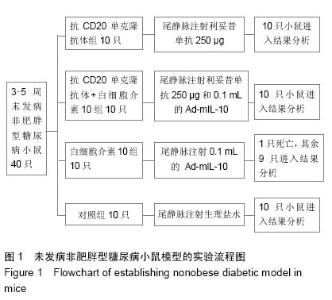
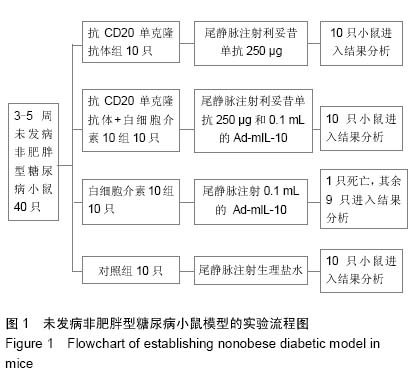
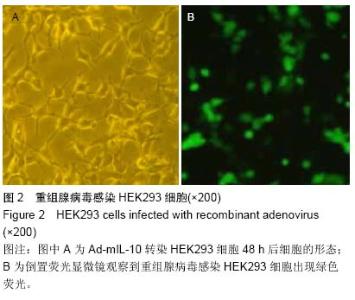
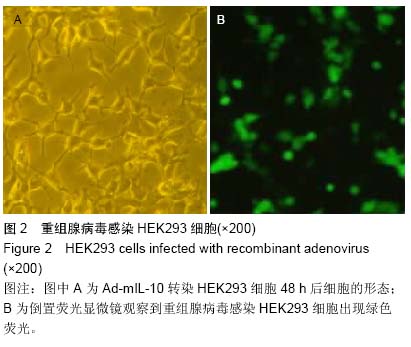
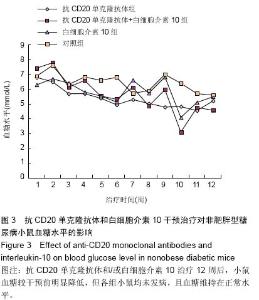
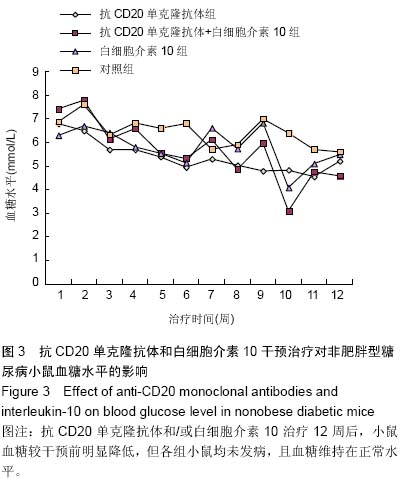
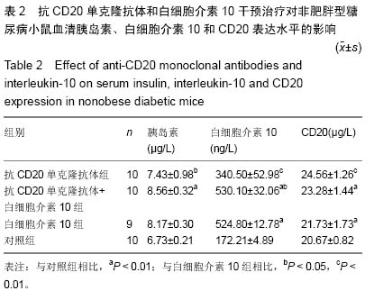
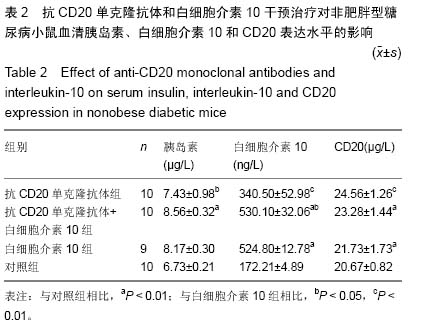
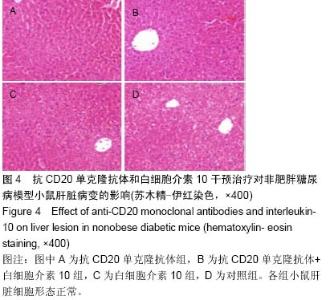
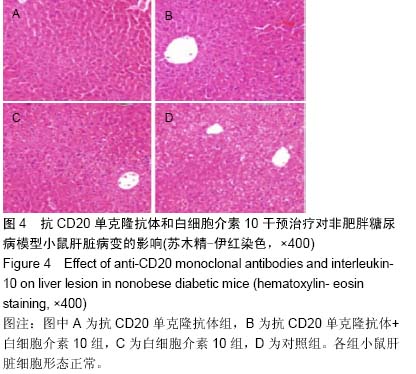
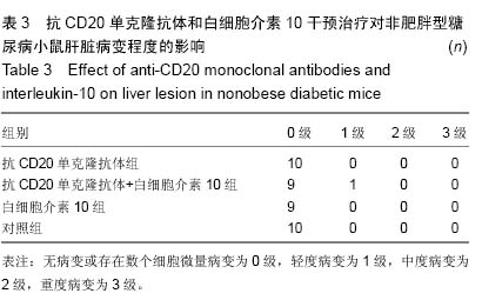
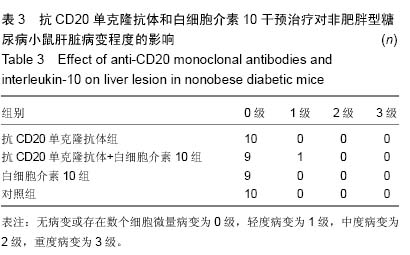
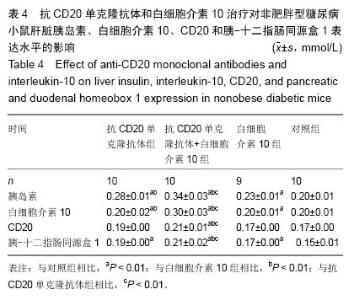
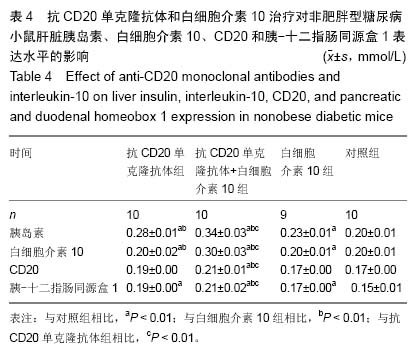
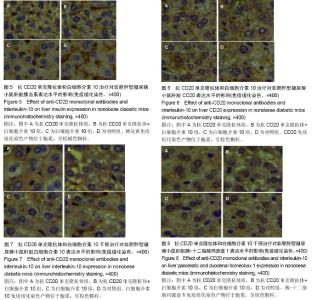
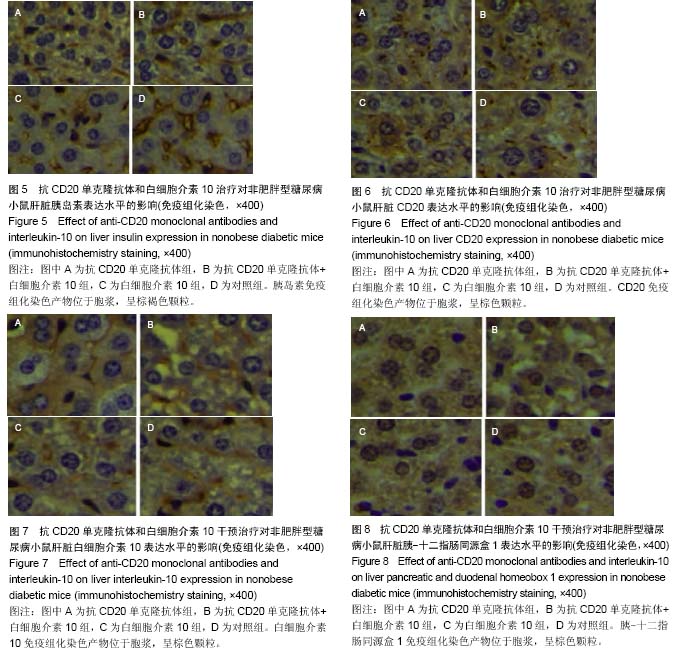
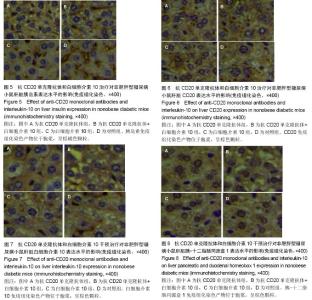
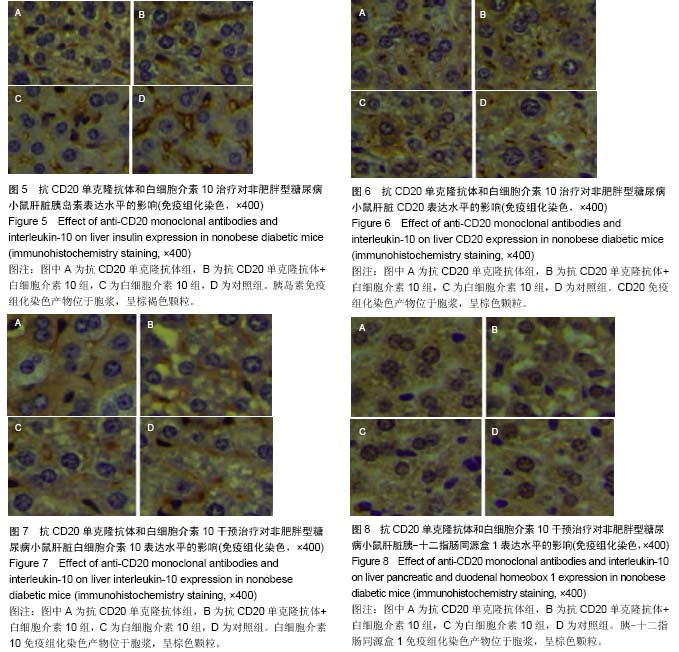
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (27): 4371-4378.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.27.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of interleukin-10 gene on liver pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 expression in nonobese diabetic mice
Yu Shu-feng, Ren An-xia, Zhang Li-juan, Li Tang
- Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
-
Online:2015-06-30Published:2015-06-30 -
Contact:Li Tang, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Yu Shu-feng, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81170762
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Shu-feng, Ren An-xia, Zhang Li-juan, Li Tang. Effect of interleukin-10 gene on liver pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 expression in nonobese diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(27): 4371-4378.
share this article
| [1] Song KH, Ko SH, Ahn YB, et al. In vitro transdifferentiation of adult pancreatic acinar cells into insulin-expressing cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;316(4):1094-1100. [2] Melloul D. Transcription factors in islet development and physiology: role of PDX-1 in beta-cell function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1014:28-37. [3] Sander M, Neubüser A, Kalamaras J, et al. Genetic analysis reveals that PAX6 is required for normal transcription of pancreatic hormone genes and islet development. Genes Dev. 1997;11(13):1662-1673. [4] Prado CL, Pugh-Bernard AE, Elghazi L, et al. Ghrelin cells replace insulin-producing beta cells in two mouse models of pancreas development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101(9): 2924-2929. [5] Heller RS, Jenny M, Collombat P, et al. Genetic determinants of pancreatic epsilon-cell development. Dev Biol. 2005;286(1): 217-224. [6] Pedersen JK, Nelson SB, Jorgensen MC, et al. Endodermal expression of Nkx6 genes depends differentially on Pdx1. Dev Biol. 2005;288(2):487-501. [7] Jacquemin P, Yoshitomi H, Kashima Y, et al. An endothelial- mesenchymal relay pathway regulates early phases of pancreas development. Dev Biol. 2006;290(1):189-199. [8] Ferber S, Halkin A, Cohen H, et al. