Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5233-5239.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1263
Previous Articles Next Articles
Systematic reviews of the accuracy of musculoskeletal ultrasound in the diagnosis of lateral epicondylalgia
Wang Yuan, Nie Fang, Wang Ting, Li Yan, Xu Ping
- Department of Ultrasound, the Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China
-
Online:2019-11-18Published:2019-11-18 -
Contact:Xu Ping, Chief physician, Associate professor, Department of Ultrasound, the Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Wang Yuan, Master, Attending physician, Department of Ultrasound, the Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yuan, Nie Fang, Wang Ting, Li Yan, Xu Ping. Systematic reviews of the accuracy of musculoskeletal ultrasound in the diagnosis of lateral epicondylalgia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5233-5239.
share this article
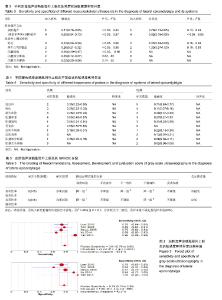
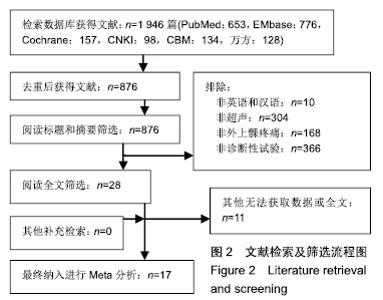
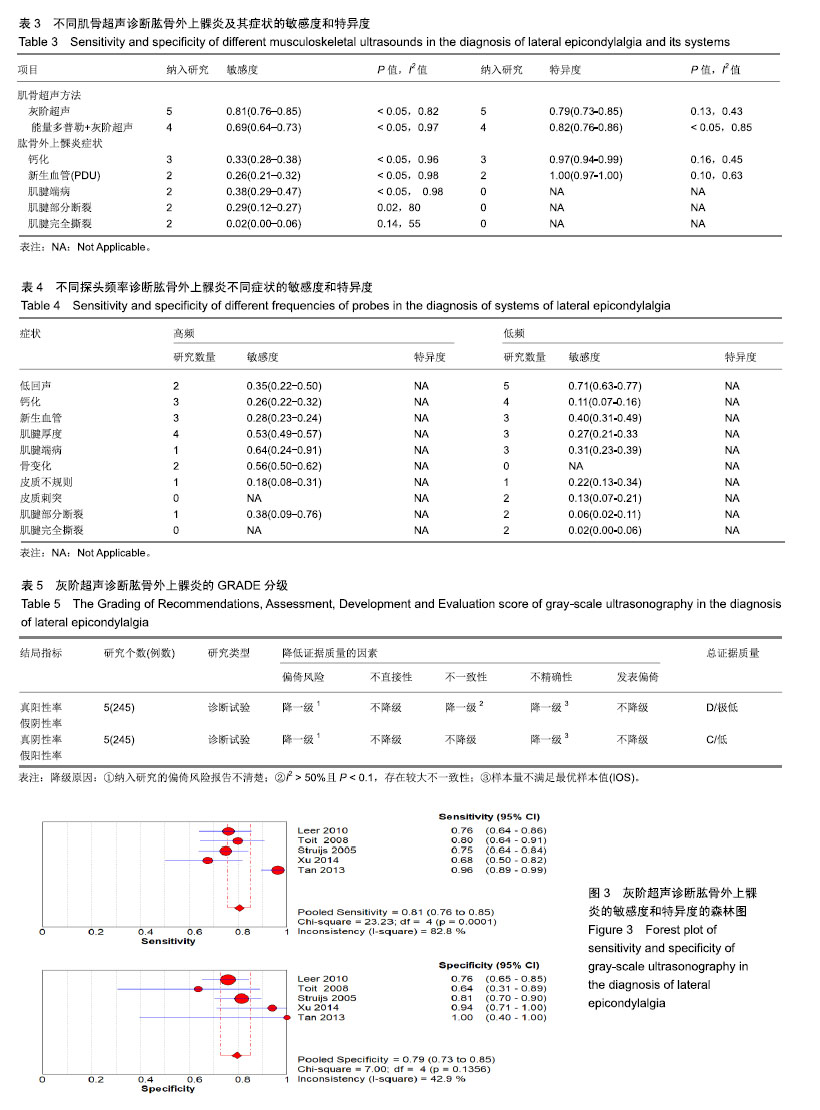
2.3 系统评价分析结果 由于纳入研究诊断方法、参考标准等差别较大,因此作者直接进行了亚组分析。亚组分析主要根据肱骨外上髁炎的症状、肌骨超声的方法以及超声频率进行。 2.3.1 肌骨超声的方法 灰阶超声诊断肱骨外上髁炎纳入5篇研究,其敏感度和特异度分别为0.81(0.76-0.85)和0.79(0.73-0.85),森林图见图3;而能量多普勒超声联合灰阶超声诊断肱骨外上髁炎纳入了4篇研究,其敏感度和特异度分别为0.69(0.64-0.73)和0.82(0.76-0.86),详见表3。 2.3.2 超声对肱骨外上髁炎不同症状的诊断 超声对肱骨外上髁炎钙化和新生血管诊断的敏感度均较低,但诊断特异度较高,分别为0.97(0.94-0.99)和1.00(0.97-1.00);而对于肌腱原因导致的肱骨外上髁炎(如肌腱端病、肌腱断裂等),其敏感度较差,详见表3。 2.3.3 不同探头频率 纳入的研究只能获取到高频超声对诊断不同肱骨外上髁炎症状时的敏感度,其中,频率偏高的超声对肌腱末端病[0.64(0.24-0.91)]和骨质变化[0.56(0.50-0.62)]有较好的敏感度;频率偏低的超声对表现为低回声的肱骨外上髁炎有较好的敏感度0.71(0.63- 0.77);对于其他表现的肱骨外上髁炎,其诊断敏感度较差,详见表4。 2.3.4 主要结局的GRADE分级 对灰阶超声诊断肱骨外上髁炎的结局进行了GRADE分级,结果详见表5。"
| [1]Kwak SH, Lee SJ, Jeong HS, et al. Subtle elbow instability associated with lateral epicondylitis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):136.[2]代飞,向明.肱骨外上髁炎病因与发病机制的研究进展[J].中华肩肘外科电子杂志,2017,5(2):142-144.[3]Arik HO, Kose O, Guler F, et al. Injection of autologous blood versus corticosteroid for lateral epicondylitis: a randomised controlled study. Orthop Surg. 2014;22(3):333-337.[4]Altinisik J, Meric G, Erduran M, et al. The BstUI and DpnII variants of the COL5A1 gene are associated with tennis elbow. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(7):1784-1789.[5]Bao SS, Kapellusch JM, Merryweather AS, et al. Impact of Work Organizational Factors on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Epicondylitis. J Occup Environ Med. 2016;58(8):760-764. [6]López-de-Celis C, Barra-López ME, González-Rueda V, et al.Effectiveness of diacutaneous fibrolysis for the treatment of chronic lateral epicondylalgia: a randomized clinical trial.Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(5):644-653.[7]Shillito M, Soong M, Martin N. Radiographic and Clinical Analysis of Lateral Epicondylitis. J Hand Surg Am. 2017;42(6): 436-442.