Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (24): 3878-3884.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.24.018
Previous Articles Next Articles
Optimization of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis for synaptic proteomics
Hu Yong-bo, Gao Li, Wang Dan, Zeng Zhong, Xu Chao-yi, Xiao Bing, Luo Fei-fei, Yang Zhi-yong, Zhou Qiang
- Department of Neurology, the Third People’s Hospital of Chengdu & the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu, Chongqing Medical University, Chengdu 610031, Sichuan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-04-23Online:2014-06-11Published:2014-06-11 -
Contact:Gao Li, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Neurology, the Third People’s Hospital of Chengdu & the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu, Chongqing Medical University, Chengdu 610031, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Hu Yong-bo, Ph.D., M.D., Attending physician, Department of Neurology, the Third People’s Hospital of Chengdu & the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu, Chongqing Medical University, Chengdu 610031, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81101009
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Yong-bo, Gao Li, Wang Dan, Zeng Zhong, Xu Chao-yi, Xiao Bing, Luo Fei-fei, Yang Zhi-yong, Zhou Qiang. Optimization of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis for synaptic proteomics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(24): 3878-3884.
share this article
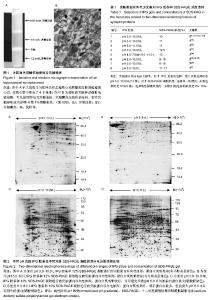
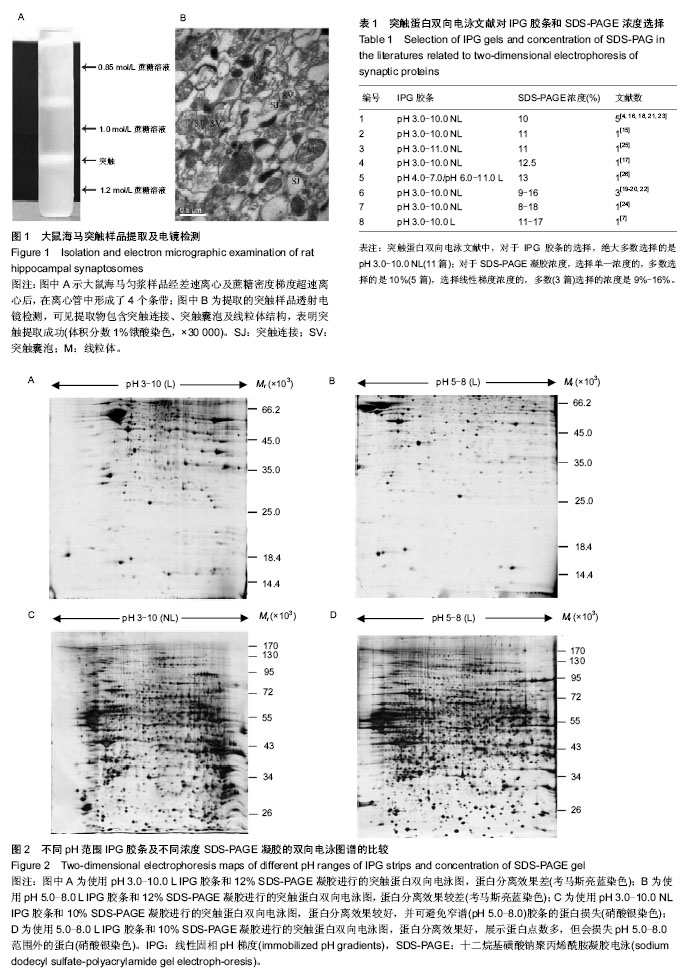
2.1 大鼠海马突触超微结构 大鼠海马匀浆样品在超速离心管中形成了4个条带,位于1.0-1.2 mol/L蔗糖溶液区间的条带为突触组分,随后的透射电镜检测进一步表明该组分确实为海马突触,见图1。 2.2 不同条件下进行的突触蛋白双向电泳图比较 实验共进行了两组突触蛋白双向电泳,第一组使用17 cm的pH 3.0-10.0 L、17 cm的pH 5.0-8.0 L IPG胶条,单一浓度 12% SDS-PAGE凝胶,700 μg蛋白质上样量,考马斯亮蓝染色(图2A,B);第二组使用pH 3.0-10.0 NL、pH 5.0-8.0 L 17 cm IPG胶条,单一浓度10% SDS-PAGE凝胶,120 μg蛋白质上样量,硝酸银染色(图2C,D)。 首先,实验对窄谱(pH 5.0-8.0)和宽谱(pH 3.0-10.0) IPG胶条突触双向电泳图进行了比较。从图2中可看出,IPG 胶条两端区域均存在横条纹,但窄谱(pH 5.0-8.0)较宽谱 (pH 3.0-10.0)胶条两端横条纹明显要少些。此外,经双向电泳分析软件PDQuest 2-DE 8.01分析,窄谱(pH 5.0-8.0)胶条(图2D)分离出效蛋白质点1 560±22个,宽谱(pH 3.0- 10.0)IPG胶条(图2C)分离出有效蛋白质点1 370±19个。也就是说,窄谱(pH 5.0-8.0)相对于宽谱(pH 3.0-10.0)胶条,虽然pH范围变窄,但因展示了部分重叠的蛋白质点,蛋白点的数量不但没有下降,反而平均值还增加了13.84%。从电泳图比较中还看到,窄谱(pH 5.0-8.0)胶条双向电泳图谱效果好,蛋白分离充分、蛋白点圆润、背景清晰,更有利于图谱的分析与比较。不足之处是会损失窄谱pH范围外的突触蛋白点。 其次,实验对10%与12%两种不同单一SDS-PAGE凝胶浓度对突触蛋白分离的影响进行了比较。可以看出,第二向电泳采用10% SDS-PAGE(图2C,D)和12% SDS-PAGE凝胶(图2A,B),蛋白点展示的相对分子质量范围更广,蛋白点分离得更充分。