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 induces expression of insulin genes in liver and ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Nat Med. 2000;6(5):568-572. [9] Ferber S, Halkin A, Cohen H, et al. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 induces expression of insulin genes in liver and ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Nat Med. 2000;6(5):568-572. [10] Kojima H, Nakamura T, Fujita Y, et al. Combined expression of pancreatic duodenal homeobox 1 and islet factor 1 induces immature enterocytes to produce insulin. Diabetes. 2002; 51(5): 1398-1408. [11] Yoshida S, Kajimoto Y, Yasuda T, et al. PDX-1 induces differentiation of intestinal epithelioid IEC-6 into insulin-producing cells. Diabetes. 2002;51(8):2505-2513. [12] Noguchi H, Kaneto H, Weir GC, et al. PDX-1 protein containing its own antennapedia-like protein transduction domain can transduce pancreatic duct and islet cells. Diabetes. 2003;52(7):1732-1737. [13] Taniguchi H, Yamato E, Tashiro F, et al. beta-cell neogenesis induced by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery of transcription factor pdx-1 into mouse pancreas. Gene Ther. 2003;10(1):15-23. [14] Ber I, Shternhall K, Perl S, et al. Functional, persistent, and extended liver to pancreas transdifferentiation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(34):31950-31957. [15] Tang DQ, Cao LZ, Burkhardt BR, et al. In vivo and in vitro characterization of insulin-producing cells obtained from murine bone marrow. Diabetes. 2004;53(7):1721-1732. [16] Miyatsuka T, Kaneto H, Kajimoto Y, et al. Ectopically expressed PDX-1 in liver initiates endocrine and exocrine pancreas differentiation but causes dysmorphogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;310(3):1017-1025. [17] Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Miyatsuka T, et al. PDX-1/VP16 fusion protein, together with NeuroD or Ngn3, markedly induces insulin gene transcription and ameliorates glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 2005;54(4):1009-1022. [18] Cao LZ, Tang DQ, Horb ME, et al. High glucose is necessary for complete maturation of Pdx1-VP16-expressing hepatic cells into functional insulin-producing cells. Diabetes. 