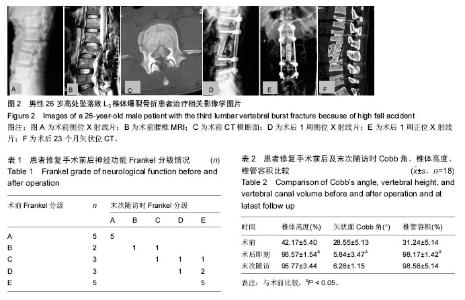
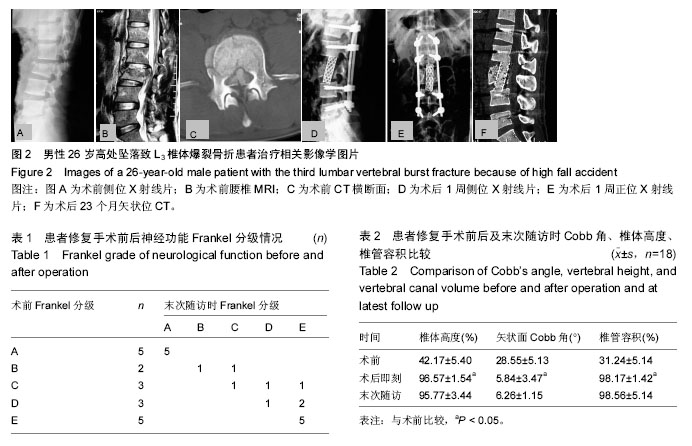
| [1] Müller U, Berlemann U, Sledge J, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit by indirect reduction and posterior instrumentation: bisegmental stabilization with monosegmental fusion. Eur Spine J. 1999;8(4):284-289.[2] Pellise F, Barastegui D, Hernandez-Fernandez A, et al. Viability and long-term survival of short-segment posterior fixation in thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine J. 2015;15(8):1796-1803.[3] Schwab F. Treatment with or without an Orthosis is Equivalent for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture without Neurologic Injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(16): 1374.[4] Hu R, Mustard CA, Burns C. Epidemiology of incident spinal fracture in a complete population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(4):492-499.[5] Scheer JK, Bakhsheshian J, Fakurnejad S, et al. Evidence-Based Medicine of Traumatic Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review of Operative Management across 20 Years. Global Spine J. 2015;5(1):73-82.[6] 高博,幸嵘,孔清泉,等.经后路椎体次全切除加椎间支撑植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折及骨折脱位的早期疗效观察[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(5):542-545.[7] Jo DJ, Kim KT, Kim SM, et al. Single-Stage Posterior Subtotal Corpectomy and Circumferential Reconstruction for the Treatment of Unstable Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016;59(2):122-128.[8] Ghobrial GM, Jallo J. Thoracolumbar spine trauma: review of the evidence. J Neurosurg Sci. 2013;57(2): 115-122.[9] Lee JK, Jang JW, Kim TW, et al. Percutaneous short-segment pedicle screw placement without fusion in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: is it effective?: comparative study with open short-segment pedicle screw fixation with posterolateral fusion. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013;155(12):2305-2312; discussion 2312.[10] Grossbach AJ, Dahdaleh NS, Abel TJ, et al. Flexion-distraction injuries of the thoracolumbar spine: open fusion versus percutaneous pedicle screw fixation. Neurosurg Focus. 2013;35(2):E2.[11] Vanek P, Bradac O, Konopkova R, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar trauma by short-segment percutaneous transpedicular screw instrumentation: prospective comparative study with a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(2):150-156.[12] Sasani M, Ozer AF. Single-stage posterior corpectomy and expandable cage placement for treatment of thoracic or lumbar burst fractures. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2009;31(1):E33-40.[13] 李建江,马信龙,邓树才,等.经后路椎体次全切除及重建治疗严重胸腰椎骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(7):761-766.[14] 林慰光,林本丹,胡奕山.经后路椎体次全切除后钛网支撑置入加椎弓根钉内固定治疗腰椎爆裂性骨折的初步报告[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(5):489-491.[15] Liu Y, Li G, Dong T, et al. One-stage partial vertebrectomy, titanium mesh implantation and pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures through a posterior approach. Clinics. 2014; 69(12):804-808.[16] Hitchon PW, Abode-Iyamah K, Dahdaleh NS, et al. Nonoperative Management in Neurologically Intact Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(6):483-489.[17] Mattei TA, Hanovnikian J, D HD. Progressive kyphotic deformity in comminuted burst fractures treated non-operatively: the Achilles tendon of the Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Score (TLICS). Eur Spine J. 2014;23(11):2255-2262.[18] Hitchon PW, Torner J, Eichholz KM, et al. Comparison of anterolateral and posterior approaches in the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;5(2):117-125.[19] Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang ZF, et al. Radiological study on disc degeneration of thoracolumbar burst fractures treated by percutaneous pedicle screw fixation. