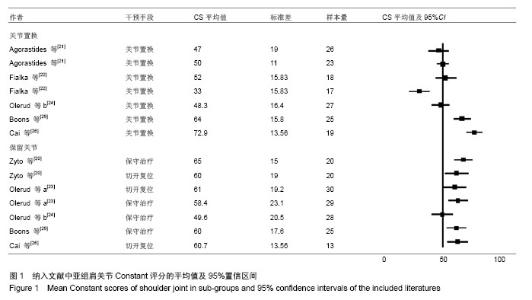
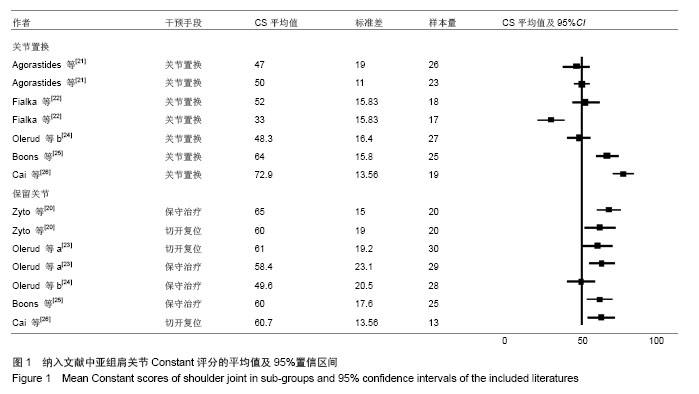
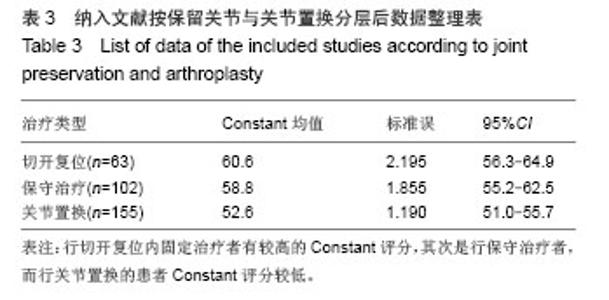
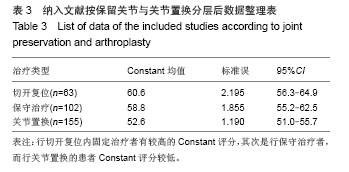
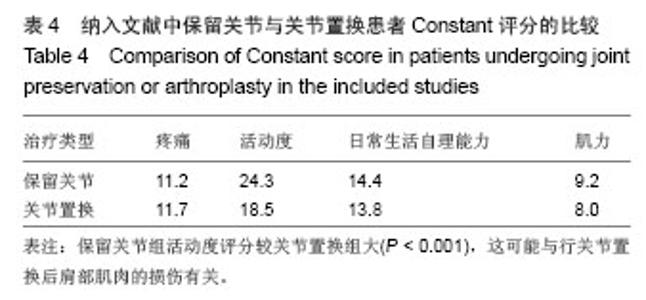
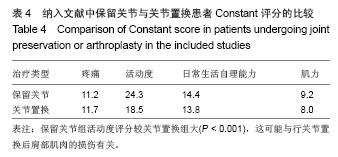
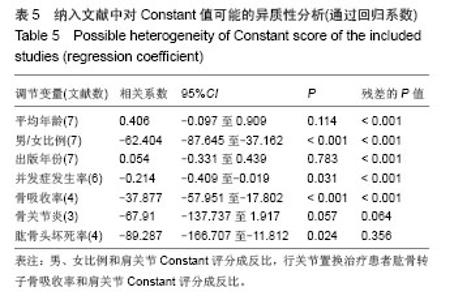
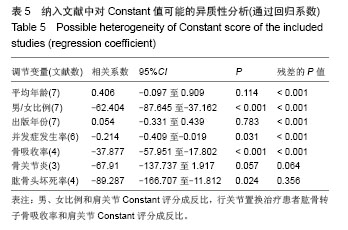
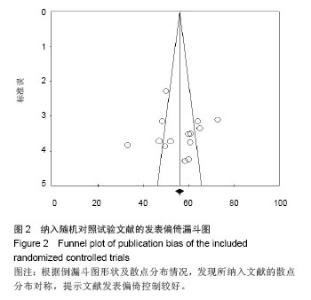
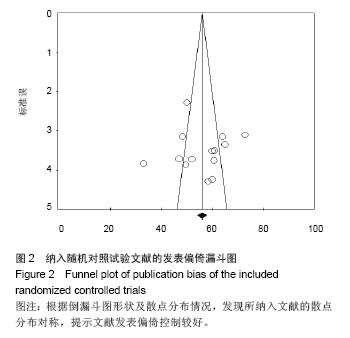
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (26): 4241-4247.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.26.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Arthroplasty versus joint preservation for displaced 3- and 4-part proximal humeral fractures: a meta-analysis
Zhang Hai-yang1, Zhao Yan1, Xie Chong2, Cheng Yong-tao1, Wang Cong-cong3
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, 2 Second Ward of Surgery (VIP), First Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3 Affiliated Hospital, Tianjin Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300120, China
-
Online:2014-06-25Published:2014-06-25 -
Contact:Zhao Yan, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Hai-yang, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Hai-yang, Zhao Yan, Xie Chong, Cheng Yong-tao, Wang Cong-cong. Arthroplasty versus joint preservation for displaced 3- and 4-part proximal humeral fractures: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(26): 4241-4247.