2004; 53(12):3168-3178. [19] Tang DQ, Shun L, Koya V, et al. Genetically reprogrammed, liver-derived insulin-producing cells are glucose-responsive, but susceptible to autoimmune destruction in settings of murine model of type 1 diabetes. Am J Transl Res. 2013; 5(2):184-199. [20] O'Neill SK, Shlomchik MJ, Glant TT, et al. Antigen-specific B cells are required as APCs and autoantibody-producing cells for induction of severe autoimmune arthritis. J Immunol. 2005; 174(6):3781-3788. [21] Goetz M, Atreya R, Ghalibafian M, et al. Exacerbation of ulcerative colitis after rituximab salvage therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007;13(11):1365-1368. [22] Zhang YC, Pileggi A, Agarwal A, et al. Adeno-associated virus-mediated IL-10 gene therapy inhibits diabetes recurrence in syngeneic islet cell transplantation of NOD mice. Diabetes. 2003;52(3):708-716. [23] Kikutani H, Makino S. The murine autoimmune diabetes model: NOD and related strains. Adv Immunol. 1992;51: 285-322. [24] Bach JF. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus as an autoimmune disease. Endocr Rev. 1994;15(4):516-542. [25] Phillips JM, Parish NM, Raine T, et al. Type 1 diabetes development requires both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and can be reversed by non-depleting antibodies targeting both T cell populations. Rev Diabet Stud. 2009;6(2):97-103. [26] Silveira PA, Johnson E, Chapman HD, et al. The preferential ability of B lymphocytes to act as diabetogenic APC in NOD mice depends on expression of self-antigen-specific immunoglobulin receptors. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32(12):3657-3666. [27] Hulbert C, Riseili B, Rojas M, et al. B cell specificity contributes to the outcome of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 2001;167(10):5535-5538. [28] Hussain S, Delovitch TL. Intravenous transfusion of BCR-activated B cells protects NOD mice from type 1 diabetes in an IL-10-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2007; 179(11):7225-7232. [29] Tedder TF, Boyd AW, Freedman AS, et al. The B cell surface molecule B1 is functionally linked with B cell activation and differentiation. J Immunol. 1985;135(2):973-979. [30] 何凌,王燕,余绮玲,等.雷公藤单体T4对胰岛 细胞免疫保护作用的机制探讨[J].热带医学杂志,2010,10(7):773-776. [31] Mathieu C, Waer M, Laureys J, et al. Prevention of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice by 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3. Diabetologia. 1994;37(6):552-558. [32] Xiu Y, Wong CP, Bouaziz JD, et al. B lymphocyte depletion by CD20 monoclonal antibody prevents diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice despite isotype-specific differences in Fc gamma R effector functions. J Immunol. 2008;180(5):2863-2875. [33] Pescovitz MD, Greenbaum CJ, Krause-Steinrauf H, et al. Rituximab, B-lymphocyte depletion, and preservation of beta-cell function. