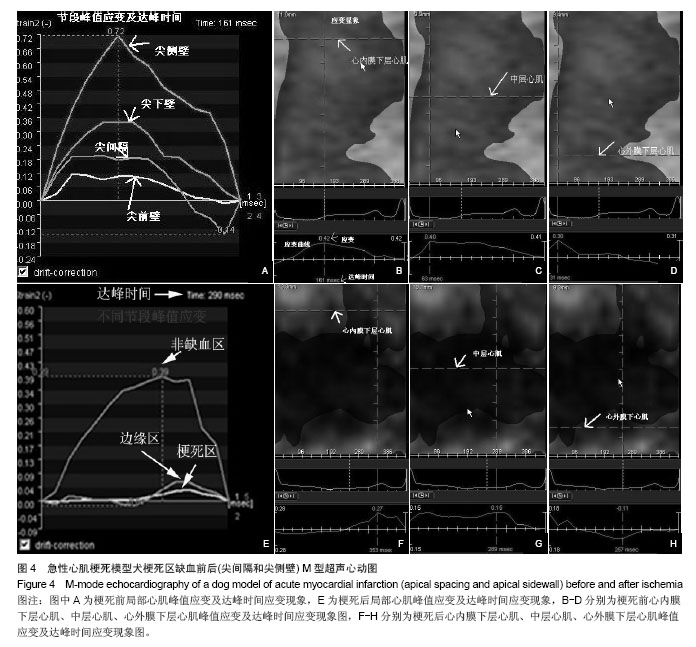
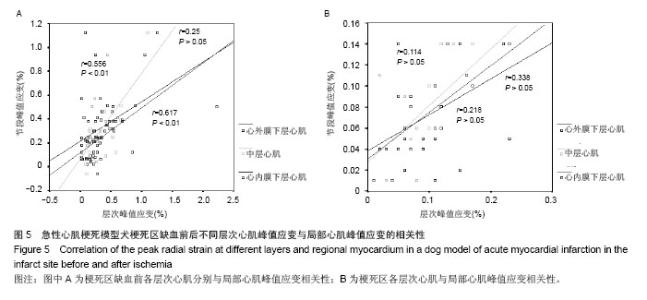
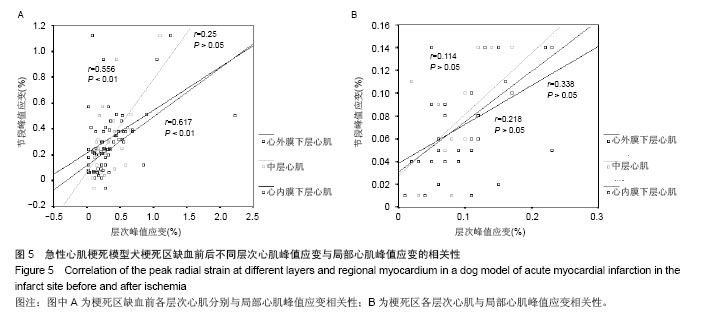
| [1]Lima JA, Judd RM, Bazille A, et al. Regional heterogeneity of human myocardial infarcts demonstrated by contrast-enhanced MRI. Potential mechanisms. Circulation. 1995;92(5):1117-1125.
[2]Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, et al. Recommendations for quantitation of the left ventricle by two-dimensional echocardiography. American Society of Echocardiography Committee on Standards, Subcommittee on Quantitation of Two-Dimensional Echocardiograms. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1989;2(5):358-367.
[3]Erbel R, Brennecke R, Goerge G, et al. Possibilities and limits of 2-dimensional echocardiography in quantitative image analysis. Z Kardiol. 1989;78 Suppl 7:131-142.
[4]Hong Y, Orihashi K, Oka Y. Intraoperative monitoring of regional wall motion abnormalities for detecting myocardial ischemia by transesophageal echocardiography. Echocardiography. 1990;7(3):323-332.
[5]Mangion JR. Right ventricular imaging by two-dimensional and three-dimensional echocardiography. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2010;25(5):423-429.
[6]Crawford MH. How reliable are echocardiographic studies in the diagnosis of myocardial dysfunction? Cardiovasc Clin. 1983;13(1):51-63.
[7]Sugishita Y, Koseki S, Matsuda M, et al. Dissociation between regional myocardial dysfunction and ECG changes during myocardial ischemia induced by exercise in patients with angina pectoris. Am Heart J. 1983;106(1 Pt 1):1-8.
[8]Penkov N, Sirakova V. Echo-apex-ECG-phonocardiographic control of left ventricular diastolic function in patients with unstable angina pectoris and other forms of ischemic heart disease. Vutr Boles. 1989;28(1):15-21.
[9]Dagianti A, Agati L, Arata L, et al. The modern cardiologist between technology and clinical medicine in the evaluation of ischemic cardiopathy. Cardiologia. 1985;30(9):759-799.
