,et al.Effect of Egg Washing and Correlation between Eggshell Characteristics and Egg Penetration by Various SalmonellaTyphimurium Strains.PLoS One.2014;9(3):e90987. [5]Hall-Stoodley L,Stoodley P.Evolving concepts in biofilm infections.Cell Microbiol.2009;11(7):1034-1043. [6]He X,Ahn J.Differential gene expression in planktonic and biofilm cells of multiple antibiotic-resistant Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus.. FEMS Microbiol Lett.2011;325(2):180-188. [7]HΦiby N.A Personal History of Research on Microbial Biofilms and Biofilm Infections.Pathog Dis.2014; doi: 10.1111/2049-632x.12165. [8]Steenackers H,Hermans K,Vanderleyden J,et al.Salmonella biofilms: An overview on occurrence, structure, regulation and eradication.Food Res Int.2012;45(2):502-531. [9]Desin TS,Mickael CS,Lam PK,et al. Protection of epithelial cells from Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis invasion by antibodies against the SPI-1 type III secretion system.Can J Microbiol.2010;56(6):522-526. [10]Spiliopoulou AI,Kolonitsiou F,Krevvata MI,et al.Bacterial adhesion, intracellular survival and cytokine induction upon stimulation of mononuclear cells with planktonic or biofilm phase Staphylococcus epidermidis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012;330:56-65. [11]Kristian SA,Birkenstock TA,Sauder U,et al.Biofilm formation induces C3a release and protects Staphylococcus epidermidis from IgG and complement deposition and from neutrophil-dependent killing.J Infect Dis. 2008;197: 1028-1035. [12]周琳,周光炎,路丽明.IL-10的双向免疫调节作用[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2012, 28(10):1100-1104. [13]王国戗,娄婷叶,裴利宏.生物膜形成菌感染局部细胞因子的变化[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2013,23(5):969-971. [14]Zelante T,Iannitti RG,De Luca A,et al.Sensing of mammalian IL-17A regulates fungal adaptation and virulence.Nat Commun.2012;3:683. [15]肖黔林,周忠海,李秋丽,等.质粒分析, 噬菌体定型及耐药谱测定在伤寒流行病学调查中的应用[J].中华流行病学杂志, 1987, 5(5):272-275. [16]黄瑞,穆荣普.伤寒沙门氏菌耐药性及其耐药质粒的监测[J].中华传染病杂志,1994,12(4):204-206. [17]黄瑞,吴淑燕,闻玉梅.伤寒沙门菌耐药质粒pRST98介导细菌毒力的研究[J].中华微生物学与免疫学杂志,2001,21(3): 302-305. [18]黄瑞,吴淑燕,闻玉梅.耐药质粒pRST98在不同种属肠道杆菌间的接合及表达[J].中华微生物学与免疫学杂志,2000,20(4): 302-305. [19]Ghigo JM.Natural conjugative plasmids induce bacteria biofilm development. Nature.2001;412(6845):442-445. [20]Wei L,Wu S,Li Y,et al.Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi plasmid impairs dendritic cell responses to infection.Curr Microbiol.2012;65(2):133-140. [21]Zhao G,Usui ML,Lippman SI,et al.Biofilms and Inflammation in Chronic Wounds. Adv Wound Care.2013;2(7):389-399. [22]Zhao T,Zhao P,Cannon JL,et al.Inactivation of salmonella in biofilms and on chicken cages and preharvest poultry by levulinic Acid and sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Food Prot. 2011; 74(12):2024-2030. [23]Bae YM,Baek SY,Lee SY.Resistance of pathogenic bacteria on the surface of stainless steel depending on attachment form and efficacy of chemical sanitizers. Int J Food Microbiol. 2012;153(3):465-473. [24]Romling U,Bokranz W,Rabsch W,et al.Occurrence and regulation of the multicellular morphotype in Salmonella serovars important in human disease.Int J Med Microbiol. 2003; 293(4):273-285. [25]Gerstel U,Park C,Romling U.Complex regulation of csgD promoter activity by global regulatory proteins.Mol Microbiol. 2003;49:639-654. [26]Latasa C,Roux A,Toledo-Arana A,et al.BapA, a large secreted protein required for biofilm formation and host colonization of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis.Mol Microbiol. 2005; 58:1322-1339. [27]Fuqua WC,Winans SC,Greenberg EP.Quorum sensing in bacteria: The LuxR-LuxI family of density-responsive transcriptional regulators.J Bacteriol.1994;176(2):269-275. [28]Dickschat JS.Quorum sensing and bacterial biofilms.Nat Prod Rep. 2010;27(3):343-369. [29]Otto M.Bacterial evasion of antimicrobial peptides by biofilm formation.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.2006;306:251-258. [30]Thurlow LR,Hanke ML,Fritz T,et al.Staphylococcus aureus biofilms prevent macrophage phagocytosis and attenuate inflammation in vivo.J Immunol.2011;186: 6585-6596. [31]Schommer NN,Christner M,Hentschke M,et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis uses distinct mechanisms of biofilm formation to interfere with phagocytosis and activation of mouse macrophage-like cells 774A.1. Infect Immun. 2011; 79:2267-2276. [32]Hanke ML,Angle A,Kielian T.MyD88-dependent signaling influences fibrosis and alternative macrophage activation during Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e42476. [33]Hanke ML,Heim CE,Angle A,et al.Targeting macrophage activation for the prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm infections. J Immunol.2013; 190:2159-2168. [34]Prabhakara R,Harro JM,Leid JG,et al.Suppression of the inflammatory immune response prevents the development of chronic biofilm infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun.2011;79:5010-5018. |
