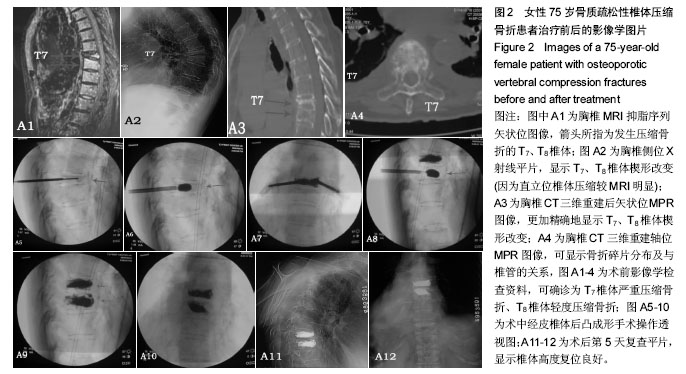
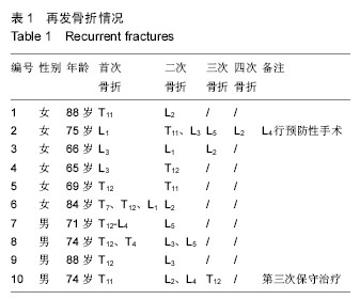
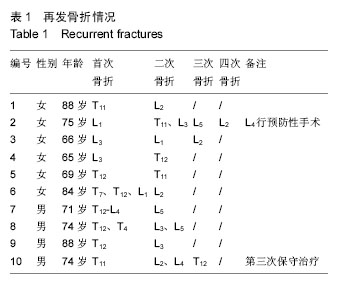
| [1] Galibert P,Deramond H,Rosat P,et al.Preliminary Note On the Treatment of Vertebral Angioma by Percutaneous Acrylic Vertebroplasty.Neurochirurgie. 1987;2:166-168.
[2] Rousing R,Hansen KL,Andersen MO,et al. Twelve-Months Follow-Up in Forty-Nine Patients with Acute/Semiacute Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures Treated Conservatively Or with Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A Clinical Randomized Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2010;5:478-482.
[3] Klazen CA,Lohle PN,de Vries J,et al.Vertebroplasty Versus Conservative Treatment in Acute Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures (Vertos II): An Open- Label Randomised Trial.Lancet.2010;9746:1085-1092.
[4] Anselmetti GC,Corrao G,Monica PD,et al.Pain Relief Following Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Results of a Series of 283 Consecutive Patients Treated in a Single Institution.Cardiovas Int Radiol.2007;3:441-447.
[5] 郝光亮,郝永强,马永成,等.椎体骨质疏松性骨折漏诊率的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2008,14(11):767-769.
[6] Hide IG,Gangi A.Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: History, Technique and Current Perspectives.Clin Radiol.2004; 6:461-467.
[7] Jarvik JG,Kallmes DF,Mirza SK.Vertebroplasty: Learning More, but Not Enough. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;14:1487-1489.
[8] 刘杰,王建.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松胸椎椎体重度压缩性骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(4):399-403.
[9] Chen C,Bian J,Zhang W,et al.Unilateral Versus Bilateral Vertebroplasty for Severe Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures.J Spinal Disord Tech.2014;8:E301-E304.
[10] Song BK,Eun JP,Oh YM.Clinical and Radiological Comparison of Unipedicular Versus Bipedicular Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fractures. Osteoporos Int.2009;10:1717-1723.
[11] Chen C,Wei H,Zhang W,et al.Comparative Study of Kyphoplasty for Chronic Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Via Unipedicular Versus Bipedicular Approach.J Spinal Disord Tech.2011;7: E62-E65.
[12] 徐宝山,胡永成.对《椎体后凸成形术治疗重度骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折》一文的几点看法[J].中华骨科杂志,2010, 30(10):984.
[13] Yeom JS,Kim WJ, Choy WS,et al.Leakage of Cement in Percutaneous Transpedicular Vertebroplasty for Painful Osteoporotic Compression Fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;1:83-89.