10% SDS-PAGE凝胶分离的蛋白相对分子质量在20 000-170 000的范围内,蛋白点可在整张凝胶上充分展开,而12% SDS-PAGE凝胶分离的蛋白分子量主要集中于14 400-66 200狭窄区域内,多数蛋白点紧密聚集于分子量为35 000-66 200间狭小的凝胶区域,难于分辨。 最后,实验比较了线性和非线性宽谱(pH 3.0-10.0) IPG胶条对突触蛋白分离的影响。从图2A,C的比较中不难看出,突触蛋白质等电点大多数还是集中于中段pH范围(pH 5.0-9.0)内,使用非线性pH 3-10 IPG胶条,较线性胶条更能充分展开等电点处于中段pH范围内的突触蛋白。 2.3 突触蛋白双向电泳文献对IPG胶条和SDS-PAGE浓度的选择 通过突触蛋白双向电泳相关文献查询,在PubMed数据库中查询到外文文献255篇,在CNKI数据库中查询到中文文献27篇,经阅读,筛选出以突触(排除突触亚组分:突触膜、突触后致密物和突触囊泡)为样品,进行IEF/SDS-PAGE双向电泳的文献有14篇。从表1中可看出,对于IPG胶条的选择,绝大多数实验选择的是pH 3.0-10.0NL文章11篇[4, 15-24],少数选择了pH 3.0-10.0 L及pH 3.0-11.0 NL各1篇[7,25],还有1篇文献是合并使用两根pH值相重叠的窄谱IPG胶条(pH 4.0-7.0/pH 6.0-11.0 L)[26];而对于SDS-PAGE凝胶浓度,选择单一浓度的,5篇选择的是10%[4, 16, 18, 21, 23],2篇选择11%[15, 25]、1篇选择12.5%[17],1篇选择13%[26];选择线性梯度浓度的3篇选择的是9%-16%[19-20, 22],1篇为8%-18%[24],1篇为11%-17%[7]。"
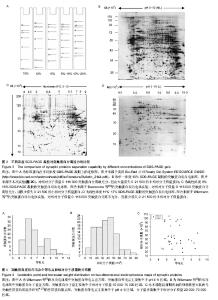
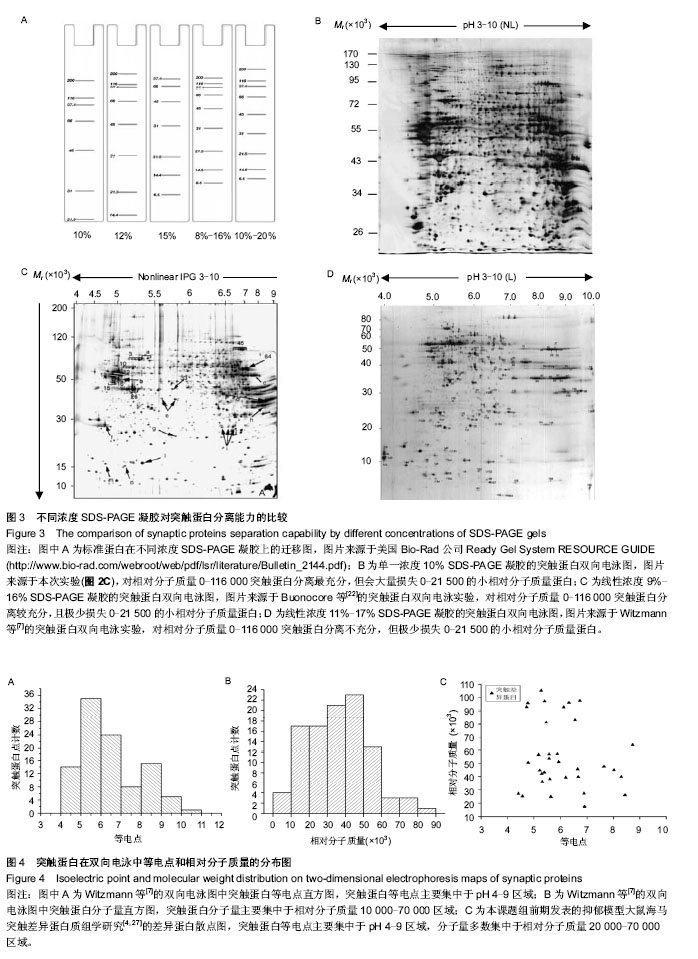
2.4 不同浓度SDS-PAGE凝胶对突触蛋白分离能力的比较 根据Bio-Rad公司实验操作指南(Ready Gel System RESOURCE GUIDE)上标准蛋白在不同浓度SDS-PAGE凝胶上电泳迁移分布图(图3A),可见不同浓度(10%,12%,8%-16%,10%-20%)的SDS-PAGE凝胶对相对分子质量为0-116 000的蛋白的分离能力是不同的,10%凝胶对这些蛋白的分离最充分,但会损失大量的0-21 500的小相对分子质量蛋白;8%-16%凝胶的分离能力要大于10%-20%凝胶,尤其是对相对分子质量0-66 000的蛋白。 实际的突触蛋白双向电泳图也符合这一规律。实验从实验及文献中共选出了3个代表性浓度(10%,9%-16%,11%-17%)SDS-PAGE凝胶的突触蛋白双向电泳图,实验的10% SDS-PAGE凝胶(图2C,3B),Buonocore等[22]的9%-16%(接近于8%-16%)SDS-PAGE凝胶(图3C)和Witzmann等[7]的11%-17%(接近于10%-20%)SDS-PAGE凝胶(图3D)。从3张电泳图的比较可发现,10% SDS- PAGE凝胶损失了大量0-21 500的小相对分子质量蛋白,但对于相对分子质量21 500-116 000(尤其是相对分子质量 21 500-66 000)的蛋白比9%-16%和11%-17% SDS- PAGE凝胶分离得更充分;此外,9%-16%比11%-17% SDS-PAGE凝胶对相对分子质量0-116 000(尤其是相对分子质量0-66 000)蛋白的分离更充分,且两者均极少损失小相对分子质量0-21 500的蛋白。 2.5 突触蛋白在双向电泳图中等电点和相对分子质量分布趋势 从图3B-D中突触蛋白双向电泳图还可看出,突触蛋白在双向电泳中,等电点主要集中于pH 4-9区域,分子量大多数处于0-120 000,以10 000-70 000区域最集中。其后的MALDI-TOF/TOF质谱鉴定得到突触蛋白等电点和分子量信息也证实了这一结论。例如,Witzman等[7]进行了大鼠脑皮质突触全蛋白质组学分析(图3D),用MALDI-TOF/ TOF质谱成功鉴定出163个突触蛋白点。实验对其成功鉴定突触蛋白的分子量和等电点信息进行了直方图分析,可以看出,突触蛋白等电点分布于pH 4-11区域(主要集中于pH 4-9,图4A);相对分子质量分布于0-90 000(集中于10 000-70 000的范围,图4B)。又如,根据本课题组前期所做的慢性轻度应激抑郁大鼠与正常大鼠海马突触差异蛋白质组学实验数据[4, 27],实验描绘了差异表达的突触蛋白的等电点和相对分子质量散点分布图,可以看出差异突触蛋白等电点分布于 pH 4-9区域内,相对分子质量处于10 000-110 000范围,以 20 000-70 000为其分布高峰(图4C)。"
| [1] Wasinger VC, Cordwell SJ, Cerpa-Poljak A, et al. Progress with gene-product mapping of the mollicutes: mycoplasma genitalium. Electrophoresis. 1995;16(7):1090-1094. [2] Li KW, Jimenez CR. Synapse proteomics: current status and quantitative applications. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2008;5(2): 353-360. [3] Morón JA, Abul-Husn NS, Rozenfeld R, et al. Morphine administration alters the profile of hippocampal postsynaptic density-associated proteins: a proteomics study focusing on endocytic proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2007;6(1):29-42. [4] Hu Y, Zhou J, Fang L, et al. Hippocampal synaptic dysregulation of exo/endocytosis-associated proteins induced in a chronic mild-stressed rat model. Neuroscience. 