| [1] | Sun Yu, Zou Qiang, Li Xuanze, Wu Zhanyu, Yang Long, Wang Jianji, Liu Qin, Ma Minxian, Ye Chuan. Construction and biocompatibility of blood biofilms based on electrospinning technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 901-905. |
| [2] | Xu Xiaoling, Pan Wangping, Lü Xiaojun, Zhang Ju, Hu Yuanhua, He Kaiyong. Immunotoxicity of absorbable silk fibroin biofilm on rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2190-2195. |
| [3] | Chen Zao-mei, Li Ru-bing. Research progress of absorbable anti-adhesion membranes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(18): 2920-2926. |
| [4] | Ma Tao, Kou Wen-guan, Liu Guo-li, Bai Jiang-bo, Yu Kun-lun, Tian De-hu. Fresh amniotic membrane for repair of acute peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(18): 2890-2899. |
| [5] | Feng Min, Chang Si-yuan, Xu Da-qian, Liu Gang. Treatment outcomes of recombinant human granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor in a model mouse with sepsis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(49): 7391-7396. |
| [6] | Jia Ren-jie, Ren Yu-qing, Xu Hao, Wang Wei-ying, Yi Zhong-ping, Zhao Bao-dong. Guided bone regeneration with acellular dermal matrix as a barrier for bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(30): 4442-4448. |
| [7] | Wang Lei, Li Tian-wang, Liu Jian-qiang, Liu Xiao-zong, Wang Zhao-guo, Tian Yan, Zhang Yong-xing, Wang Wei. Downregulated Hsa-let-7f contributes to the loss of type II collagen by targeting interleukin-10/STAT3 signaling pathway in degenerative lumbar scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(15): 2225-2232. |
| [8] | Guo Su-ping, Song Yan, Wang Fan-tao, Xu Xin, Jia Wei. The cleaning of plaque biofilm on the surface of macromolecule ocular prosthesis material [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(43): 6993-6997. |
| [9] | Shen You-liang, Zhu Tong-e, Zhang Jing-jing, Qi Chao, Yu Teng-bo. Construction of a rabbit model of knee prosthesis infection: environmental factors in vivo affect Staphylococcus epidermidis and biofilms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(39): 6240-6245. |
| [10] | Yu Shu-feng, Ren An-xia, Zhang Li-juan, Li Tang. Effect of interleukin-10 gene on liver pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 expression in nonobese diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(27): 4371-4378. |
| [11] | Ma Yao, Chu Shun-li, Sun Yue, Ma Shan-shan, Li Xue, Zhang Tian-shou, Zhou Yan-min. Poly(butylene succinate)/polypropylenecarbonate biofilms: preparation and performanc [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(21): 3355-3360. |
| [12] | Zhu Jian-hua, Liu Na, Zhao Chang-rong, Liu Ji-guang. Interferon-gamma and interleukin-10 levels in serum and saliva are related to different types of oral lichen planus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(2): 236-240. |
| [13] | Yuan Shu-fang, Hu Lan-ying, Jiang Tao, Sun Li-hua, Zheng Rong-jiong, Zhao Jin-yan, Zhang Yue-xin . Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on the expression of CD163 and interleukin-10 in rats with acute hepatic liver failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 919-925. |
| [14] | Wang Shan-shan, Dong Ming, Wang Li-na, Niu Wei-dong. Antibacterial effect of sodium hypochlorite on in vitro biofilm formation of Enterococcus faecalis in different phases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8509-8514. |
| [15] | Li Xiang, Zha Guo-qing, Zhu Shuang-xi. Osteogenic effect of guided bone regeneration in maxillary sinus augmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(25): 4020-4025. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||