[8]赵亮,孔令跃,任逸众.等.肱骨外上髁炎研究进展[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2017,23(10):904-907.[9]Geoffroy P, Yaffe MJ, Rohan I.Diagnosing and treating lateral epicondylitis.Can Fam Physician. 1994;40:73-78.[10]Lebrun C: What are the best diagnostic criteria for lateral epicondylitis?//Evidence-based Orthopaedics: the Best Answers to Clinical Questions. Edited by Wright JG. London: Elsevier Health Sciences; 2008:148-157.[11]Matteo A, De Angelis R, Cipolletta E, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus arthropathy: the sonographic perspective. Lupus. 2018;27(5):794-801.[12]Hamper UM, Dejong MR, Caskey CI, et al. Power Doppler imaging: clinical experience and correlation with color Doppler US and other imaging modalities. Radiographics. 1997;17(2): 499-513.[13]Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):529-536.[14]陈耀龙,姚亮,杜亮,等. GRADE在诊断准确性试验系统评价中应用的原理、方法、挑战及发展趋势[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2014, 14(11):1402-1406.[15]姚亮,陈耀龙,杜亮,等. GRADE在诊断准确性试验系统评价中应用的实例解析[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2014,14(11):1407-1412.[16]陈昊,王艳,胡轩铭,等. GRADE pro GDT在干预性系统评价证据质量分级中的应用[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2015,15(5): 600-606.[17]De Zordo T, Lill SR, Fink C, et al. Real-time sonoelastography of lateral epicondylitis: comparison of findings between patients and healthy volunteers. Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:180-185.[18]Noh KH, Moon YL, Jacir AM, et al. Sonographic probe- induced tenderness for lateral epicondylitis: an accurate technique to confirm the location of the lesion. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2010; 18:836-839.[19]Struijs PA, Spruyt M, Assendelft WJ, et al. The predictive value of diagnostic sonography for the effectiveness of conservative treatment of tennis elbow. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2005;185:1113-1118.[20]Obradov M, Anderson PG. Ultrasonographic findings for chronic lateral epicondylitis. JBR-BTR 2012;95:66-70.[21]Toprak U, Baskan B, Ustuner E, et al. Common extensor tendon thickness measurements at the radiocapitellar region in diagnosis of lateral elbow tendinopathy. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2012;18:566-570.[22]Lee MH, Cha JG, Jin W, et al. Utility of sonographic measurement of the common tensor tendon in patients with lateral epicondylitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2011;196: 1363-1367.[23]Zeisig E, Ohberg L, Alfredson H. Extensor origin vascularity related to pain in patients with tennis elbow. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2006;14:659-663.[24]Connell D, Burke F, Coombes P, et al. Sonographic examination of lateral epicondylitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:777-782.