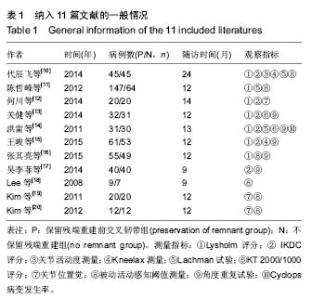
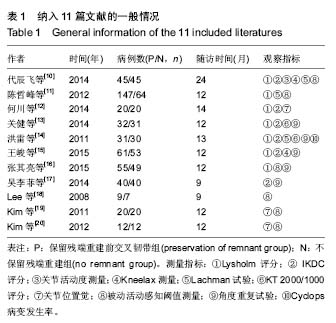
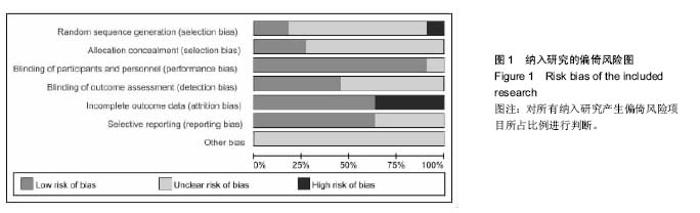
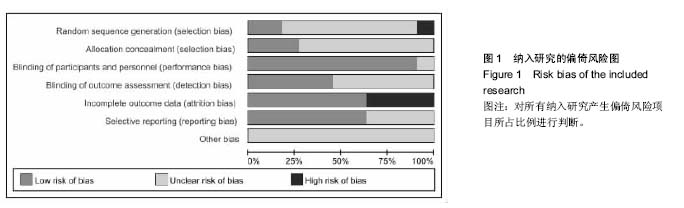
| [1] 冯华,洪雷,耿向苏,等.前十字韧带损伤合并内侧半月板RAMP损伤[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(11):651-655.[2] Childs SG. Pathogenesis of anterior cruciate ligament injury. Orthop Nurs. 2002;21:35-40.[3] Malliou P, Gioftsidou A, Pafis G, et al. Proprioception and functional deficits of partial meniscectomized knees. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2012;48(2):231-236.[4] 郝永红,刘宏丽,孙鸿安,等.本体感觉强化训练在前交叉韧带重建术后康复中的应用[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2013,35(5): 398-399.[5] 解东风,李奎,李鑫,等.本体感觉训练在膝关节周围骨折术后所致关节僵硬患者康复治疗中的作用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2013,28(10):945-947.[6] 倪锋, 赵金忠.前十字韧带重建术保留残端纤维与本体感觉功能的恢复[J].中华骨科杂志,2012, 32(2):106-110.[7] Kazusa H,Nakamae A,Ochi M.Augmentation techique for anterior cruciate ligament injury. Clin Sports Med. 2013;32(1): 127-140.[8] Song GY, Zhang J, Li X, et al. Biomechanical and biological findings between acute anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with and without an augmented remnant repair: a comparative in vivo animal study. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(2): 307-319.[9] 逯代锋,肖模超,张云鹏,等.关节镜下前交叉韧带保留残端重建的二次关节镜检查研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2015,29(8): 941-944.[10] 代辰飞,白伦浩,高琳,等.前交叉韧带重建术后本体感觉恢复评价:股骨牵张保残法与标准方法比较[J].中国运动医学杂志,2014, 33(1):5-9.[11] 陈哲峰,王青,郭敦明,等.前交叉韧带断裂的关节镜下保留残端重建手术治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(8):693-696.[12] 何川,李彦林,李晓刚,等.前交叉韧带保留残端重建术对膝关节本体感觉功能恢复的疗效分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014, 28(4):442-447.[13] 关健,聂喜增,李锋,等.关节镜下前交叉韧带断裂保残重建的疗效分析[J].河北医药,2014,36(11):1647-1649.[14] 洪雷,李旭,王雪松,等.关节镜下保留残端重建前交叉韧带的临床前瞻性对照研究[J].中华外科杂志,2011,49(7):586-591.[15] 王峻,李雁,于腾波,等.保留与非保留残端的前交叉韧带重建:6个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(29):4640-4644.[16] 张其亮,赵蕾,滕学仁.保留残端前交叉韧带重建对膝关节本体感觉恢复的影响临床研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(8): 739-743.[17] 吴李菲,蔡贤华,黄卫兵,等.保残重建ACL对膝关节本体感觉恢复的影响[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2014,22(12):47-48.[18] Lee BI, Kwon SW, Kim JB,et al.Comparison of clinical results according to amount of preserved remnant in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using quadrupled hamstring graft. Arthroscopy. 2008;24(5):560-568. [19] Kim DK,Park WH.Proprioceptive and strength comparison of remnant preserved versus conventional anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Korean J Sports Med. 2011;29(2): 99-104.[20] Kim KM,Han JK,Yi Y,et al.Proprioceptive and knee joint kinematics for comparison of remnant preserved versus non-remnant anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using achilles allograft. Korean J Sports Med. 2012;30(2):100-109.[21] Dhillon MS,Bali K, Prabhakar S.Proprioception in anterior cruciate ligament deficient knees and its relevance in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Indian J Orthop. 2011;45(4): 294-300. [22] Lee DH, Lee JH, Ahn SE, et al.Effect of time after anterior cruciate ligament tears on proprioception and postural stability. PLoS One.2015;10(9):e0139038.[23] Dhillon MS,Bali K,Vasistha RK. Immunohistological evaluation of proprioceptive potential of the residual stump of injured anterior cruciate ligaments. Int Orthop.2010;34(5): 737-741. [24] Li H,Chen J,Chen S. Remnant repair-enhanced polyethylene terepthalate artificial ligament graft ligamentization. Int J Sports Med. 2015;36(12):1015-1020.[25] Takazawa Y,Ikeda H,Kawasaki T,et al.ACL reconstruction preserving the ACL remnant achieves good clinical outcomes and can reduce subsequent graft rupture. Orthop J Sports Med. 2003;1(4):1-7.[26] Kondo E, Yasuda K, Onodera J, et al. Effects of remnant tissue preservation on clinical and arthroscopic results after anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(8): 1882-1892.[27] Hong L, Li X, Zhang H, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with remnant preservation: a prospective, randomized controlled study. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(12): 2747-2755.[28] Song GY, Zhang J, Li X,et al. Acute anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with an augmented remnant repair: a comparative macroscopic and biomechanical study in an animal model.Arthroscopy. 2014;30(3): 344-351.[29] Arockiaraj J,Korula RJ,Oommen AT,et al.Proprioceptive changes in the contralateral knee joint following anterior cruciate injury. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(2):188-191. |