Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (24): 3870-3877.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.24.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Construction and identification of pIRES2-LIF-VEGF165 bicistronic eukaryotic expression vector
Li Bing-nan, Li Wei-dong, Lin Jun-tang, Feng Hui-gen, Yuan Zhi-qing
- Department of Life Sciences and Technology, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-05-03Online:2014-06-11Published:2014-06-11 -
Contact:Li Bing-nan, Department of Life Sciences and Technology, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, Henan Province, China -
About author:Li Bing-nan, Ph.D., Lecturer, Department of Life Sciences and Technology, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, Henan Province, China Li Wei-dong, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Life Sciences and Technology, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang 453003, Henan Province, China Li Bing-nan and Li Wei-dong contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:Tender Subject of Key Research Areas of Xinxiang Medical University in 2011, No. ZD2011-16; Key Projects in Scientific Research of Henan Provincial Education Department, No. 13A180850; Scientific Research Fund of Xinxiang Medical University, No. 2013QN117; Innovation Supporting Project of Xinxiang Medical University for Graduate Students Scientific Research, No. YJSCX201231Y; Key Science and Technology Project of Henan Province, No. 122101310100; Henan Provincial Academy of Science and Technology Cooperation Project, No. 102106000017
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Bing-nan, Li Wei-dong, Lin Jun-tang, Feng Hui-gen, Yuan Zhi-qing. Construction and identification of pIRES2-LIF-VEGF165 bicistronic eukaryotic expression vector[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(24): 3870-3877.
share this article
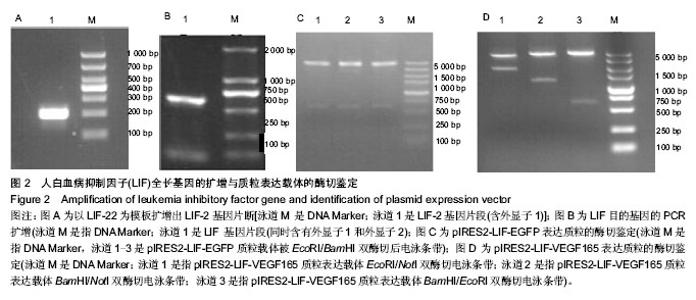
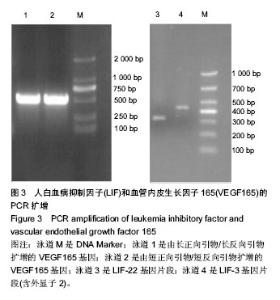
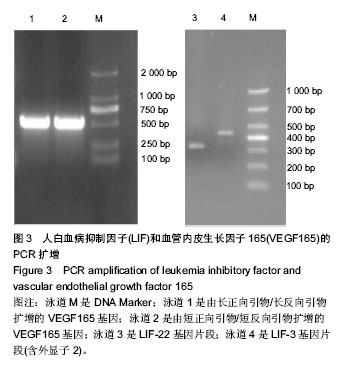
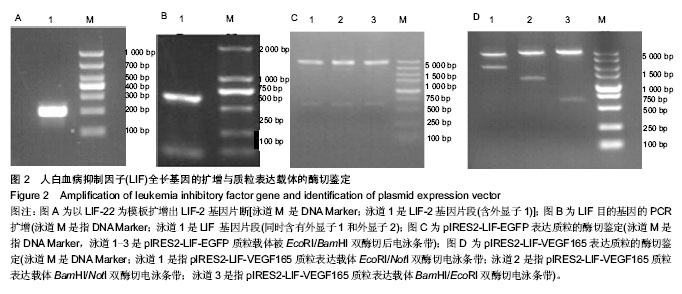
2.1 LIF与VEGF165基因的扩增 从人外周血单核细胞的基因组DNA通过PCR获得LIF基因(图2A和2B)。LIF基因的大小为609 bp,以pIRES2-VEGF165-EGFP为模板通过PCR方法获取VEGF165,VEGF165基因的大小为 576 bp(图3)。 2.2 pIRES2-LIF-EGFP质粒的鉴定 质粒载体pIRES2- LIF-EGFP被EcoRI和BamHI双酶切后进行凝胶电泳,结果在609 bp处出现一条目的条带,与LIF基因大小完全一致(图2C)。 2.3 pIRES2-LIF-VEGF165双基因表达质粒的鉴定 质粒载体pIRES2-LIF-VEGF165被EcoRI和BamHI双酶切后进行凝胶电泳,结果在约609 bp处出现一条目的条带,与LIF基因大小完全一致;质粒载体pIRES2- LIF-VEGF165被EcoRI和NotI双酶切后,结果在约 1 791 bp处出现一条目的条带与LIF-IRES-VEGF165基因片段大小一致;质粒载体pIRES2-LIF-VEGF165被BamHI和NotI双酶切后,结果在约1 170 bp出现一条目的条带大小与IRES-VEGF165基因片段一致。载体pIRES2-LIF-VEGF165经DNA测序后可知LIF与VEGF165与基因库中的序列完全一致(图2D)。"
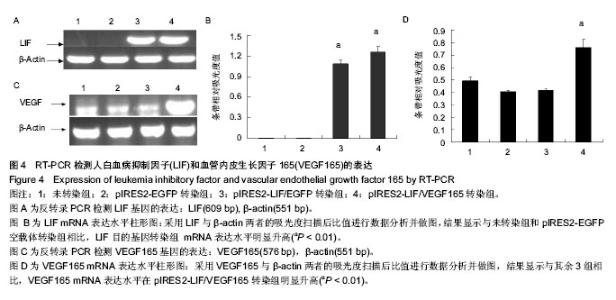
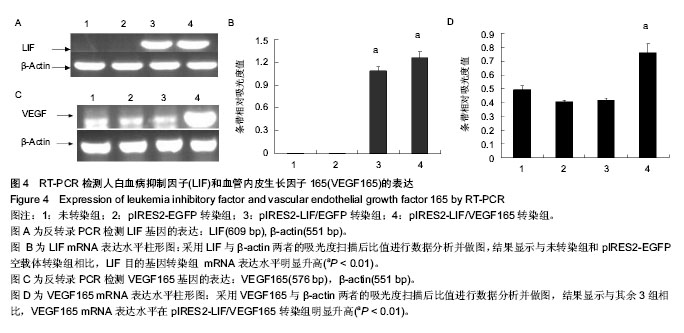