[25]Du Toit C, Stieler M, Saunders R, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of power Doppler ultrasound in patients with chronic tennis elbow. Br J Sports Med.2008;42:872-876.[26]Levin D, Nazarian LN, Miller TT, et al. Lateral epicondylitis of the elbow: US findings. Radiology. 2005; 237:230-234.[27]Lin J, Fessell D, Jacobson J, et al. An illustrated tutorial of musculoskeletal ultrasonography: part 1, introduction and general principles. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2000;175:637-645.[28]Miller TT, Shapiro MA, Schultz E, et al. Comparison of sonography and MRI for diagnosing epicondylitis. J Clin Ultrasound.2002;30:193-202.[29]Zeisig E, Fahlstrom M, Ohberg L, et al. A two-year sonographic follow-up after intratendinous injection therapy in patients with tennis elbow. Br J Sports Med.2010; 44:584-587.[30]Tarhan S, Unlu S, Ovali Z, et al.Value of ultrasonography on diagnosis and assessment of pain and grip strength in patients with lateral epicondylitis. Turk J Rheumatol.2009; 24:123-130.[31]Maffulli N, Khan KM, Puddu G. Overuse tendon conditions: time to change a confusing terminology. Arthroscopy.1998;14: 840-843.[32]许华宁,殷立平,杨益虎,等. 彩色多普勒超声对肱骨外上髁炎的诊断价值[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2014,8(15):14-16.[33]谭庆亭,傅先水,柳曦,等. 超声对网球肘的诊断价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2013,29(10):924-928.[34]Valentin C Dones III, Karen Grimmer, Kerry Thoirs, et al. The diagnostic validity of musculoskeletal ultrasound in lateral epicondylalgia: a systematic review. BMC Medical Imaging. 2014; 14:10.[35]李智尧,张磊. 网球肘研究新进展[J]. 中国骨伤, 2011, 24(11): 969-972.[36]Clarke AW, Ahmad M, Curtis M, et al. Lateral elbow tendinopathy: correlation of ultrasound findings with pain and functional disability. Am J Sports Med.2010;38(6):1209-1214.[37]傅先水,刘吉斌,王金锐.等. 肌肉骨关节超声检查规范(草案)-美国超声医学会(AIUM)美国放射学会(ACR)制订[J]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版),2010,7(1):141-152. |
| [1] | Xiang Haibin, Li Xinxia, Liang Qiuzhen, Song Xinghua. Specific bone-targeting nanoscale drug delivery system: advantages and clinical applicability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 612-618. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinhuan, Yuan Weiqu, Chen Chen, Huang Xingxian, Yu Haibo. Different acupuncture therapies for treating periarthritis of the shoulder: overview of systematic reviews and network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5723-5732. |
| [3] | Zhao Jianfeng, Geng Yu, Chen Qianbo, Yang Jinghui, Li Yan. Changes in insulin resistance and inflammatory factors in cataract patients with glaucoma after phacoemulsification and trabeculectomy: a self-controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1750-1755. |
| [4] | Wang Changbing1, 2, Lu Mingfeng2, He Lilei2, Xing Jisi2, Xu Ting2, Zhao Lilian2, Liu Xiaofang1 . Diagnosis and treatment of early joint infection after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5592-5599. |
