Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (22): 3551-3559.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.22.019
Previous Articles Next Articles
Two surgical methods for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis on safety and efficacy
Mahmootjan•Muhammat, Zhu Shao-bo, Li Jing-feng, Jin Lin, Su Ri-han, Wang Xi
- Department of Orthopedics, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China
-
Revised:2014-04-09Online:2014-05-28Published:2014-05-28 -
Contact:Zhu Shao-bo, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Mahmootjan.Muhammat, Studying for master’s degree, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, Hubei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Mahmootjan•Muhammat, Zhu Shao-bo, Li Jing-feng, Jin Lin, Su Ri-han, Wang Xi. Two surgical methods for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis on safety and efficacy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(22): 3551-3559.
share this article
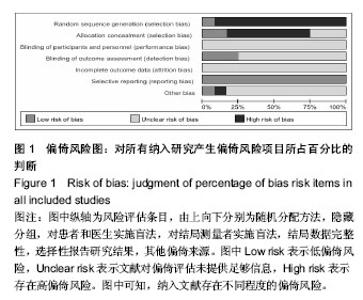
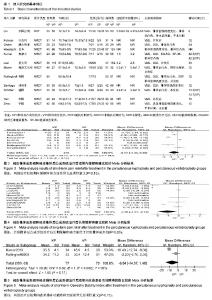
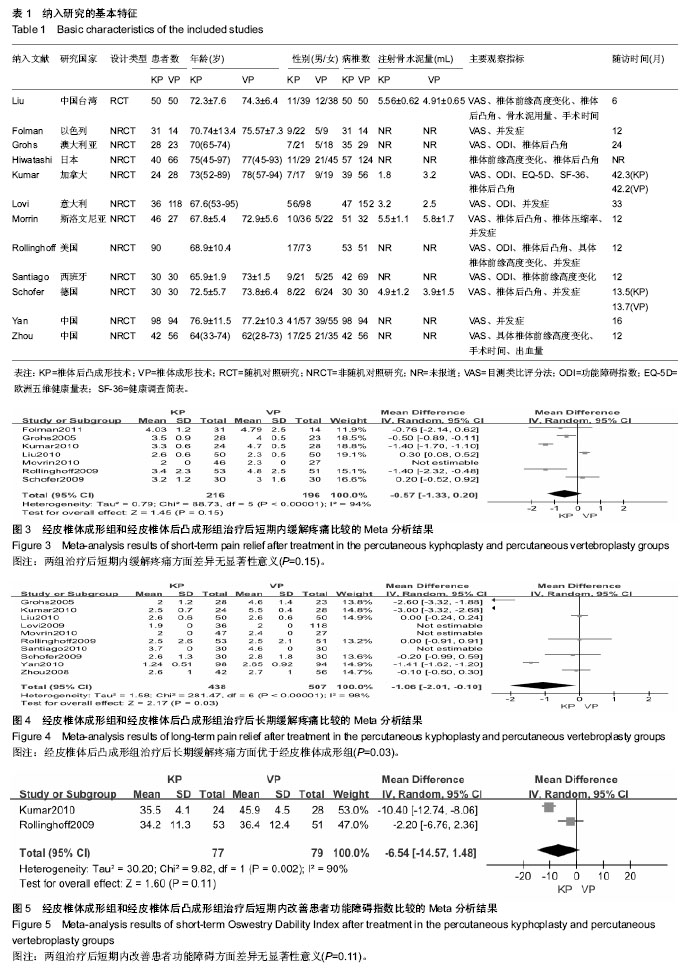
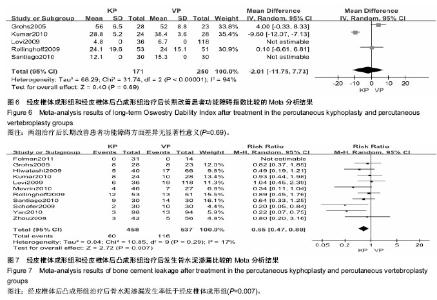
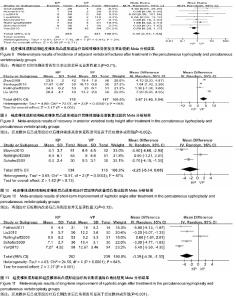
2.3 Meta分析统计学结果 2.3.1 缓解疼痛差异 所有12个研究中11个研究提供了经皮椎体后凸成形技术和经皮椎体成形技术治疗前后疼痛目测类比评分[21-23,25-32]。其中有7个研究报道两种治疗方式对短期(治疗后1周内)疼痛缓解进行分析[21-23,25,27-28,30]。纳入研究间存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=94%),故采用随机效应模型合并分析。Meta分析结果显示,经皮椎体后凸成形技术与经皮椎体后凸成形技术在短期内缓解疼痛差异无显著性意义(MD=-0.57,95%CI=-1.33,0.20;P=0.15)(图3)。