2.4 RT-PCR检测LIF与VEGF165的表达 采用RT-PCR方法检测各处理组HEK293细胞中LIF与VEGF165的mRNA相对表达量。首先采用LIF与VEGF165及β-actin特异性引物进行PCR反应,其中β-actin基因作为内参,可以通过计算目的基因和内参的比值,得到基因表达的相对表达量。 采用倒置荧光显微镜观察pIRES2-EGFP与pIRES2-LIF/EGFP 转染组3 d后绿色荧光表达量约80%以上。通过提取等质量各处理组总RNA反转录cDNA后采用基因特异性引物进行PCR扩增,电泳跑胶后利用光密度扫描软件进行表达量分析。结果显示:LIF基因在pIRES2- LIF/EGFP与pIRES2-LIF/VEGF165转染组表达量明显高于pIRES2-EGFP转染组与空白对照组(图4A,B)。与上述方法相似,结果显示VEGF165基因在pIRES2- LIF/VEGF165转染组的表达量明显高于其他3组(图4C,D)。实验结果表明可知LIF与VEGF165基因成功导入了HEK293细胞中并且得到了表达。"
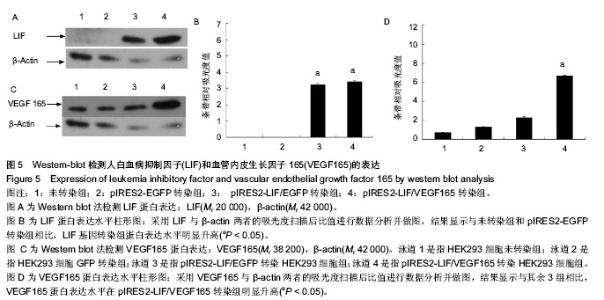
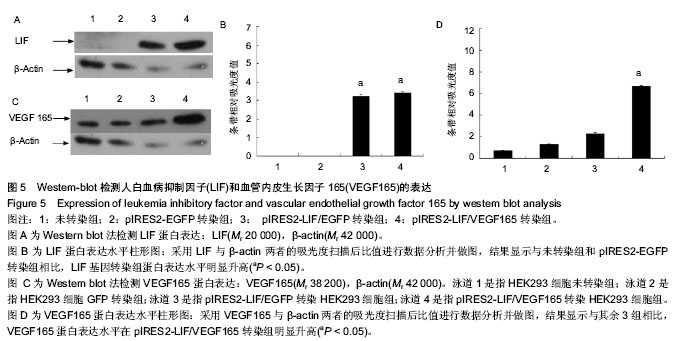
2.5 Western-blot检测LIF与VEGF165的表达 采用Western-blot方法检测各处理组HEK293细胞中LIF与VEGF165的蛋白水平的表达,以β-肌动蛋白一抗作为目的蛋白表达的内参,即提取各处理组的HEK293细胞上清液,经BCA法检测蛋白浓度后行SDS-PAGE电泳分离后,电转、抗体孵育,在暗室中经压片、显影、定影。条带的灰度采用Gel-Pro analyzer软件进行分析。倒置荧光显微镜观察pIRES2-EGFP与pIRES2-LIF/EGFP转染组的绿色荧光表达约80%以上。结果显示:LIF基因在pIRES2-LIF/EGFP与pIRES2-LIF/VEGF165转染组表达量明显高于pIRES2- EGFP转染组与空白对照组(图5A,B),与上述方法相似,结果显示VEGF165基因在pIRES2- LIF/VEGF165转染组的表达量明显高于其他3组(图5C,D)。表明LIF与VEGF165基因成功导入了HEK293细胞中并且在蛋白质水平得到了表达。"
| [1] Kershaw MH, Westwood JA, Darcy PK.Gene-engineered T cells for cancer therapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(8): 525-541. [2] Fischer J, Kolk A, Wolfart S,et al.Future of local bone regeneration - Protein versus gene therapy.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2011;39(1):54-64. [3] Zimmermann GR, Lehár J, Keith CT.Multi-target therapeutics: when the whole is greater than the sum of the parts.Drug Discov Today. 2007;12(1-2):34-42. [4] Kouprina N, Tomilin AN, Masumoto H,et al. Human artificial chromosome-based gene delivery vectors for biomedicine and biotechnology.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014;11(4): 517-535. [5] Segura MM, Mangion M, Gaillet B,et al.New developments in lentiviral vector design, production and purification.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13(7):987-1011. [6] Galli C, Perota A, Brunetti D,et al.Genetic engineering including superseding microinjection: new ways to make GM pigs.Xenotransplantation. 2010;17(6):397-410. [7] Wozniak CE, Chevance FF, Hughes KT.Multiple promoters contribute to swarming and the coordination of transcription with flagellar assembly in Salmonella.J Bacteriol. 2010; 192(18):4752-4762. [8] Li L, Huang J, Ju Z,et al.Multiple promoters and targeted microRNAs direct the expressions of HMGB3 gene transcripts in dairy cattle.Anim Genet. 2013;44(3):241-250. [9] Rydenfelt M, Cox RS 3rd, Garcia H,et al.Statistical mechanical model of coupled transcription from multiple promoters due to transcription factor titration.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2014 ;89(1):012702. [10] Cichocki F, Miller JS, Anderson SK.Killer immunoglobulin- like receptor transcriptional regulation: a fascinating dance of multiple promoters.J Innate Immun. 2011;3(3):242-248. [11] Brenner JC, Ateeq B, Li Y,et al. Mechanistic rationale for inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in ETS gene fusion-positive prostate cancer.Cancer Cell. 2011;19(5): 664-678. [12] Steidl C, Shah SP, Woolcock BW,et al.MHC class II transactivator CIITA is a recurrent gene fusion partner in lymphoid cancers.Nature. 