[14] Lee IJ,Choi AL,Yie MY,et al.CT Evaluation of Local Leakage of Bone Cement After Percutaneous Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty.Acta Radiologica. 2010;6:649-654.
[15] 郑毓嵩,张勇,林金丁,等.椎体成形术骨水泥渗漏的相关危险因素分析[J].中华创伤杂志, 2015,31(4):312-316.
[16] 钟远鸣,程俊,仇振茂,等.单双侧经椎弓根入路PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(10):892-897.
[17] Chen WJ, Kao YH,Yang SC,et al.Impact of Cement Leakage Into Disks On the Development of Adjacent Vertebral Compression Fractures.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;1:35-39.
[18] 张朗仪,陈德立,钟少华,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗胸腰椎压缩骨折骨水泥分布和剂量对疗效的影响[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2015,36(12):1730-1732.
[19] 申勇,任虎,张英泽,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折骨水泥渗漏的相关因素分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(1):27-31.
[20] 郑毓嵩,张勇,林金丁,等.椎体成形术骨水泥渗漏的相关危险因素分析[J].中华创伤杂志, 2015,31(4):312-316.
[21] Heo DH,Chin DK,Yoon YS,et al.Recollapse of Previous Vertebral Compression Fracture After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty.Osteop Int.2009;3:473-480.
[22] Kim YY,Rhyu KW.Recompression of Vertebral Body After Balloon Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture.EurSpine J.2010;11:1907-1912.
[23] Chen LH,Hsieh MK,Liao JC,et al.Repeated Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Refracture of Cemented Vertebrae.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011; 7:927-933.
[24] 钟远鸣,付拴虎,张家立,等.骨质疏松脊柱压缩性骨折经皮穿刺椎体成形术后再骨折因素的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,23(18):1829-1832.
[25] 王智运,尹庆水,章凯,等.经皮椎体成形术后再发骨折的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(1):14-16.
[26] 宋洁富,艾自胜,荆志振,等.椎体成形术后周围椎体新发骨折的相关因素分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(6): 588-590.
[27] Wu AM,Chi YL,Ni WF.Vertebral Compression Fracture with Intravertebral Vacuum Cleft Sign: Pathogenesis, Image, and Surgical Intervention.Asian Spine J. 2013; 2:148-155.
[28] 杨刘柱,陈仲,严鑫平,等.椎体骨水泥注入联合抗骨质疏松药物治疗急性骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,17(39):6265-6270.
[29] 欧阳超,陈志明,马华松,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折术后非手术椎体新发骨折的相关因素分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(3):222-227.
[30] Zhang Z,Fan J,Ding Q,et al.Risk Factors for New Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures After Vertebroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta- Analysis.J Spinal Disord Tech.2013;4:E150-E157.
[31] Ma X,Xing D,Ma J,et al.Risk Factors for New Vertebral Compression Fractures After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Qualitative Evidence Synthesized From a Systematic Review.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 12:E713-E722.
[32] Tseng YY,Yang TC,Tu PH,et al.Repeated and Multiple New Vertebral Compression Fractures After Percutaneous Transpedicular Vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;18:1917-1922.
[33] Lin WC,Cheng TT,Lee YC,et al.New Vertebral Osteoporotic Compression Fractures After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Retrospective Analysis of Risk Factors.J Vas Int Radiol. 2008;2 Pt 1:225-231.
[34] Lee WS,Sung KH,Jeong HT,et al.Risk Factors of Developing New Symptomatic Vertebral Compression Fractures After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Patients.Eur Spine J.2006;12:1777-1783.
[35] Uppin AA,Hirsch JA,Centenera LV,et al.Occurrence of New Vertebral Body Fracture After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients with Osteoporosis.Radiology. 2003;1:119-124.
[36] 张华俦,余存泰,沈惠良,等.骨质疏松性骨折药物治疗的优化方案研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2007,13(3):201-203.
[37] Chiu YC,Yang SC,Chen HS,et al.Clinical Evaluation of Repeat Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Symptomatic Cemented Vertebrae.J Spinal Disord Tech.2012;8: E245-E253. |