| [5] | Du Jianhong, Fan Chunshui, Du Yuelian, Sun Xiaoyu, Wang Qingfeng. Preparation, sustained release and anti-tumor characteristics of hydroxypropyl chitosan/heparin nano-drug system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3536-3541. |
| [6] | Hu Xiaoli, Gu Ying, Cai Yan, Xie Jin, Liu Chan. Musculoskeletal ultrasound evaluates the pathological features and inflammatory lesions of rheumatoid finger arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(20): 3182-3187. |
| [7] | Li Jingjing, Guo Xuan, Xie Jun, Huang Lei, Suo Jinrong, Fu Songtao. Preparation of agarose/gelatin/hyaluronic acid/extracellular matrix hydrogel and its property characterization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2900-2908. |
| [8] | Hu Xiaoli, Gu Ying, Cai Yan, Xie Jin, Liu Chan. Assessment of seven joint ultrasound score for early rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2523-2528. |
| [9] | Zhou Xuetian, Ma Yong, Guo Yang, Si Yuhao, Zong Yonggang, Zhong Chao. Application status and mechanism of musculoskeletal ultrasound in orthopedic diagnosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2573-2578. |
| [10] | Dai Jing, Chen Yan-bin, Chen Shan, Ren Jing, Li Kun-man, Yang Jun-ying . In vitro antibacterial effect of benzalkonium chloride on five common oral pathogens [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(18): 2849-2854. |
| [11] | Huang Kai-wei, Liu Hua, Bai Gang, Zhang Wen-jun. Early detection of left ventricular global longitudinal peak strain in the diagnosis of high-risk coronary atherosclerotic heart disease in elderly patients: study protocol for a single-center diagnostic trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(28): 4499-4504. |
| [12] | Li Wang-yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Hui, Li Ai-ling, Guo Ling. Influence of Gluma desensitizing agents on dentin bond strength: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(47): 7119-7126. |
| [13] | Wang Guo-qiang, Zhao Yan, Zhao Yan-tao, Ding Ying. Visual function of senile cataract patients after implantation of an aspheric multifocal versus an aspheric monofocal intraocular lens [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(21): 3171-3177. |
| [14] | Lv Quan, Yuan Jun, Cai Yi-qi, Liu Yi. Safety and stability of posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens implantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(39): 6386-6391. |
| [15] | Zhang Xiao-dong, Li Xiao-ping, Song Jie, Li Ying1, Li Hui. Effect of semi-permanent double-lumen central venous catheter on micro-inflammatory state in maintenance hemodialysis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(5): 913-919. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||