2013;230:1-12. [5] Fernandez F, Trinidad JC, Blank M, et al. Normal protein composition of synapses in Ts65Dn mice: a mouse model of Down syndrome. J Neurochem. 2009;110(1):157-169. [6] Li KW. Proteomics of synapse. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007; 387(1):25-28. [7] Witzmann FA, Arnold RJ, Bai F, et al. A proteomic survey of rat cerebral cortical synaptosomes. Proteomics. 2005;5(8): 2177-201. [8] 覃万安,苏伟,黄钊,等.三种大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞双向电泳样品制备方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(14):2520-2523. [9] 林永亮,黄冰,廖东江,等.人表皮细胞与角膜上皮细胞蛋白质组的差异表达初步研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(28):5531-5535. [10] 黄传钟,林科灿,王斌,等.肝癌切除肝缺血再灌注损伤前后的蛋白质组学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(40):7539-7543. [11] 黄国飞,王济明,罗诗樵,等.人胆汁双向凝胶电泳分离技术的建立与优化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(15):2937-2941. [12] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [13] Carlin RK, Grab DJ, Cohen RS, et al. Isolation and characterization of postsynaptic densities from various brain regions: enrichment of different types of postsynaptic densities. J Cell Biol. 1980;86(3):831-845. [14] Yan JX, Wait R, Berkelman T, et al. A modified silver staining protocol for visualization of proteins compatible with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis. 2000;21(17): 3666-3672. [15] Li KW, Hornshaw MP, Van Der Schors RC, et al. Proteomics analysis of rat brain postsynaptic density. Implications of the diverse protein functional groups for the integration of synaptic physiology. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(2):987-1002. [16] Bajor M, Michaluk P, Gulyassy P, et al. Synaptic cell adhesion molecule-2 and collapsin response mediator protein-2 are novel members of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 degradome. J Neurochem. 2012;122(4):775-788. [17] [Ji B, Zhang Z, Zhang M, et al. Differential expression profiling of the synaptosome proteome in a rat model of antipsychotic resistance. Brain Res. 2009;1295:170-178. [18] Singh OV, Yaster M, Xu JT, et al. Proteome of synaptosome- associated proteins in spinal cord dorsal horn after peripheral nerve injury. Proteomics. 