2011;471(7338):377-381. [13] Ju YS, Lee WC, Shin JY,et al.A transforming KIF5B and RET gene fusion in lung adenocarcinoma revealed from whole-genome and transcriptome sequencing.Genome Res. 2012;22(3):436-445. [14] Nord KH, Lilljebjörn H, Vezzi F,et al.GRM1 is upregulated through gene fusion and promoter swapping in chondromyxoid fibroma.Nat Genet. 2014;46(5):474-477. [15] Pierron G, Tirode F, Lucchesi C,et al.A new subtype of bone sarcoma defined by BCOR-CCNB3 gene fusion.Nat Genet. 2012;44(4):461-466. [16] Licursi M, Christian SL, Pongnopparat T,et al.In vitro and in vivo comparison of viral and cellular internal ribosome entry sites for bicistronic vector expression.Gene Ther. 2011;18(6): 631-636. [17] Blau L, Knirsh R, Ben-Dror I,et al.Aberrant expression of c-Jun in glioblastoma by internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-mediated translational activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(42):E2875-2884. [18] Liang S, Lin Y, Li C,et al.Internal ribosome entry site mediates protein synthesis in yeast Pichia pastoris.Biotechnol Lett. 2012; 34(5):957-964. [19] Sadikoglou E, Daoutsali E, Petridou E,et al.Comparative analysis of internal ribosomal entry sites as molecular tools for bicistronic expression.J Biotechnol. 2014;181C:31-34. [20] Ho SC, Bardor M, Feng H,et al.IRES-mediated Tricistronic vectors for enhancing generation of high monoclonal antibody expressing CHO cell lines.J Biotechnol. 2012; 157(1):130-139. [21] Xie BH, Xie YF. Twin PCRs:a simple and efficient method for directional cloning of PCR products. World J Microbiol Biotechnol.2011;27:2223-2225. [22] Fischer D, Leibinger M.Promoting optic nerve regeneration. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012;31(6):688-701. [23] Fukumitsu H, Ohtsuka M, Murai R, et al.Brain-derived neurotrophic factor participates in determination of neuronal laminar fate in the developing mouse cerebral cortex.J Neurosci. 2006;26(51):13218-13230. [24] Leaver SG, Cui Q, Plant GW,et al.AAV-mediated expression of CNTF promotes long-term survival and regeneration of adult rat retinal ganglion cells.Gene Ther. 2006;13(18): 1328-1341. [25] Pernet V, Di Polo A.Synergistic action of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and lens injury promotes retinal ganglion cell survival, but leads to optic nerve dystrophy in vivo.Brain. 2006;129(Pt 4):1014-1026. [26] Wu N, Yin ZQ, Wang Y.Traumatic optic neuropathy therapy: an update of clinical and experimental studies.J Int Med Res. 2008;36(5):883-889. [27] Hu Y, Cho S, Goldberg JL.Neurotrophic effect of a novel TrkB agonist on retinal ganglion cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51(3):1747-1754. [28] Blanco RE, Soto I, Duprey-Díaz M,et al.Up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor by application of fibroblast growth factor-2 to the cut optic nerve is important for long-term survival of retinal ganglion cells.J Neurosci Res. 