share this article
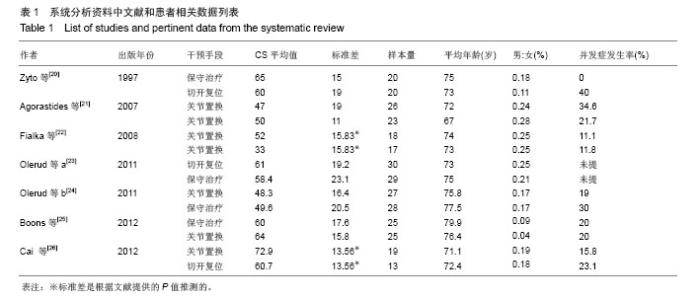
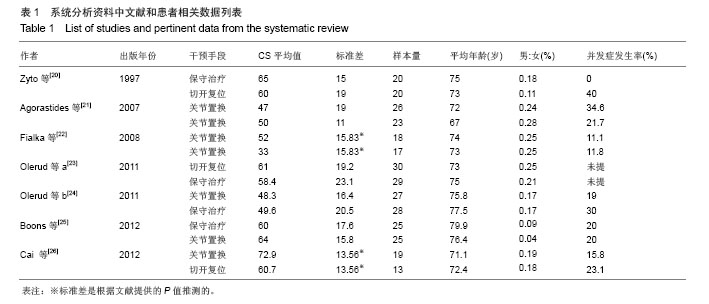
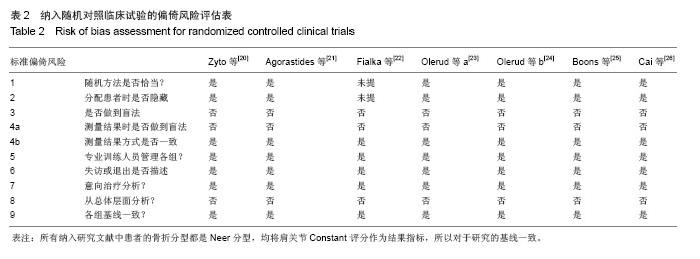
| [1]Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures:A review. Injury. 2006;37:691-697. [2]Südkamp N, Bayer J, Hepp P, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with use of the locking proximal humerus plate. Results of a prospective, multicenter, observational study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:1320-1328. [3]Thanasas C, Kontakis G, Angoules A, et al. Treat-ment of proximal humerus fractures with locking plates: a systematic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18:837-844. [4]Barrett JA, Baron JA, Karagas MR, et al. Fracture risk in the U.S. Medicare population. J Clin Epidemiol. 1999;52:243- 249. [5]Calvo E, Morcillo D, Foruria AM, et al. Nondisplaced proximal humeral fractures: high incidence among outpatient-treated osteoporotic fractures and severe impact on upper extremity function and patient subjective health perception. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5):795-801. [6]Guy P, Slobogean GP, McCormack RG, et al. Treatment preferences for displaced three-and four-part proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Rauma. 2010;24(4):250. [7]Court-Brown CM, Garg A, McQueen MM. The epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001;72(4): 365-371. [8]Gaebler C, McQueen MM, Court-Brown CM. Minimally displaced proximal humeral fractures: epidemiology and outcome in 507 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74:580- 585. [9]Handoll HH,Gibson JN,Madhok R. Interventions for treating proximal humeral Fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; 4 :CD000434. [10]Misra A,Kapur R,Maffulli N. Complex proximal humeral fractures in adults-a systematic review of management. Injury. 2001; 32(5):363-372. [11]Kontakis G,Koutras C,Tosounidis T,et al. Early management of proximal humeral fractures with heimiarthroplasty: a systematic review. Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90:1407-1413. [12]Neer CSII. Displaced proximal humeral fractures: I. Classification and evalua-tion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970; 52:1077-1089. [13]Kontakis G, Koutras C, Tosounidis T, et al. Early management of proximal humeral fractures with hemiarthroplasty: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90(11): 1407-1413. [14]Fjalestad T, Strømsøe K,Blücher J. Fractures in the proximal humerus:functional outcome and evaluation of 70 patients treated in hospital. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;(5): 310-316. [15]Hanson B, Neidenbach P, de Boer P, et al. Functional outcomes after nonoperative management of fractures of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(4): 612-621. [16]Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; 214:160-164. [17]Majed A, Macleod I, Bull AM, et al. Proximal humeral fracture classification systems revisited. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20(7):1125-1132. [18]Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials.1996;17(1):1-12. [19]Egger M, Davey SG, Schneider M. