Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (44): 6599-6605.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.44.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Different fixations for intertrochanteric fracture affect proximal femur stress: a finite element analysis
Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiao-hui, Hu Qun-sheng, Pang Zhi-hui, Zhou Guang-quan, Li Yue
- Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2016-08-09Online:2016-10-28Published:2016-10-28 -
About author:Jiang Zi-wei, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2014A030310379; the General Program of Science and Technology Plan of Guangzhou City, No. 1563000664
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Zheng Xiao-hui, Hu Qun-sheng, Pang Zhi-hui, Zhou Guang-quan, Li Yue . Different fixations for intertrochanteric fracture affect proximal femur stress: a finite element analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6599-6605.
share this article
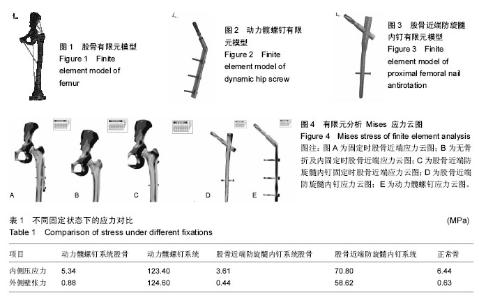
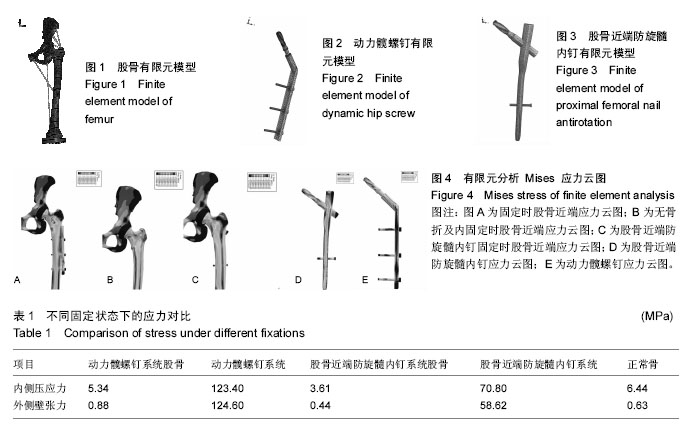
在加载各方向应力下,经有限元运算,得到有限元分析 Mises 应力云图显示:①股骨近端防旋髓内钉及动力髋螺钉内固定组都可以明显减少股骨内侧压应力,但股骨近端防旋髓内钉组对内侧皮质特别是骨折端的压应力减小更明显(图4A-C);②股骨近端防旋髓内钉及动力髋螺钉均为压应力及张应力的主要承担着,但股骨近端防旋髓内钉承担的力量更小,分布更加均匀,而动力髋螺钉可见较多的应力集中区域(图4D,E);③股骨近端防旋髓内钉在减少骨折端应力的同时,对正常骨质应力的传导的影响要小于动力髋螺钉,其力学传导图更接近于正常股骨(图4A-C);④对于大转子外侧壁来说,股骨近端防旋髓内钉组外侧壁承受的张力小于动力髋螺钉组,其张力主要集中在螺旋刀尾以下的股骨皮质(图4A-C)。作者采用在不同状态下股骨及固定器械压力及张力集中的相同区域分别计算压应力、张应力均值来确定相应的应力改变,具体数值见表1。"
| [1] Fichman SG, Mäkinen TJ, Safir O, et al. Arthroplasty for unstable pertrochanteric hip fractures may offer a lower re-operation rate as compared to cephalomedullary nailing. Int Orthop. 2015;40(1):1-6. [2] Bhakat U, Bandyopadhayay R. Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing and Dynamic Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur. Open J Orthop. 2013;3(7):291-295. [3] Aktselis I, Kokoroghiannis C, Fragkomichalos E, et al. Prospective randomised controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus a sliding hip screw for intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. Int Orthop. 2014; 38(1):155-161. [4] Guo XF, Zhang KM, Fu HB, et al. A comparative study of the therapeutic effect between long and short intramedullary nails in the treatment of intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly. Chin J Traumatol. 2015;18(6):332-335. [5] Simmermacher RK,Ljungqvist J,Bail H,et al.The new proximal femoral nail antirotation(PFNA) in daily practice:results of a multicentre clinical study.Injury. 2008;39(8):932-939. [6] 杨灵,江伟,刘跃洪,等.股骨近端锁定钢板治疗股骨转子间骨折的生物力学研究[J].创伤外科杂志, 2015,(02): 135-137. [7] Chang CW, Chen YN, Li CT, et al. Role of the compression screw in the dynamic hip–screw system: A finite-element study. Med Eng Phys. 2015;37(12): 1174-1179. [8] Widjaja W, Hartung C. Finite element analysis of an additional implant for intramedullary nailing. Biomed Tech Ber. 2000;45(12):338-342. [9] Wu X, Yang M, Wu L. A Biomechanical Comparison of Two Intramedullary Implants for Subtrochanteric Fracture in Two Healing Stages: A Finite Element Analysis. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2015;2015:1-7. [10] Chen Y, Wang G, Zhou D, et al. Computational Study in Effects of Nail- and Plate-Implants on the Treatment of Pertrochanteric and Intertro-chanteric Fractures. Mat Perf Characterizat. 2015;4(1):17-28. [11] Hou W, Zhang W, Zhao H. Analysis on three-dimensional finite element of rebuilding femoral calcar in femoral head replacement. J Modern Med Health. 2015;21(6):1585-1592. [12] 王丽珍,赵峰,樊瑜波.新型带锁髓内钉在股骨转子间骨折愈合过程中的生物力学研究[J].