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(22):2143-2152. [34] Minard-Colin V, Xiu Y, Poe JC, et al. Lymphoma depletion during CD20 immunotherapy in mice is mediated by macrophage FcgammaRI, FcgammaRIII, and FcgammaRIV. Blood. 2008;112(4):1205-1213. [35] Kojima H, Fujimiya M, Matsumura K, et al. NeuroD- betacellulin gene therapy induces islet neogenesis in the liver and reverses diabetes in mice. Nat Med. 2003;9(5):596-603. [36] Yechoor V, Liu V, Espiritu C, et al. Neurogenin3 is sufficient for transdetermination of hepatic progenitor cells into neo-islets in vivo but not transdifferentiation of hepatocytes. Dev Cell. 2009;16(3):358-373. [37] Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Miyatsuka T, et al. PDX-1/VP16 fusion protein, together with NeuroD or Ngn3, markedly induces insulin gene transcription and ameliorates glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 2005;54(4):1009-1022. [38] Wang AY, Ehrhardt A, Xu H, et al. Adenovirus transduction is required for the correction of diabetes using Pdx-1 or Neurogenin-3 in the liver. Mol Ther. 2007;15(2):255-263. [39] Jacquemin P, Lemaigre FP, Rousseau GG. The Onecut transcription factor HNF-6 (OC-1) is required for timely specification of the pancreas and acts upstream of Pdx-1 in the specification cascade. Dev Biol. 2003;258(1):105-116. [40] Fujitani Y, Fujitani S, Boyer DF, et al. Targeted deletion of a cis-regulatory region reveals differential gene dosage requirements for Pdx1 in foregut organ differentiation and pancreas formation. Genes Dev. 2006;20(2):253-266. [41] Jensen JN, Cameron E, Garay MV, et al. Recapitulation of elements of embryonic development in adult mouse pancreatic regeneration. Gastroenterology. 2005;128(3):728-741. [42] Miyatsuka T, Kaneto H, Shiraiwa T, et al. Persistent expression of PDX-1 in the pancreas causes acinar-to-ductal metaplasia through Stat3 activation. Genes Dev. 2006;20(11):1435-1440. [43] Kaneto H, Matsuoka TA, Nakatani Y, et al. A crucial role of MafA as a novel therapeutic target for diabetes. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(15):15047-15052. [44] Imai J, Katagiri H, Yamada T, et al. Constitutively active PDX1 induced efficient insulin production in adult murine liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;326(2):402-409. [45] Kulkarni RN, Jhala US, Winnay JN, et al. PDX-1 haploinsufficiency limits the compensatory islet hyperplasia that occurs in response to insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(6):828-836. [46] Holland AM, Góñez LJ, Naselli G, et al. Conditional expression demonstrates the role of the homeodomain transcription factor Pdx1 in maintenance and regeneration of beta-cells in the adult pancreas. Diabetes. 