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997,315(7109): 629-634. [20]Zyto K, Ahrengart L, Sperber A, et al. Treatment of displaced proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(3):412-417. [21]Agorastides I, Sinopidis C, EI Meligy M, et al. Early versus late mobilization after hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2007;16(3 Suppl.):S33–38. [22]Fialka C, Stampfl P, Arbes S, et al. Primary hemiarthroplasty in four-part fractures of the proximal humerus: randomized trial of two different implant systems. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(2):210–215. [23]Olerud P, Ahrengart L, Ponzer S, et al. Internal fixation versus nonoperative treatment of displaced 3-part proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(5):747-755. [24]Olerud P,Ahrengart L,Ponzer S,et al. Hemiarthroplasty versus nonoperative treatment of displaced4-part proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20:1025-1033. [25]Boons HW, Goosen JH, van Grinsven S, et al. Hemiarthroplasty for humeral four-part fractures for patients 65 years and older: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(12):3483-3491. [26]Cai M, Tao K, Yang C, et al.Internal fixation versus shoulder hemiarthroplasty for displaced 4-part proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients. Trauma. 2012; 35(9):e1340- 1346. [27]Baker P, Nanda R, Goodchild L, et al. A comparison of the Constant and Oxford shoulder scores in patients with conservatively treated proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(1):37-41. [28]Thalhammer G, Platzer P, Oberleitner G, et al. Angular stable fixation of proximal humeral fractures. Trauma. 2009;66: 204-210. [29]Misra A, Kapur R, Maffulli N. Complex proximal humeral fractures in adults-a systematic review of management. Injury. 2001;32(5):363-372. [30]Levy J, Frankle M, Mighell M, et al. The use of the reverse shoulder pros-thesis for the treatment of failed hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fracture.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(2):292-300. [31]冯彦华,王诗波.肱骨近端3,4部分骨折手术与非手术治疗疗效比较的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(14):1260-1264. [32]Li Y, Zhao L, Zhu L, et al. Internal Fixation Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced 3-part or 4-part Proximal Humeral Fractures in Elderly Patients:A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75464. [33]Kelsey JL, Browner WS, Seeley DG, et al. Risk factors for fractures of the distal forearm and proximal humerus, the study of osteoporotic fractures research group. Am J Epidemiol. 1992;135:477-489. [34]Bell JE, Leung BC, Spratt KF, et al.Trends and variation in incidence, surgical treatment, and repeat surgery of proximal humeral fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011; 93(2):121-131. [35]Court-Brown CM, Garg A, McQueen MM. The epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001; 72(4):365-371. [36]Kontakis G, Koutras C, Tosounidis T, et al. Early management of proximal humeral fractures with hemiarthroplasty: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90(11): 1407-1413. [37]Baker P, Nanda R, Goodchild L, et al. A comparison of the Constant and Oxford shoulder scores in patients with conservatively treated proximal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2008;17(1):37-41. [38]Neer CS 2nd. Four-segment classification of proximal humeral fractures: purpose and reliable use. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002;11(4):389-400. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||