2009;9(5):1241-1253. [19] Corti V, Sanchez-Ruiz Y, Piccoli G, et al. Protein fingerprints of cultured CA3-CA1 hippocampal neurons: comparative analysis of the distribution of synaptosomal and cytosolic proteins. BMC Neurosci. 2008;9:36. [20] Liberatori S, Canas B, Tani C, et al. Proteomic approach to the identification of voltage-dependent anion channel protein isoforms in guinea pig brain synaptosomes. Proteomics. 2004; 4(5):1335-1340. [21] Jimenez CR, Eyman M, Lavina ZS, et al. Protein synthesis in synaptosomes: a proteomics analysis. J Neurochem. 2002; 81(4):735-744. [22] Buonocore G, Liberatori S, Bini L, et al. Hypoxic response of synaptosomal proteins in term guinea pig fetuses. J Neurochem. 1999;73(5):2139-2148. [23] Zhou K, Yang Y, Gao L, et al. NMDA receptor hypofunction induces dysfunctions of energy metabolism and semaphorin signaling in rats: a synaptic proteome study. Schizophr Bull. 2012;38(3):579-591. [24] Mallei A, Giambelli R, Gass P, et al. Synaptoproteomics of learned helpless rats involve energy metabolism and cellular remodeling pathways in depressive-like behavior and antidepressant response. Neuropharmacology. 2011;60(7-8): 1243-53. [25] Smalla KH, Mikhaylova M, Sahin J, et al. A comparison of the synaptic proteome in human chronic schizophrenia and rat ketamine psychosis suggest that prohibitin is involved in the synaptic pathology of schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry. 2008; 13(9):878-896. [26] Eravci M, Fuxius S, Broedel O, et al. The whereabouts of transmembrane proteins from rat brain synaptosomes during two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proteomics. 2008;8(9): 1762-1770. [27] 胡永波,周健,刘海朋,等.抑郁模型大鼠海马突触的差异蛋白质组学分析[J].世界科技研究与发展,2011,33(2):305-310. [28] 郭强,张茂修,李玉瑭,等.窄范围pH梯度干胶条可提高胃癌细胞蛋白质组表达谱分辨率[J].医学检验与临床,2006,17(4):60-62. [29] 王一鸣,胡昊,王有年,等.两种固相pH梯度胶条对桃果实蛋白质双向电泳的影响[J].北京农学院学报,2007,22(2):13-16. [30] Wildgruber R, Harder A, Obermaier C, et al. Towards higher resolution: two-dimensional electrophoresis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins using overlapping narrow immobilized pH gradients. Electrophoresis. 2000;21(13):2610-2616. [31] Oguri T, Takahata I, Katsuta K, et al. Proteome analysis of rat hippocampal neurons by multiple large gel two-dimensional electrophoresis. Proteomics. 2002;2(6):666-672. [32] 郑学学,商娜,耿鑫,等.不同浓度和梯度的SDS-PAGE胶对双向电泳中蛋白分离的影响[J].生物技术通讯,2009,20(5):683-686. |
| [1] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [2] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [3] | Chen Junyi, Wang Ning, Peng Chengfei, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Bei Chaoyong. Decalcified bone matrix and lentivirus-mediated silencing of P75 neurotrophin receptor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 510-515. |