对此进行敏感性分析发现,分别剔除7项研究,各合并效应量均无本质性改变,且森林图方向未改变,说明该研究结果较可靠、稳定。有10个研究报道两种治疗方式对长期(治疗后6个月或更长时间)疼痛缓解进行分析[21,23,25-32]。各研究间有异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=98%),故采用随机效应模型合并分析。Meta分析结果表明:两种治疗方式长期缓解疼痛差异有显著性意义(MD=-1.06,95%CI=-2.01,-0.10;P=0.03)(图4),经皮椎体后凸成形技术组治疗后长期疼痛缓解方面优于经皮椎体成形技术组。去除任一项研究进行敏感性分析发现,各合并效应量仍都具有显著性意义,森林图方向未改变,说明该研究结果可信度大。 2.3.2 改善患者功能障碍方面差异 在5个研中提到治疗前及治疗后的功能障碍指数[23,25-26,28-29],2个研究具有充足的短期功能障碍指数[25,28],各研究间有异质性(P < 0.002,I2=90%),采用随机效应模型合并分析。统计学分析结果示,两种治疗方法在短期内改善患者功能障碍方面差异无显著性意义(MD=-6.54,95%CI=-14.57,1.48;P=0.11)(图5)。敏感性分析发现,分别剔除5项研究,各合并效应量均未出现本质性改变,且森林图方向未改变,说明该研究结果可靠。共有5个研究提供了远期功能障碍指 数[23,25-26,28-29]。各研究间有异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=94%),采用随机效应模型合并分析。Meta分析结果表明:两种治疗方法远期改善患者功能障碍的差异也无显著性意义(MD=-2.01,95%CI=-11.75,7.73;P=0.69)(图6)。敏感性分析结果示,分别剔除5项研究,各合并效应量均未出现本质性改变,且森林图方向未改变,说明该研究结果可靠。 2.3.3 骨水泥渗漏发生率的差异 有11个研究给出了骨水泥渗漏有关的数据[22-32]。各研究间有较好的同质性(P=0.29,I2=17%),故采用固定效应模式进行统计学分析。Meta分析结果示,两种方法治疗后骨水泥渗漏的发生率差异有显著性意义(RR=0.65,95%CI=0.47,0.89;P=0.007,图7)。经皮椎体后凸成形组较经皮椎体成形组具有较低的骨水泥渗漏发生率的优势。 2.3.4 相邻椎体骨折发生率的差异 共有8个研究报道了治疗后发生相邻椎体骨折相关的数据[21,23,25-28,30-31]。各研究间有同质性(P=0.41,I2=2%),故采用固定效应模式进行统计学分析。Meta分析结果表明:两种方法治疗后相邻椎体骨折发生率的比较差异无显著性意义(RR=0.90,95%CI=0.53,1.53;P=0.71)(图8)。"
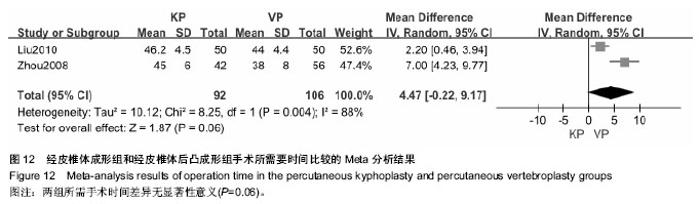
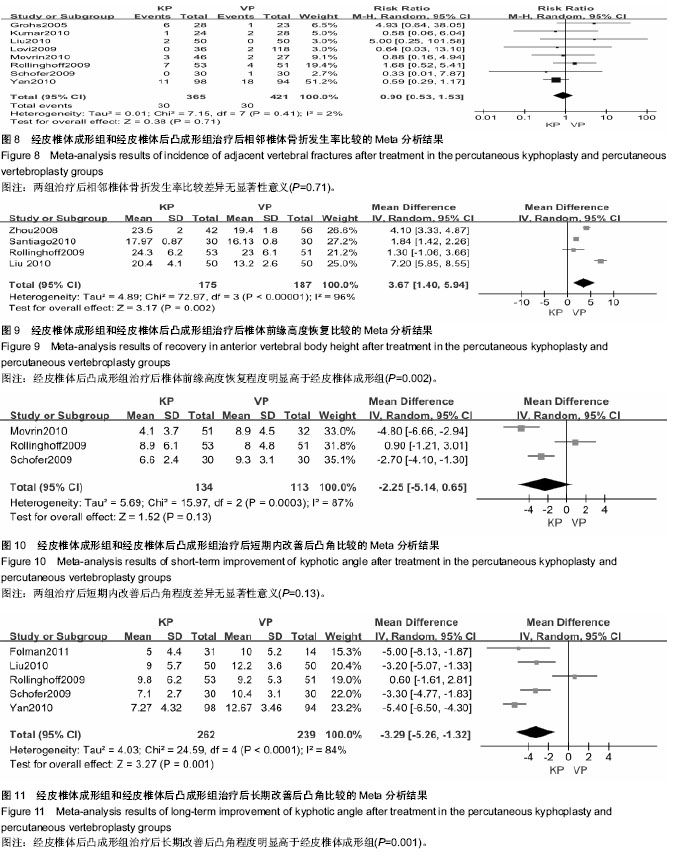
2.3.5 椎体前缘高度的恢复程度的差异 有4个研究提供了治疗前后病患椎体前缘高度恢复情况[21,28- 29,32]。研究间有较大的异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=96%),采用随机效应模型合并分析。Meta分析结果表明:治疗后椎体高度恢复方面两种治疗方法差异有显著性意义(MD=3.67,95%CI=1.40,5.94;P=0.002)(图9)。