医用生物力学,2011, 26(4): 305-309. [13] Brown TD, Hild GL. Pre-collapse stress redistributions in femoral head osteonecrosis--a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Biomech Eng. 1983;105(2): 171-176. [14] Grecu D, Pucalev I, Negru M, et al. Numerical simulations of the 3D virtual model of the human hip joint, using finite element method. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2010;51(1):151-155. [15] Stewart KJ, Edmonds-Wilson RH, Brand RA, et al. Spatial distribution of hip capsule structural and material properties. J Biomech. 2002;35(11): 1491-1498. [16] Wang YS, Zhang MC, Huang BS. A finite element stress analysis of severe intertrochanic fractures treated with artificial femoral head replacement. Chin J Clin Anat. 2013;31(5):577-581. [17] Evans EM.The treatment of trochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 1949;31:190-203. [18] Jensen JS.Classification of trochanteric fracture.Acta Orthop Scand.1980;51(5):803-810. [19] Parker MJ. Trochanteric hip fracture.Fixation failure commoner with femoral medialization,a comparision of 101 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996;67(4):329-332. [20] Liang GK, Zakaria Z, Sharifudin MA, et al. Intertrochanteric fracture fixation with Dynamic Hip Screw: Is tip-apex distance measurement useful for predicting fixation failure? Int Med J Malays. 2016; 15(1):31-34. [21] Li S, Chang SM, Jin YM, et al. A mathematical simulation of the tip-apex distance and the calcar-referenced tip-apex distance For Intertrochanteric fractures reduced with lag screws. Injury. 2016;47(6):1302-1308. [22] Gotfried Y.The lateral trochateric wall:a key element in the reconstruction og unstable pertrochateric hip fracture.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;425:82-86. [23] Palm H,Jacobsen S,Sonne-Holm S,et al.Integrity of the lateral femoral wall in intertrochanteric hip fracture:an important predictor of reoperation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;9(3):470-475. [24] Haq RU, Manhas V, Pankaj A, et al. Proximal femoral nails compared with reverse distal femoral locking plates in intertrochanteric fractures with a compromised lateral wall; a randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2014;38(7):1443-1449. [25] Mirzaei M, Keshavarzian M, Naeini V. Analysis of strength and failure pattern of human proximal femur using quantitative computed tomography (QCT)-based finite element method. Bone. 2014;64(7):108-114. [26] Hambli R, Allaoui S. A Robust 3D Finite Element Simulation of Human Proximal Femur Progressive Fracture Under Stance Load with Experimental Validation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(12): 2515-2527. [27] Kim Y,Bahk WJ,Yoon YC, et al. Radiologic healing of lateral femoral wall fragments after intramedullary nail fixation forA3.3 Intertrochan-teric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(10):1349-1356. [28] Kim Y, Bahk WJ, Yoon YC, et al. Radiologic healing of lateral femoral wall fragments after intramedullary nail fixation for A3.3 intertro-chanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(10):1349-1356. [29] Russell TA,Sander R.Pertrochanteric hip fracture:time for change. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(4):189-190. [30] Kuzyk PR, Lobo J, Whelan D, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of extramedullary versus intramedullary fixation for reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(1):31-38. [31] 杨声波,陈文帅,沈伟冰.PFNA与DHS治疗23例老年股骨转子间骨折疗效对比分析[J].