2005;54(9):2586- 2595. [47] Noguchi H, Bonner-Weir S, Wei FY, et al. BETA2/NeuroD protein can be transduced into cells due to an arginine- and lysine-rich sequence. Diabetes. 2005;54(10):2859-2866. [48] Li SW, Koya V, Li Y, et al. Pancreatic duodenal homeobox 1 protein is a novel beta-cell-specific autoantigen for type I diabetes. Lab Invest. 2010;90(1):31-39. [49] Mingozzi F, Liu YL, Dobrzynski E, et al. Induction of immune tolerance to coagulation factor IX antigen by in vivo hepatic gene transfer. J Clin Invest. 2003;111(9):1347-1356. [50] Dobrzynski E, Mingozzi F, Liu YL, et al. Induction of antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell anergy and deletion by in vivo viral gene transfer. Blood. 2004;104(4):969-977. [51] Martino AT, Nayak S, Hoffman BE, et al. Tolerance induction to cytoplasmic beta-galactosidase by hepatic AAV gene transfer: implications for antigen presentation and immunotoxicity. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6376. [52] Shternhall-Ron K, Quintana FJ, Perl S, et al. Ectopic PDX-1 expression in liver ameliorates type 1 diabetes. J Autoimmun. 2007;28(2-3):134-142. [53] Uchida J, Hamaguchi Y, Oliver JA, et al. The innate mononuclear phagocyte network depletes B lymphocytes through Fc receptor-dependent mechanisms during anti-CD20 antibody immunotherapy. J Exp Med. 2004;199(12):1659-1669. [54] Zhang C, Moriguchi T, Kajihara M, et al. MafA is a key regulator of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(12):4969-4976. [55] Noguchi H, Matsushita M, Matsumoto S, et al. Mechanism of PDX-1 protein transduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;332(1):68-74. [56] Heremans Y, Van De Casteele M, in't Veld P, et al. Recapitulation of embryonic neuroendocrine differentiation in adult human pancreatic duct cells expressing neurogenin 3. J Cell Biol. 2002;159(2):303-312. [57] Domínguez-Bendala J, Klein D, Ribeiro M, et al. TAT-mediated neurogenin 3 protein transduction stimulates pancreatic endocrine differentiation in vitro. Diabetes. 2005; 54(3):720-726. [58] Samaras SE, Cissell MA, Gerrish K, et al. Conserved sequences in a tissue-specific regulatory region of the pdx-1 gene mediate transcription in Pancreatic beta cells: role for hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 beta and Pax6. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(13):4702-4713. [59] Samaras SE1, Zhao L, Means A, et al. The islet beta cell-enriched RIPE3b1/Maf transcription factor regulates pdx-1 expression. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(14):12263-12270. |