对此进行敏感性分析后发现,剔除任一项研究,各合并效应量仍有统计学差异,且森林图方向未改变,说明该研究结果稳定。 可见经皮椎体后凸成形组治疗后椎体前缘高度的恢复程度明显高于经皮椎体成形组。 2.3.6 改善后凸角差异 有3个研究对于两种治疗方法在治疗后短期内后凸角恢复效果进行了调查[27-28,30]。研究间存在异质性(P<0.000 3,I2=87%),采用随机效应模型合并分析。Meta分析结果表明:经皮椎体后凸成形组及经皮椎体成形组治疗后短期内减小后凸角差异无显著性意义(MD=2.25,95%CI=-5.14,0.65;P=0.13)(图10)。敏感性分析结果示,剔除任一项研究,各合并效应量均无统计学差异,且森林图方向未改变,说明该研究结果稳定。有5个研究提供了治疗后长期后凸角的变化[21-22,28,30-31]。研究间存在异质性(P < 0.000 1,I2=84%),采用随机效应模型合并分析。Meta分析结果表明:两种方法治疗后远期改善后凸角差异有显著性意义(MD=-3.29,95%CI=-5.26,-1.32;P=0.001)(图11)。经皮椎体后凸成形组治疗后长期改善后凸角的程度明显高于经皮椎体成形组。敏感性分析结果示,剔除任一项研究,各合并效应量仍有统计学差异,且森林图方向未改变,说明该研究结果稳定。 2.3.7 手术所需时间的差异 有2个研究记录了两种治疗方法所需要的手术时间[21,32]。研究间存在异质性(P < 0.004,I2=88%),采用随机效应模型合并分析Meta分析结果显示,经皮椎体后凸成形组及经皮椎体成形组手术所需时间差异无显著性意义(MD=4.47,95%CI=-0.22,9.17;P=0.06)(图12)。"
| [1] Warriner AH, Saag KG.Osteoporosis diagnosis and medical treatment.Orthop Clin North Am. 2013;44(2):125-135.
[2] Fenniri H.The Canadian Regenerative Medicine and Nanomedicine Enterprise (CARMENE).Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1(3):225-227.
[3] Liu ZH, Zhao YL, Liu LN. Epidemiological investigation of peak bone density and the incidence of osteoporosis in China. J Bone Miner Res.1997;12:S245.
[4] Njeh CF, Boivin CM, Langton CM.The role of ultrasound in the assessment of osteoporosis: a review.Osteoporos Int. 1997; 7(1):7-22.
[5] Chen LH, Lai PL, Chen WJ.Current status of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture.Chang Gung Med J. 2011;34(4):352-359.
[6] Silverman SL.The clinical consequences of vertebral compression fracture.Bone. 1992;13 Suppl 2:S27-31.