福建医药杂志, 2007,29(6): 35. [32] Adams CL,Robinson CM,Court-brown CM,et al.Prospective radomized controlled trial of an intramedullary nailversus dynamic scrand plate for intertrochanteric fracture of femur.J Orthop Traum. 2001;15(2):394. [33] 方大标,王秋根.医源性因素对DHS治疗髋部骨折疗效的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(5):525. [34] 王建辉,刘长贵,刘瑞波.PFN和DHS治疗股骨转子间骨折的生物力学研究及临床疗效观察[J].骨与关节损伤杂志, 2004,19(11):739. [35] Li H, Hepp P, Komer J, et al. Proximal humeral fractures: how stiff should an implant be? A comparative mechanical study with-implants in human spedmens. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123(2-3): 74-81. [36] Kuzyk PR, Lobo J, Whelan D,et al. Biomechanical evaluation of extramedullary versus intramedullary fixation for reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(1):31-38. [37] Studer P, Suhm N, Wang Q, et al. Displaced trochanteric fragments lead to poor functional outcome in pertrochanteric fractures treated by cephalomedullary nails. Injury. 2015;329(12): 2384-2388. [38] Boopalan PR, Oh JK, Kim TY, et al. Incidence and Radiologic Outcome of Intraop-erative Lateral Wall Fractures in OTA 31A1 and A2 Fractures Treated With Cephalomedullary Nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26: 638-642. [39] 姜自伟,黄枫,庞智晖,等.股骨转子间骨折的三角固定理论[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(9):70-72. |
| [1] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [2] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [4] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [5] | Huang Xiang-wang, Liu Hong-zhe. A new low elastic modulus of beta titanium alloy Ti2448 spinal pedicle screw fixation affects thoracic stability: biomechanical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1031-1035. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Li Jing, Yang Long, Wang Jian-ji, Liu Qin, Zou Qiang, Sun Yu, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Three-dimensional reconstruction based on DICOM data and its application for orthopedic implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1046-1051. |
| [9] | Jiang Zi-wei, Huang Feng, Cheng Si-yuan, Zheng Xiao-hui, Sun Shi-dong, Zhao Jing-tao, Cong Hai-chen,Sun Han-qiao, Dong Hang. Design and finite element analysis of digital splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1052-1056. |
| [10] | Wang Fei, Liu Zhi-bin, Tao Hui-ren, Zhang Jian-hua, Li Chang-hong, Cao Qiang, Zheng Jun, Liu Yan-xiong, Qu Xiao-peng. Clinical efficacy of preoperative osteotomy designs using paper-cut technology versus photoshop software for ankylosing spondylitis with kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1057-1063. |
| [11] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [12] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [13] | Fu Wei-min, Wang Ben-jie. Assessing the degree of necrotic femoral head, and association of blood supply with pathlogical changes: study protocol for a diagnostic animal trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1086-1091. |
| [14] | Zhang Wen-qiang, Ding Qian, Zhang Na. Associations between alpha angle and herniation pit on oblique axial magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic hip joints of adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1098-1103. |
| [15] | Sun Xiao-xin1, Zhou Wei2, Zuo Shu-ping3, Liu Hao1, Song Jing-feng1, Liang Chun-yu1. Morphological characteristics for the magnetic resonance imaging assessment of discoid lateral meniscal tears in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1104-1109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||