2008;86(15):3382-3392. [29] Lee YJ, Zachrisson O, Tonge DA,et al.Upregulation of bradykinin B2 receptor expression by neurotrophic factors and nerve injury in mouse sensory neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2002;19(2):186-200. [30] Ishibashi T, Lee PR, Baba H,et al.Leukemia inhibitory factor regulates the timing of oligodendrocyte development and myelination in the postnatal optic nerve.J Neurosci Res. 2009;87(15):3343-3355. [31] Zhou XF, Deng YS, Chie E,et al.Satellite-cell-derived nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3 are involved in noradrenergic sprouting in the dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury in the rat.Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11(5): 1711-1722. [32] Terenghi G. Peripheral nerve regeneration and neurotrophic factors.J Anat. 1999; 194(Pt 1):1-14. [33] Lee FS, Kim AH, Khursigara G,et al.The uniqueness of being a neurotrophin receptor.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11(3): 281-286. [34] Chattopadhyay M, Krisky D, Wolfe D,et al. HSV-mediated gene transfer of vascular endothelial growth factor to dorsal root ganglia prevents diabetic neuropathy.Gene Ther. 2005; 12(18):1377-1384. [35] Rosenstein JM, Krum JM, Ruhrberg C.VEGF in the nervous system.Organogenesis. 2010;6(2):107-114. [36] Yoon CS, Jung HS, Kwon MJ,et al.Sonoporation of the minicircle-VEGF(165) for wound healing of diabetic mice. Pharm Res. 2009;26(4):794-801. [37] Fujiki M, Abe E, Nagai Y,et al.Electroconvulsive seizure-induced VEGF is correlated with neuroprotective effects against cerebral infarction: Involvement of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway.Exp Neurol. 2010;225(2):377-383. [38] Baksh D, Song L, Tuan RS.Adult mesenchymal stem cells: characterization, differentiation, and application in cell and gene therapy.J Cell Mol Med. 2004;8(3):301-316. [39] Atkinson H, Chalmers R.Delivering the goods: viral and non-viral gene therapy systems and the inherent limits on cargo DNA and internal sequences.Genetica. 2010;138(5): 485-498. [40] Najafian B, Alpers CE, Fogo AB.Pathology of human diabetic nephropathy.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;170:36-47. |
| [1] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| [2] | Liu Hao, Liu Jun, Rui Yongjun, Tang Fenglin, Lu Miao, Ding Tao. Co-transfection by Nell-1 and Noggin-shRNA promotes osteoblast differentiation of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4966-4970. |
| [3] | Wang Wenhong, Li Yanjun, Cui Caiyun. Factors influencing differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla into odontoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5071-5078. |
| [4] |
Wang Ning, Chen Junyi, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao, Wang Ye, Li Zhijun, Bei Chaoyong.
Lentivirus-mediated P75 neurotrophin receptor silencing combined with nerve growth factor overexpression promotes proliferation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3988-3993. |
