Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (23): 3676-3681.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.23.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transfusion on different damaged organs in graft-versus-host disease
Lu Ying1, 2, Zhang Xiang-zhong1, Liu Xiang-fu2, Li Fang2, Lin Dong-jun1, 2
- 1Department of Hematology, 2Department of Blood Transfusion, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2014-04-10Online:2014-06-04Published:2014-06-04 -
Contact:Lin Dong-jun, Master, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Hematology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Blood Transfusion, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Lu Ying, Master, Attending physician, Department of Hematology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Blood Transfusion, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Ying, Zhang Xiang-zhong, Liu Xiang-fu, Li Fang, Lin Dong-jun. Therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transfusion on different damaged organs in graft-versus-host disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(23): 3676-3681.
share this article
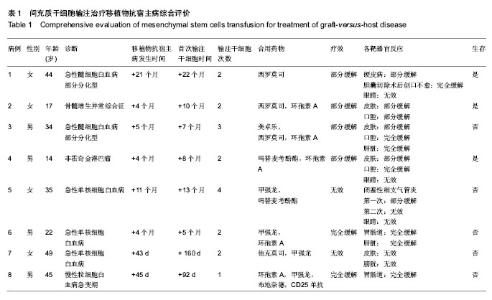
2.1 参与者数量分析 纳入患者8例,治疗过程无脱落,均进入结果分析。 2.2 移植物抗宿主病的累及器官 8例移植物抗宿主病患者中,2例为急性移植物抗宿主病; 6例为慢性移植物抗宿主病,其中2例(病例4,病例6)由急性移植物抗宿主病演变而来。8例移植物抗宿主病患者的病变累及多个器官,其中皮肤5例,口腔3例,眼睛3例,肝脏2例,胃肠道2例,肺脏1例,膀胱1例。 2.3 间充质干细胞的治疗效果 所有患者均在原有免疫抑制剂治疗的基础上接受间充质干细胞治疗。1例输注1次,5例输注2次,1例输注3次,1例输注4次。输注期间所有患者均未出现输液相关不良反应。8例患者中6例经间充质干细胞治疗有效(2例完全缓解,4例部分缓解),2例无效。各受损靶器官治疗反应见表1。5例皮肤病变中4例均得到改善,1例无效,1例在移植后21个月出现硬皮病样慢性移植物抗宿主病,用雷帕鸣治疗后有所改善,1个月后因急性阑尾炎行阑尾切除术,术后切口一直无法愈合,在输注间充质干细胞2次后伤口痊愈。3例口腔病变中2例得到完全缓解,1例部分缓解。2例肝脏病变以及2例胃肠道病变均获得完全缓解。3例眼睛病变用间充质干细胞治疗无效。 2.4 间充质干细胞输注治疗移植物抗宿主病综合评价 见表1。 2.5 间充质干细胞对闭塞性系支气管炎的治疗效果 病例6在移植后11个月出现胸闷、气促,肺部CT提示双肺炎症,左肺下叶不张,右肺上叶、中叶、左肺上叶肺气肿。 纤维支气管镜取右肺背段组织病理检查提示:肺泡间隔增厚伴淋巴细胞浸润。诊断为闭塞性细支气管炎,用抗生素以及大剂量甲基强的松龙治疗后气促逐渐好转,但是患者需要依赖氧疗生活,在输注间充质干细胞2个疗程后患者可以脱离吸氧。2个月后患者又出现严重气促,再次输注间充质干细胞2个疗程后无效果。 2.6 间充质干细胞对膀胱移植物抗宿主病的治疗效果 病例7在移植后25 d出现出血性膀胱炎,检测血以及尿巨细胞病毒DNA均为阳性,在持续膀胱冲洗的基础上,先后予更昔洛韦以及膦甲酸钠治疗后巨细胞病毒DNA转为阴性,但是患者仍有出血性膀胱炎。考虑膀胱移植物抗宿主病的可能性,先后予甲强龙、他克莫司的免疫抑制治疗,患者出血性膀胱炎症状仍有反复。于输注间充质干细胞2次后症状无改善。最后患者行膀胱镜+膀胱黏膜电切活检术,膀胱黏膜病理:送检少许变性纤维组织,表面未见确切披覆上皮,可见少量血块,间质小血管丰富,呈慢性炎症改变。 2.7 临床转归 截止至2013年12月31日,随访中位时间28(7-62)个月。2例完全缓解患者中,病例6在移植后13个月(输注间充质干细胞后7个月)因疾病复发死亡,病例8在移植后4个月(输注间充质干细胞后1个月)因并发中枢神经系统移植后淋巴增殖性疾病而死亡。4例部分缓解患者中,病例3因急性髓细胞白血病复发导致的中枢神经系统白血病,于移植后30个月(输注间充质干细胞后23个月)死亡;其他3例患者随访中位时间41 (26-59)个月,目前已经停用免疫抑制剂;病例4移植后11个月(输注间充质干细胞后3个月)出现外周移植后淋巴增殖性疾病,经美罗华治疗后缓解。2例无效患者均死亡,病例5因闭塞性细支气管炎于移植后23个月(输注间充质干细胞后10个月)死于呼吸功能衰竭;病例7因并发严重感染以及移植后淋巴增殖性疾病死亡。 2.8 不良反应 8例患者总共输注间充质干细胞18次,所有患者均未出现输液相关不良反应。"

| [1] Shlomchik WD. Antigen presentation in graft-vs-host disease. Exp Hematol.2003;31(12):1187-1197. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 128
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 219
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||