[10]Ishibashi M, Yasuda T, Tamaki N, Evaluation of symptomatic vs. silent myocardial ischemia using the ambulatory left ventricular function monitor (VEST). Isr J Med Sci. 1989;25(9): 532-538.
[11]Ianovski GV, Terzov AI, Belonozhko AG, et al. Differential evaluation of signs of myocardial ischemia during exertion in patients with ischemic heart disease. Vrach Delo. 1983;(10): 18-21.
[12]Smiseth OA, Ihlen H. Strain rate imaging: why do we need it? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42(9):1584-1586.
[13]Galderisi M, Mele D, Marino PN, et al. Quantitation of stress echocardiography by tissue Doppler and strain rate imaging: a dream come true? Ital Heart J. 2005;6(1):9-20.
[14]Hoffmann R. Tissue Doppler and innovative myocardial-deformation imaging techniques for assessment of myocardial viability. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2006;21(5):438-442.
[15]Perk G, Tunick PA, Kronzon I. Non-Doppler two-dimensional strain imaging by echocardiography--from technical considerations to clinical applications. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007;20(3):234-243.
[16]Friedberg MK, Mertens L. Tissue velocities, strain, and strain rate for echocardiographic assessment of ventricular function in congenital heart disease. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2009;10(5): 585-593.
[17]Urheim S, Edvardsen T, Torp H, et al. Myocardial strain by Doppler echocardiography. Validation of a new method to quantify regional myocardial function. Circulation. 2000;102 (10):1158-1164.
[18]施新猷.医学动物实验方法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1980.
[19]褚俊,徐美清,何华,等.犬急性心肌梗死模型制备的方法学研究[J].安徽医学, 2002,23(2):6-8.
[20]钱蕴秋.冠心病的超声心动图诊断[J].中国超声学杂志,1992,8(2): 84.
[21]陈永洪,杨俊华.二维超声心动图与心电图在急性心肌梗死左前降支病变部位判定的应用比较[J].实用临床医学杂志,2006, 7(9): 25-26.
[22]魏广和,李清贤,李桂玲,等.冠心病无创检查与冠状动脉造影诊断价值的对比分析[J].济宁医学院学报,2004,27(3):28-29.
[23]姚艳,黄从新,陈高.Cav1.2和Cav3.1在犬左心室不同部位中表达的比较[J].第四军医大学学报,2006,27(19):1752-1754.
[24]Antzelevitch C, Sun ZQ, Zhang ZQ, et al. Cellular and ionic mechanisms underlying erythromycin-induced long QT intervals and torsade de pointes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996; 28(7):1836-1848.
[25]Kuroda T, Seward JB, Rumberger JA, et al. Left ventricular volume and mass: Comparative study of two-dimensional echocardiography and ultrafast computed tomography. Echocardiography. 1994;11(1):1-9.
[26]Spotnitz HM, Spotnitz WD, Cottrell TS, et al. Cellular basis for volume related wall thickness changes in the rat left ventricle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1974;6(4):317-331.
[27]Costa KD, Takayama Y, McCulloch AD, et al. Laminar fiber architecture and three-dimensional systolic mechanics in canine ventricular myocardium. Am J Physiol. 1999;276 (2 Pt 2):H595-607.
[28]Wu MT, Tseng WY, Su MY, et al. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging mapping the fiber architecture remodeling in human myocardium after infarction: correlation with viability and wall motion. Circulation. 2006;114(10):1036-1045.
[29]Chen J, Song SK, Liu W, et al. Remodeling of cardiac fiber structure after infarction in rats quantified with diffusion tensor MRI. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285(3): H946-954.
[30]Wu EX, Wu Y, Nicholls JM, et al. MR diffusion tensor imaging study of postinfarct myocardium structural remodeling in a porcine model. Magn Reson Med. 2007;58(4):687-695.
[31]Voigt JU, Lindenmeier G, Exner B, et al. Incidence and characteristics of segmental postsystolic longitudinal shortening in normal, acutely ischemic, and scarred myocardium. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003;16(5): 415-423.
[32]Skulstad H, Edvardsen T, Urheim S, et al. Postsystolic shortening in ischemic myocardium: active contraction or passive recoil? Circulation. 2002;106(6):718-724.
[33]阮霞,舒先红,潘翠珍,等.左心室壁收缩后收缩在正常、缺血和梗死心肌中的分布及特征[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2007,16(5): 377-381.
[34]张涓,吴雅峰,曾定尹,等.定量组织速度成像技术评价心肌梗死患者局部心肌的收缩后收缩[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2003,12(10): 585-589.
[35]Rynning SE, Hexeberg E, Birkeland S, et al. Non-uniform recovery of performance in stunned myocardium evaluated by two-dimensional sonomicrometry. Acta Physiol Scand. 1993; 149(4): 441-449. |