[7] Lee HM, Park SY, Lee SH,et al.Comparative analysis of clinical outcomes in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (OVCFs): conservative treatment versus balloon kyphoplasty.Spine J. 2012;12(11):998-1005.
[8] Papaioannou A, Watts NB, Kendler DL,et al.Diagnosis and management of vertebral fractures in elderly adults.Am J Med. 2002;113(3):220-228.
[9] Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB,et al.Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group.Lancet. 1996;348(9041):1535-1541.
[10] Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P,et al.Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty.Neurochirurgie. 1987;33(2):166-168.
[11] Yu SW, Yang SC, Kao YH,et al.Clinical evaluation of vertebroplasty for multiple-level osteoporotic spinal compression fracture in the elderly.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(1):97-101.
[12] Zampini JM, White AP, McGuire KJ.Comparison of 5766 vertebral compression fractures treated with or without kyphoplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(7):1773-1780.
[13] Zoarski GH, Snow P, Olan WJ,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: quantitative prospective evaluation of long-term outcomes.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002;13(2 Pt 1):139-148.
[14] Lieberman I, Reinhardt MK.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for osteolytic vertebral collapse.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (415 Suppl):S176-186.
[15] Watts NB, Harris ST, Genant HK.Treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty.Osteoporos Int. 2001;12(6): 429-437.
[16] Evans AJ, Jensen ME, Kip KE, et al.Vertebral compression fractures: pain reduction and improvement in functional mobility after percutaneous polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty retrospective report of 245 cases.Radiology. 2003;226(2):366-372.
[17] Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22(2): 373-381.
[18] Klazen CA, Lohle PN, de Vries J,et al.Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial.Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1085-1092.
[19] Wardlaw D, Cummings SR, Van Meirhaeghe J, et al.Efficacy and safety of balloon kyphoplasty compared with non-surgical care for vertebral compression fracture (FREE): a randomised controlled trial.Lancet. 2009;373(9668):1016-1024.
[20] Boonen S, Wahl DA, Nauroy L,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in the management of vertebral compression fractures.Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(12):2915-2934.
[21] Liu JT, Liao WJ, Tan WC,et al.Balloon kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a prospective, comparative, and randomized clinical study.Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(2): 359-364.
[22] Folman Y, Shabat S.A comparison of two new technologies for percutaneous vertebral augmentation: confidence vertebroplasty vs. sky kyphoplasty.Isr Med Assoc J. 2011; 13(7):394-397.
[23] Grohs JG, Matzner M, Trieb K,et al.Minimal invasive stabilization of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective nonrandomized comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(3):238-242.
[24] Hiwatashi A, Westesson PL, Yoshiura T,et al.Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty produce the same degree of height restoration.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(4):669-673.
[25] Kumar K, Nguyen R, Bishop S. A comparative analysis of the results of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Neurosurgery. 2010;67 (3 Suppl Operative):ons171-188.
[26] Lovi A, Teli M, Ortolina A,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: complementary techniques for the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. A prospective non-randomised study on 154 patients.Eur Spine J. 2009;18 Suppl 1:95-101.
[27] Movrin I, Vengust R, Komadina R.Adjacent vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a comparison of balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(9):1157-1166.
[28] Röllinghoff M, Siewe J, Zarghooni K,et al.Effectiveness, security and height restoration on fresh compression fractures--a comparative prospective study of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2009;52(5-6):233-237.
[29] Santiago FR, Abela AP, Alvarez LG,et al.Pain and functional outcome after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. A comparative study.Eur J Radiol. 2010;75(2):e108-113.
[30] Schofer MD, Efe T, Timmesfeld N,et al.Comparison of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in the treatment of fresh vertebral compression fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(10):1391-1399.
[31] Yan D, Duan L, Li J,et al.Comparative study of percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(5):645-650.
[32] Zhou JL, Liu SQ, Ming JH,et al.Comparison of therapeutic effect between percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty on vertebral compression fracture.Chin J Traumatol. 2008; 11(1):42-44.
[33] Xing D, Ma JX, Ma XL,et al.A meta-analysis of balloon kyphoplasty compared to percutaneous vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20(6):795-803.
[34] Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Jasper LE,et al.The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of cement volume on mechanical behavior.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1537-1541.
[35] Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Deramond H,et al.An ex vivo biomechanical evaluation of a hydroxyapatite cement for use with kyphoplasty.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22(6): 1212-1216.