| [1] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [2] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [3] | Liu Yang, Gong Yi, Fan Wei. Anti-hepatoma activity of targeted Pluronic F127/formononetin nanocomposite system in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 526-531. |
| [4] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [5] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Chen Song, He Yuanli, Xie Wenjia, Zhong Linna, Wang Jian. Advantages of calcium phosphate nanoparticles for drug delivery in bone tissue engineering research and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3565-3570. |
| [8] | Qin Yanchun, Rong Zhen, Jiang Ruiyuan, Fu Bin, Hong Xiaohua, Mo Chunmei. Chinese medicine compound preparation inhibits proliferation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells and the expression of stemness transcription factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3016-3023. |
| [9] | Gan Zhoujie, Pei Xibo. Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles in tumor therapy: superiority of nanoparticles in accumulation and drug release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2562-2568. |
| [10] | Zhou Xiaohong, Li Bocun, Li Jia, Peng Rui. Relationship between joint function and circadian rhythm in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis undergoing acupuncture and moxibustion at acupoints selected based on liver theory [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2192-2198. |
| [11] | Li Liqiang, Jiao Longxing, Zhang Wu, Yan Wentao, Li Jian, Li Minghao. Effect of immature dendritic cells derived from bone marrow on rejection of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2025-2029. |
| [12] | Ye Quanying, Chen Qisheng, Li Yanwen, Wang Ting, Chen Xiaoyan, Yue Yun. Effect of cassia seed aqueous extract on blood pressure level in N-nitro-L-arginine-methyl ester induced hypertensive rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1705-1711. |
| [13] | Hu Sheng, Yuan Haiyan, Hu Meng, Jin Shanhu. Effects of moderate treadmill exercise on alpha-smooth muscle actin and type IV collagen in the liver of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1723-1727. |
| [14] | Ma Minghe, Niu Yi . Thymosin alpha1 protects against liver injury in rats with zymosan-induced multiple organ failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1753-1758. |
| [15] | Fan Xuemin, Fang Shanbao, Chen Zhixing, Mo Shuixue. Status and application prospects of nano-clay Laponite [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1622-1627. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||