| [4] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [5] | Lin Haiqi, Chen Liang, Tang Lu, Weng Xiquan, Lin Wentao. Significance of urinary proteomics assessing pathological changes in the body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3259-3266. |
| [6] | Huang Zhusong, Lin Yu, Chen Xiang, Lan Jinfu, Guan Yong, Gao Xi. Alcohol extract of Morinda officinalis improves lipid metabolism and bone metabolism in ovariectomized obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 205-210. |
| [7] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [8] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Liu Chao. Adipose-derived stem cells integrated with concentrated growth factors prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2982-2987. |
| [9] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| [10] | Hu Wandong, He Jialin, Zhang Longsheng, Liao Wenbo. Differential proteomics study of patients with sternal ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2625-2629. |
| [11] | Jiang Tao, Wu Shuo, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Mayire·Nuermaimaiti, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB promotes the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of Sprague-Dawley rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1976-1981. |
| [12] | Li Shengqiang, Xie Bingying, Chen Juan, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, Ge Jirong. Interaction proteomics of long noncoding RNA uc431+ gene in postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1641-1646. |
| [13] | Zang Jing, Luan Zuo, Wang Qian, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wu Youjia, Guo Aisong. Two kinds of stem cell nasal transplantation for treating white matter injury in premature rat infants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 101-107. |
| [14] | Wang Guoyu, Cheng Zhijian, Yang Baohui, Li Haopeng, He Xijing. Olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation promotes the ultrastructure repair at the lesion site of rat models of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 699-703. |
| [15] | Wang Jing, Lu Changfeng, Peng Jiang, Zhu Chen, Xu Wenjing, Cheng Xiaoqing, Fang Jie, Zhu Yaqiong, Zhao Yanxu, Jiang Wen, Xu Hongguang, Wang Yu. Establishment and evaluation of traumatic neuroma model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 716-719. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||