| [5] | Zou Gang, Zhang Jun, You Qi, Tang Jingfeng, Jin Ying, Yang Jibin, Zhu Xizhong, Liu Yi. Scleraxis lentivirus-transfected human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells promote tendon-bone healing in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2080-2086. |
| [6] | Sun Li, Zong Yanyan, Wei Jianfeng. Comparison of two passage methods affecting the transfection efficiency of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 72-76. |
| [7] | Zhong Yanping, Zou Hongyan, Quan Zhanrou, Deng Zhihui, Hong Wenxu. Analysis of full-length sequence and 18 point mutations of HLA-B in a leukemia patient and her family [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 77-82. |
| [8] | Xu Huijun, Shi Dongmei, Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Effect of sex combing protein 1 on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in inflammatory microenvironment#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 130-135. |
| [9] | Wang Yifei, Song Yang, Guan Yongge, Xu Chunyan. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of thin endometrium based on HOXA10 regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1397-1402. |
| [10] | Gao Kun1, Zhu Wenxiu2, Li Heng1, Liu Weidong1, Li Quan1, Yu Weiji1, Wang Lixin1, Cao Yafei1. Exosomes in serum of ovariectomized rats promote primary osteoblast proliferation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 958-989. |
| [11] | Wu Min1, Li Xue1, Gao Jie1, Yang Shuai1, Cai Yizhi2, Wang Mingguo1 . Micro-CT changes and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in reconstructed mandibular condylar cartilage under continuous mandibular advancement in growing and adult rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1001-1006. |
| [12] | Wang Yang, Nie Jinshan, Gu Zhun, Zhu Kai. Construction and in vitro evaluation of a biodegradable cationic gene delivery system based on hyperbranched polyamidoamine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 936-944. |
| [13] | Ma Yuegang, Li Qiang, Tao Xuan, Zhou Zhenjie, Zhu Lunjing, Duan Jiangtao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells co-transfected by lentivirus-mediated bone morphogenetic protein 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor 165 in combination with demineralized bone matrix for treating rabbit femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5275-5280. |
| [14] | Yuan Peiyan, Chen Lei, Xu Shuaimei, Tong Fangli, Xu Pingping. Construction of circular RNA mmu_circ_Rab11a overexpression vector to transfect 293T cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5372-5377. |
| [15] | Liu Shaojin1, Wan Lei2, Qiao Rongqin2, Huang Hongxing2, Wang Jili1, Li Zhaozheng1 . Mechanism of XCT-790 reducing activity and osteogenesis of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 329-334. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||