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(3):489-494.[20] Payer M. Unstable burst fractures of the thoraco-lumbar junction: treatment by posterior bisegmental correction/fixation and staged anterior corpectomy and titanium cage implantation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006;148(3):299-306; discussion 306.[21] 吴冰,吴天泉,程德良,等.经后路伤椎置入椎弓根螺钉短节段固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学研究[J].浙江医学,2015,37(23):1923-1927.[22] 陈海波,滕红林.不同入路椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床效果研究[J]. 浙江创伤外科, 2015,20(4): 785-787.[23] 李健,肖斌,赵洪普,等.经伤椎椎弓根钉固定结合经椎弓根植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2009, 17(8):590-592.[24] Pingel A, Castein J, Kandziora F. Vertebral body replacement in the thoracolumbar spine via a mini-open, thoracoscopically assisted transthoracic approach. Eur Spine J. 2015;24 (Suppl 8):S949-950.[25] Parker JW, Lane JR, Karaikovic EE, et al. Successful short-segment instrumentation and fusion for thoracolumbar spine fractures: a consecutive 4½-year series. Spine. 2000;25(9):1157-1170.[26] Sasso RC, Renkens K, Hanson D, et al. Unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures: anterior-only versus short-segment posterior fixation. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(4):242-248.[27] Lin B, Chen ZW, Guo ZM, et al. Anterior Approach Versus Posterior Approach With Subtotal Corpectomy, Decompression, and Reconstruction of Spine in the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011.[28] Peters T, Chinthakunta SR, Hussain M, et al. Pedicle Screw Configuration for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture Treatment: Short versus Long PosteriorFixation Constructs with and without Anterior Column Augmentation. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(1):35-43. doi: 10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.35.[29] McDonnell M, Shah KN, Paller DJ, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Pedicle Screw Fixation for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. Orthopedics. 2016; 39(3):e514-518.[30] Bolesta MJ, Caron T, Chinthakunta SR, et al. Pedicle screw instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: Biomechanical evaluation of screw configuration with pedicle screws at the level of the fracture. Int J Spine Surg. 2012;6:200-205.[31] Louis CA, Gauthier VY, Louis RP. Posterior approach with Louis plates for fractures of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spine with and without neurologic deficits. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 998;23(18):2030-2039; discussion 2040.[32] Verlaan JJ, Somers I, Dhert WJ, et al. Clinical and radiological results 6 years after treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar burst fractures with pedicle screw instrumentation and balloon assisted endplate reduction. Spine J. 2015;15(6):1172-1178.[33] Alizadeh M, Kadir MR, Fadhli MM, et al. The use of X-shaped cross-link in posterior spinal constructs improves stability in thoracolumbar burst fracture: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(9): 1447-1454.[34] Mahar A, Kim C, Wedemeyer M, et al. Short-segment fixation of lumbar burst fractures using pedicle fixation at the level of thefracture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32(14):1503-1507.[35] 欧云生,蒋电明,权正学,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺 66 复合生物活性人工椎体在胸腰椎骨折前路重建手术中的应用[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(10): 1084-1089.[36] 毛宁方,石志才,朱晓东,等.全脊椎切除术后三种不同重建方法的稳定性比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(6): 446-449.[37] McLain RF. The biomechanics of long versus short fixation for thoracolumbar spine fractures. Spine. 2006; 31(11S):S70-S79. |