[36] Heini PF, Wälchli B, Berlemann U.Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty with PMMA: operative technique and early results. A prospective study for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures.Eur Spine J. 2000;9(5):445-540.
[37] Togawa D, Bauer TW, Lieberman IH,et al.Histologic evaluation of human vertebral bodies after vertebral augmentation with polymethyl methacrylate.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(14):1521-1527.
[38] Hulme PA, Krebs J, Ferguson SJ,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(17):1983-2001.
[39] Eck JC, Nachtigall D, Humphreys SC,et al.Comparison of vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the literature.Spine J. 2008;8(3):488-497.
[40] Berlemann U, Franz T, Orler R,et al.Kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a prospective non-randomized study.Eur Spine J. 2004;13(6):496-501. |
| [1] | Li Jing, Yang Long, Wang Jian-ji, Liu Qin, Zou Qiang, Sun Yu, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Three-dimensional reconstruction based on DICOM data and its application for orthopedic implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1046-1051. |
| [2] | Ye Xiang-yang, Sun Xiang, Tang Li-xin, Zhen Ping, Geng Bin, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo. Acetabular liner wear of cross-linked versus conventional polyethylene for total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1143-1148. |
| [3] | Wang Ling, Zhao Hong-xia, Hua Qiang. Percutaneous vertebroplasty, percutaneous kyphoplasty and expansive pedicle screw fixation for repairing primary osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 350-355. |
| [4] | Lu Zhong-lin, Cao Zhi-qiang, Gao Guo-liang, Jing Qing-ling, Zhang Wei, Huang Yong. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis during waiting period before operation for calcaneal fractures by ultrasound elastography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 423-427. |
| [5] | Zhang Tai-liang, Zhang Lei, Lian Zhi-ming, Yang Guang-zhong. Effect of remnant preservation on recovery of knee proprioception in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 471-477. |
| [6] | Zha Yuan-yu, Yang Yang, Chen Shu-zhen, Wei Ren-xiong, Zhang Shu-wei, Jin Wei. Meta-analysis of posterior laminectomy and instrumented fusion versus laminoplasty in treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 485-492. |
| [7] | Bai Zhao-hui, Zhang Ying, Yin Qing-shui, Xia Hong, Wang Jian-hua, Xu Jun-jie. Navigational template applied in the orthopaedic field in China: a bibliometric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3023-3030. |
| [8] | Qiu Hao, Lu Min-peng, Dong Jing, Zhang Zhong-zu, Chu Tong-wei, Wang Qun-bo, Quan Zheng-xue, Jiang Dian-ming. Subtotal corpectomy and reconstruction with titanium mesh cage implantation and pedicle screw fixation through posterior approach in treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture or thoracolumbar fracture dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 7932-7938. |
| [9] | Hu Bing-yan, Ai Jin-wei, Chen Qiong, Yao Zhong-jun . InterTan nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for femoral intertrochanteric fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(53): 8010-8021. |
| [10] | Zha Yuan-yu, Yang Yang, Zhou Yi-chi, Wei Ren-xiong, Zhang Shu-wei, Jin Wei. Meta-analysis of anterior screw fixation versus posterior cervical fusion in treatment of odontoid fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7288-7296. |
| [11] | Gu Yong, Wang Qiang, Xin Tian-wen, Yang Hui-lin, Chen Liang . Posterior cervical open-door expansive laminoplasty with mini-titanium plate: correlation between cervical sagittal alignment and repair effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6570-6576. |
| [12] | Xu Jian-da, Gao Yi, Zhao Hong, Peng Li-bo, Zheng Chong, Wang Bin, Qu Yu-xing, Zhao Jian-ning. Viper system and pedicle screw fixation for treating thoracolumbar compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6583-6589. |
| [13] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiao-hui, Hu Qun-sheng, Pang Zhi-hui, Zhou Guang-quan, Li Yue . Different fixations for intertrochanteric fracture affect proximal femur stress: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6599-6605. |
| [14] | Xu Can, Li Ming-qing, Wang Cheng-gong, Li Kang-hua, Liu Hua. Research progress of bone microarchitecture and microdamage detection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6673-6681. |
| [15] | Zhang Hui, Gao Zhong-yu, Xu Cai-yuan, Zhang Tong-xing, Zhang Tao. Vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: missed diagnosis, severe vertebral compression, bone cement leakage and recurrent fractures in 225 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5256-5262. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||