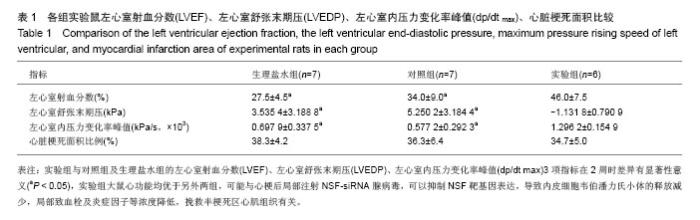
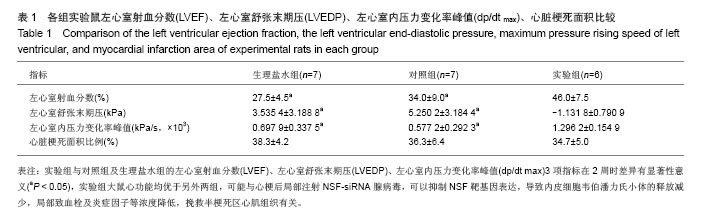
| [1]Into T, Kanno Y, Dohkan J,et al.Pathogen recognition by Toll-like receptor 2 activates Weibel-Palade body exocytosis in human aortic endothelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2007;282(11):8134-8141.
[2]Yamakuchi M, Kirkiles-Smith NC, Ferlito M,et al.Antibody to human leukocyte antigen triggers endothelial exocytosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(4):1301-1306.
[3]Lowenstein CJ, Tsuda H. N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor: a redox sensor in exocytosis.Biol Chem. 2006;387(10-11):1377-1383.
[4]Lowenstein CJ, Morrell CN, Yamakuchi M.Regulation of Weibel-Palade body exocytosis.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2005;15(8):302-308.
[5]Yang SX, Yan J, Deshpande SS,et al.Rac1 regulates the release of Weibel-Palade Bodies in human aortic endothelial cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2004;117(8):1143-1150.
[6]杨水祥,魏晓菲,崔淯夏,等.RNA干扰抑制内皮细胞韦伯潘力氏小体的释放[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2012,14(6): 630-634.
[7]Ming X.Cellular delivery of siRNA and antisense oligonucleotides via receptor-mediated endocytosis.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(4):435-449.
[8]吕铁伟,田杰,江德勤,等.急性心肌梗塞动物模型的建立[J].中国比较医学杂志,2004,14(3):166-169.
[9]Sioud M.Promises and challenges in developing RNAi as a research tool and therapy.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;703:173-187.
[10]Shimizu H, Fujita T.New short interfering RNA-based therapies for glomerulonephritis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011; 7(7):407-415.
[11]Burnett JC, Rossi JJ, Tiemann K.Current progress of siRNA/shRNA therapeutics in clinical trials.Biotechnol J. 2011; 6(9):1130-1146.
[12]Tesz GJ, Aouadi M, Prot M,et al.Glucan particles for selective delivery of siRNA to phagocytic cells in mice.Biochem J. 2011; 436(2):351-362.
[13]Jeong JH, Kim SH, Lee M,et al.Non-viral systemic delivery of Fas siRNA suppresses cyclophosphamide-induced diabetes in NOD mice.J Control Release. 2010;143(1):88-94.
[14]Janson CG, Romanova LG, Leone P,et al.Comparison of Endovascular and Intraventricular Gene Therapy With Adeno-Associated Virus-α-L-Iduronidase for Hurler Disease. Neurosurgery. 2014;74(1):99-111.
[15]Hsu PY, Yang YW.Gene delivery via the hybrid vector of recombinant adeno-associated virus and polyethylenimine. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014;52:62-68.
[16]DeVincenzo J, Lambkin-Williams R, Wilkinson T,et al.A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of an RNAi-based therapy directed against respiratory syncytial virus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(19):8800-8805.
[17]Matsushita K, Morrell CN, Mason RJ,et al.Hydrogen peroxide regulation of endothelial exocytosis by inhibition of N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor.J Cell Biol. 2005;170(1):73-79.
[18]Cipriano DJ, Jung J, Vivona S,et al.Processive ATP-driven substrate disassembly by the N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) molecular machine.J Biol Chem. 2013;288(32): 23436-23445.
[19]Lowenstein CJ, Morrell CN, Yamakuchi M.Regulation of Weibel-Palade body exocytosis.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2005;15(8):302-308.
[20]Morrell CN, Matsushita K, Lowenstein CJ. A novel inhibitor of N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor decreases leukocyte trafficking and peritonitis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;314(1):155-161.
[21]Liu Y, Cheng K, Gong K,et al.Pctaire1 phosphorylates N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein: implications in the regulation of its hexamerization and exocytosis.J Biol Chem. 2006;281(15):9852-9858. |