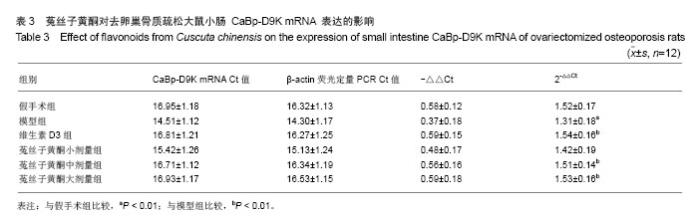
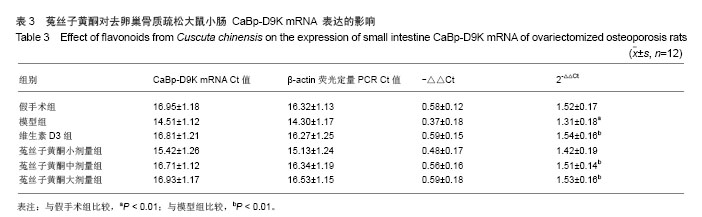
| [1]Belkacemi L, Züegel U, Steinmeyer A, et al. Calbindin-D28k (CaBP28k) identification and regulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhuman choriocarcinoma cell line JEG-3. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005;236(1-2):31-41.
[2]Baimbridge KG, Celio MR, Rogers JH. Calcium-binding proteins in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992;15(8): 303-308.
[3]Healy KD, Frahm MA, DeLuca HF. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 up-regulates the renal vitamin D receptor through indirect geneactivation and receptor stabilization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005;433(2):466-473.
[4]Ellison TI, Eckert RL, MacDonald PN. Evidence for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-independent transactivation by the vitamin D receptor: uncoupling the receptor and ligand in keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(15):10953-10962.
[5]武密山,赵素芝,任立中,等.密骨打老儿丸对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的影响[J].中成药,2013,35(1):5-11.
[6]金晓,李家实,阎文枚. 菟丝子黄酮成分的研究[J].中国中药杂志, 1992,17(5):292-294.
[7]武密山,赵素芝,任立中,等. 淫羊藿苷对去卵巢大鼠骨和下丘脑不同核团 ER β mRNA表达的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2011, 27(1):29-33.
[8]Parfitt AM, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, et al. Bone histomorphometry: standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units. Report of the ASBMR histomorphometry nomenclature committee. J Bone Miner Res. 1987;2(6):595-610.
[9]Hendy GN, Hruska K A, Mathew S, et al. New insights into mineral and skeletal regulation by active forms of vitamin D . Kidney Int. 2006;69(2):218-223.
[10]Cao LP, Bolt MJ, Wei M, et al. Regulation of calbindin-D9k expression by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) and parathyroid hormone in mouse primary renal tubular cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 2002;400(1):118-224.
[11]Siaw EK, Walters MR. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D-stimulated calmodulin binding proteins: a sustained effect on distal tubules. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002;282(1):77-84.
[12]Shearer MJ. Role of vitamin K and Gla proteins in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis and vascular calcification. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2000;3 (6):433-438.
[13]Chen J, Thomas HF, Jin H, et al.Expression of rat bone sialoprotein promoter in transgenic mice. J Bone Miner Res 1996;11(5):654-664.
[14]Nozaki K, Kadosawa T, Nishimura R, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3, recombinant human transforming growth factor-beta 1, and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 induce in vitro differentiation of canine osteosarcoma cells. J Vet Med Sci. 1999;61(6):649-656.
[15]Wasserman RH, Fullmer CS. Vitamin D and intestinal calcium transport: facts, speculations and hypotheses. J Nutr. 1995; 125(7):1971-1979.
[16]毛盟,王道聪.VD及CaBP-Ds在肠道和肾脏钙转运中的作用[J].国外医学•儿科学分册,1996,11(6):289.
[17]刘和娣,李恩,佟晓旭,等.补肾中药对骨质疏松大鼠CaBP-D9K基因及表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,1996,2(3):62-64. |