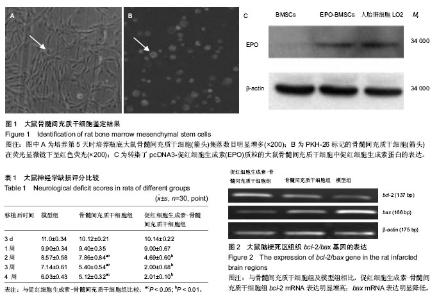
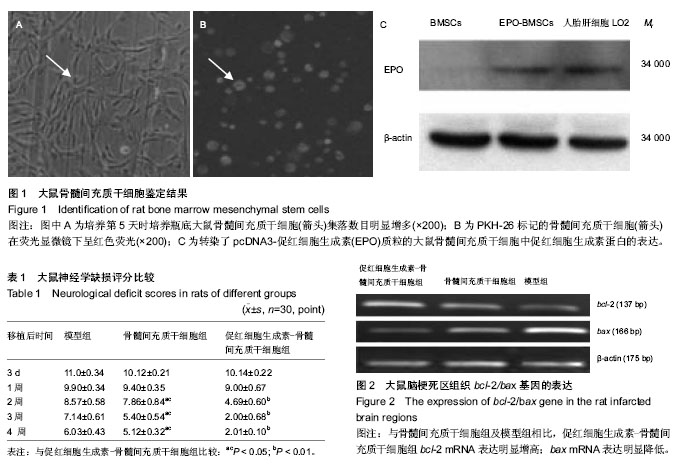
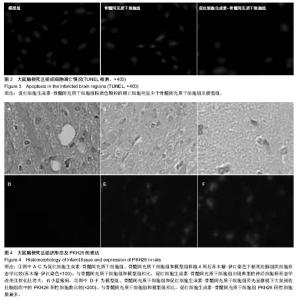
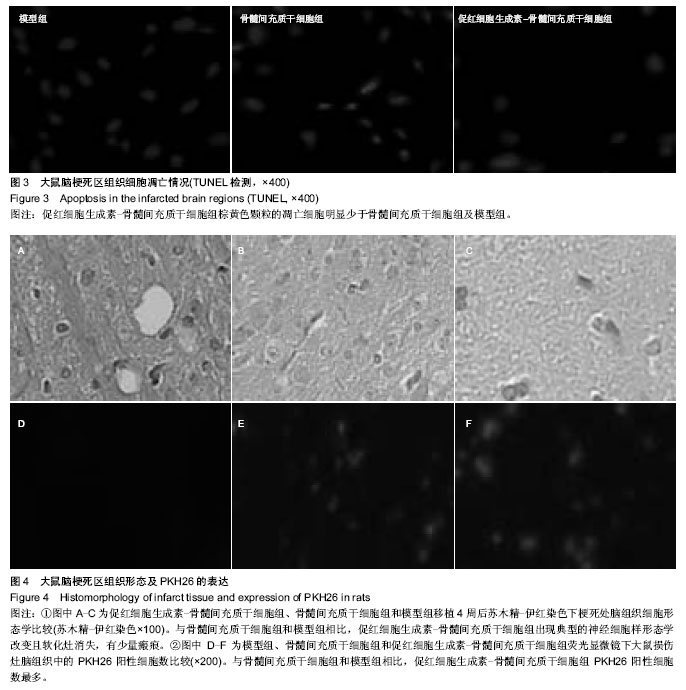
| [1] 王小红,郑美霞.438例脑梗死患者自身免疫性抗体检测的结果分析[J].放射免疫学杂志,2013,26(1):118-119.
[2] 崔立玲,黄国志,王康玲,等.重复经颅磁刺激联合高压氧治疗脑梗死患者的初步研究[J].中华物理医学杂志,2013,35(3):193-196.
[3] Li J, Zhu H, Liu Y, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation protects against cerebral ischemic injury and upregulates interleukin10 expression in Macaca fascicularis. Brain Res. 2010;1334:65-72.
[4] 张婷勇.骨髓间充质干细胞移植并用单唾液酸神经节苷脂治疗大鼠脑梗死[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(14): 2557-2561.
[5] 张洪连,吴晓牧.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死及存在问题[J].中华脑血管病杂志,2010,4(4):300-307.
[6] Wen J, Feng X. Patterns of Nogo-A, NgR, and RhoA expression in the brain tissues of rats with focal cerebral infarction. Transl Res. 2009;154(1):40-48.
[7] 周国庆,金怡,张鹏.沉默RhoA基因对骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗脑梗死大鼠的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,45(14):8416-8420.
[8] 郭敏,巨容,刘秀香,等.重组人促红细胞生成素治疗新生儿缺氧缺血性脑病疗效分析[J].中华神经医学杂志,2007,6(5):523-525.
[9] 肖峰,胡涛.促红细胞生成素对脑出血神经再生影响的临床研究[J].现代预防医学,2011,38(17):3576-3578.
[10] 孟玮,顾兵.重组人促红细胞生成素与神经疾病[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27(12):1640-1643.
[11] 袁丽丽,杜红梅,管英俊,等.促红细胞生成素体外培养鼠胚脑皮质神经干细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,(49): 9174-9177.
[12] 叶夷露,俞月萍,张琦,等.促红细胞生成素鼻腔给药对大鼠慢性脑缺血后血管生成的作用[J].浙江预防医学,2011,23(3):16-18.
[13] Peng Y, Zhang QM, You H, et al. Growth-associated protein 43 and neural cell adhesion molecule expression follow-ing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2010; 5(13):975-980.
[14] Chu K, Kim M, Park KI, et al. Human neural stem cells improve sensorimotor deficits in the adult rat brain with experimental focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2004;1016(2): 145-153.
[15] Laing RJ, Jakubowski J, Laing RW. Middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Which method works best? Stroke. 1993;24(2):294-297.
[16] Li Y, Chen J, Chen XG, et al. Human marrow stromal cell therapyfor troke in rat: Neurotrophins and functional recovery. Neurology. 2002;59(4):514-523.
[17] Kim SS, Yoo SW, Park TS, et al. Neural induction withneurogenin1 increases the therapeutic effects of mesenchymalstem cells in the ischemic brain. Stem Cells. 2008; 26(9):2217-2228.
[18] 柳太云,熊符,林军,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进脑梗死大鼠神经细胞再生和神经功能恢复[J].黑龙江医学,2011,35(9):663-664.
[19] 孟文格,陈小贺.依达拉奉在急性脑梗死时抗氧化及神经内皮保护作用的研究[J].河北医药,2010,32(1):9-10.
[20] Kim SS, Yoo SW, Park TS, et al. Neural induction with neurogenin1 increases the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in the ischemic brain. Stem Cells. 2008;26(9):2217-2228.
[21] 赵小妹,刘永刚.骨髓间充质干细胞与上清液治疗大鼠脑梗死的疗效[J].新乡医学院学报,2012,29(8):571-574.
[22] Li Y, Chen J, Chen XG, et al. Human marrow stromal cell therapyfor troke in rat: neurotrophins and functional recovery. Neurology. 2002;59(4):514-523.
[23] 李伟,薛荣亮.转bcl-2基因大鼠全脑缺血再灌注后c-Myc蛋白的表达[J].山西医科大学学报,2011,42(10):793-796. |