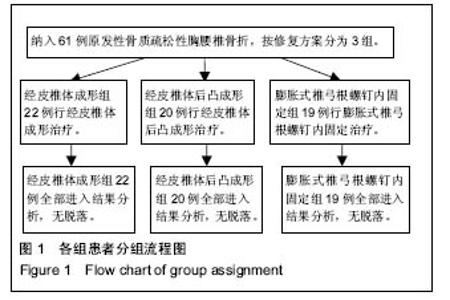
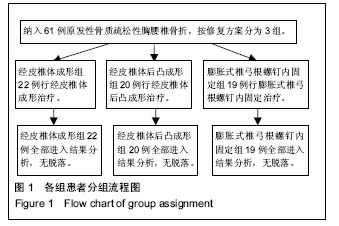
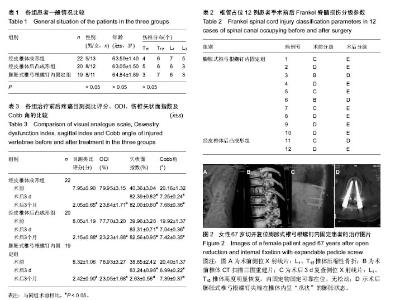
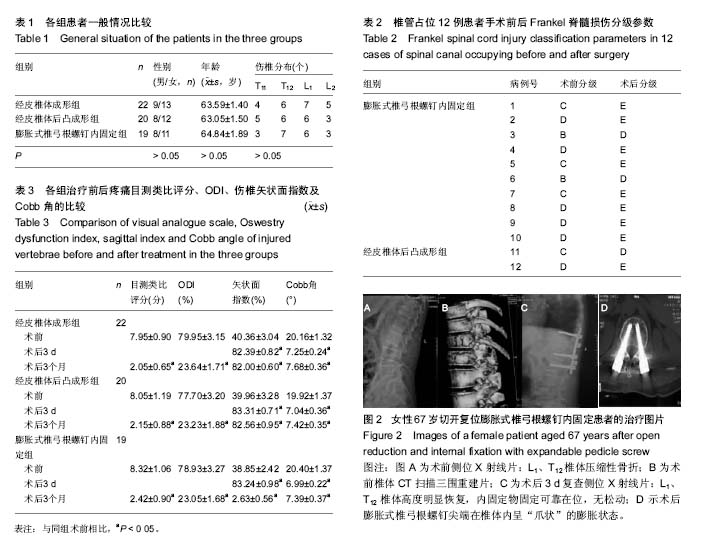
| [1] 郑光新,赵晓鸥,刘广林,等. Oswestry功能障碍指数评定腰痛患者的可信性[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2002,12(1):13-15.[2] Kharal M, Al-Hajjaj A, AI-Ammri M, et al. Meeting the American Diabetic Association standards of diabetic care. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2010;21(4):678-685.[3] 周伟. 高黏度骨水泥及其椎体成形治疗重度骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(46):7534-7538.[4] 郑灿,胡德志,李笔锋,等.术前垫枕结合经皮椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折的临床效果观察[J]. 中国医药导报, 2016,13(30):91-94.[5] 唐波.垫枕复位配合经椎弓根植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的临床疗效观察[D].湖南中医药大学,2014.[6] Gong HS,Oh WS,Chung MS,et al. Patients with wrist fractures are less likely to be evaluated and managed for osteoporosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:2376-2380.[7] 邓飞鹏.椎体骨水泥注入联合抗骨质疏松药物治疗急性骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折临床疗效观察[J].现代诊断与治疗,2015, 26(19):4428-4429.[8] 刘瑶瑶,孙东,张泽华,等.用于骨质疏松椎体固定的椎弓根螺钉进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(23): 1982-1986.[9] Gaines RW Jr. The use of pedicle-screw internal ixation for the operative treatment of spinal disorders. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2000;82-A(10): 1458-1476.[10] Campbell PG, Harrop JS. Incidence of fracture in adjacent levels in patients treated with balloon kyphoplasty: a review of the literature. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2008;1(1): 61-64.[11] Tseng YY, Su CH, Lui TN, et al. Prospective comparison of the therapeutic effect of teriparatide with that of combined vertebroplasty with antiresorptive agents for the treatment of new-onset adjacent vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(5): 1613-1622.[12] 王翀,李京,田征,等.经皮椎体成形术与非手术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(6): 493-498.[13] Nagad P, Rawall S, Kundnani V, et al. Postvertebroplasty instability. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(4):387-393.[14] 周炳荣,张杰,朱建平,等. PKP球囊扩张体积对骨水泥注射剂量及邻椎再骨折的影响[J].江苏医药,2016,42(15):1713-1715.[15] 王月,孔庆海,王铁铸,等. 椎体成形术后相邻椎体再骨折的临床研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(3):243-246.[16] 张震. 球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术治疗老年骨质疏松脊柱压缩骨折的适应症和并发症的初步探讨[J]. 中国医学工程,2014,22(2):167.[17] 高明暄,李旭升,甄平,等.骨密度对膨胀式椎弓根螺钉固定强度影响的力学研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013, 27(8): 969-973.[18] Lei W, Wu Z. Biomechanical evaluation of an expansive pedicle screw in calf vertebrae. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(3): 321-326.[19] 石磊,王陵,雷伟,等.低弹性模量膨胀螺钉在骨质疏松绵羊的体内研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2011, 17(9): 761-765.[20] Chen LH, Hsieh MK, Liao JC, et al. Repeated percutaneous vertebroplasty for refracture of cemented vertebrae. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(7):927-933.[21] 谢继平. PVP与PKP治疗老年骨质疏松性压缩性骨折早期缓解疼痛的效果对比[D].河北医科大学,2015.[22] Nagad P, Rawall S, Kundnani V, et al. Postvertebroplasty instability. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(4):387-393.[23] 何保玉,刘宝戈,李学民,等.骨水泥弥散容积率在骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折PKP术后疗效评价中的应用[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2016,15(1):68-73.[24] 丁惠宇,夏建龙. PVP、PKP治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折的疗效评价标准研究进展[J].山东医药,2014,54(14):101-103.[25] 张玉忠.老年骨质疏松性脊柱压缩骨折治疗进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(18):5316-5318.[26] 卢昌怀,刘志军,张宏波,等.骨水泥量及分布对椎体成形术后相邻椎体生物力学影响的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(1):29-33.[27] Matsumoto T, Ohnishi I, Bessho M, et al. Prediction of vertebral strength under loading conditions occurring in activities of daily living using a computed tomography-based nonlinear finite element method. Spine. 2009;34(14):1464-1469. |