Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (22): 3560-3566.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.22.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of complications after volar and dorsal plate fixations for repair of distal radius fractures
Zhang Yi, Yang Tuo, Li Hui, Deng Zhen-han, Yang Ye, Zeng Chao, Lei Guang-hua
- Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-04-02Online:2014-05-28Published:2014-05-28 -
Contact:Lei Guang-hua, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Yi, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yi, Yang Tuo, Li Hui, Deng Zhen-han, Yang Ye, Zeng Chao, Lei Guang-hua. Meta-analysis of complications after volar and dorsal plate fixations for repair of distal radius fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(22): 3560-3566.
share this article
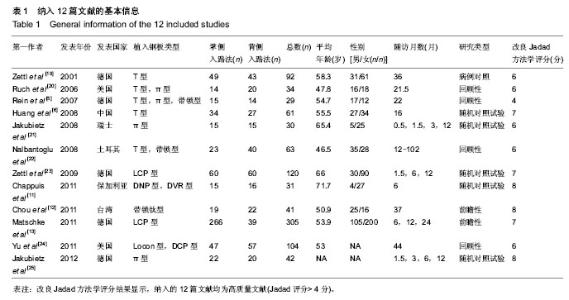
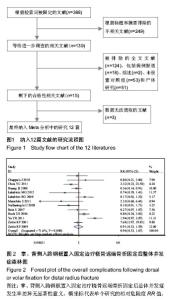
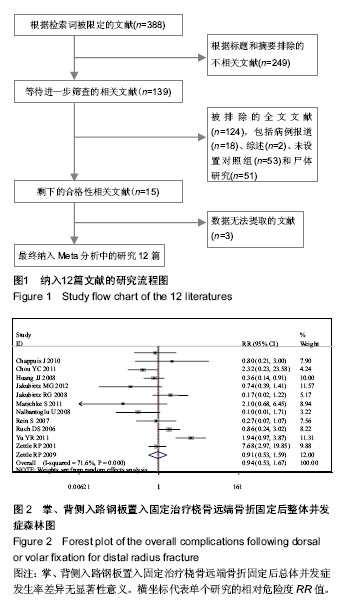
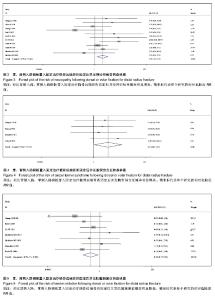
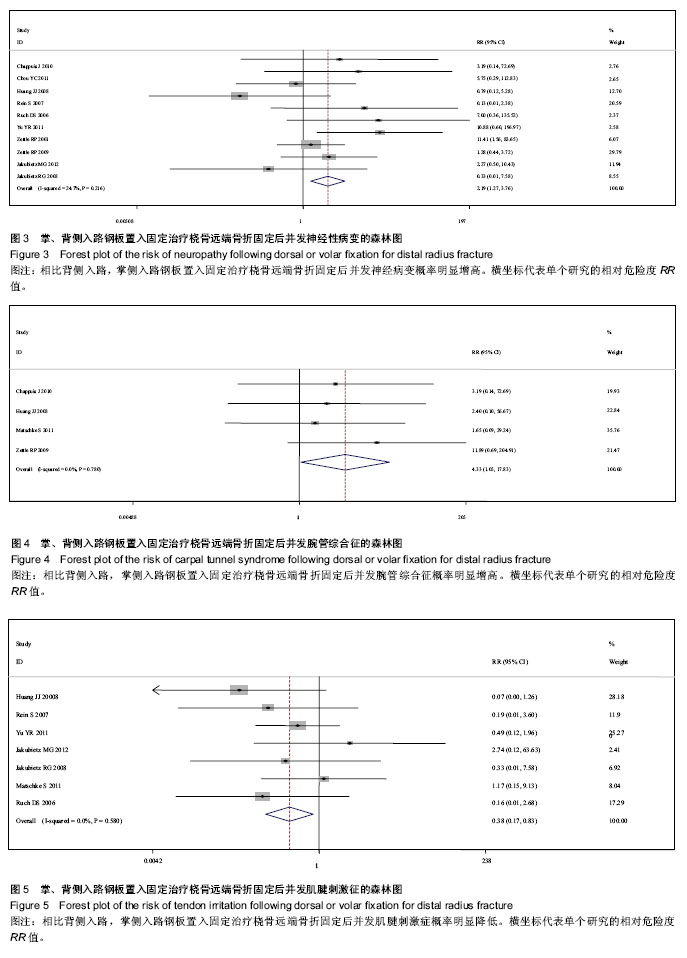
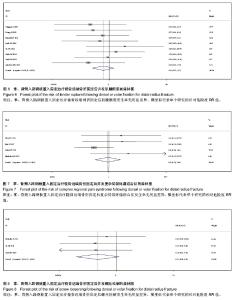
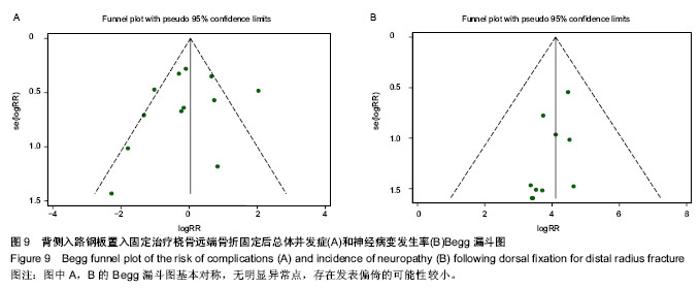
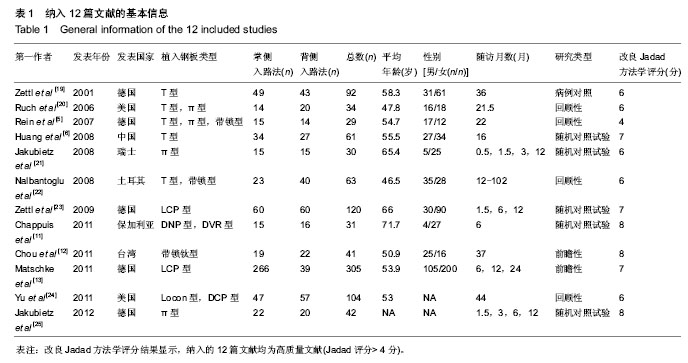
2.1 检索结果分析 根据检索策略共检索出388篇文献,最终纳入12篇文献(n=952)[5-6, 11-13, 19-25]。表1是目标文献的基本特征, 改良Jadad方法学评分结果显示,纳入的12篇文献均为高质量文献。图1显示了文章是如何依据文献纳入和排除标准来检索相关文献。 2.2 Meta分析结果 通过随机效应模型发现,掌背侧入路钢板置入固定之间固定后并发症的总体发生率无显著差异,见图2,而文献存在显著的异质性(P < 0.001;I2=72%),通过排除Zettl等[19](P=0.03;49%)的文献减少了异质性。 敏感性分析结果提示任何一项研究都不影响所合并的结果。亚组分析显示:与背侧入路钢板置入固定相比,使用掌侧入路钢板置入固定后并发神经病变(RR=2.19,95%CI:1.27-3.76;P < 0.05;图3)与腕管综合征(RR=4.33,95%CI:1.05-17.83;P < 0.05;图4)的概率显著增加[5-6, 11-13, 19-21, 23-25],并发肌腱刺激症(RR= 0.38,95%CI:0.17-0.86;P < 0.05;图5)的概率显著降低[5-6, 13, 20-21, 24-25],而并发肌腱断 裂[6, 11, 13, 19-20, 23-25](图6),复杂局部疼痛综合征与螺丝松解的概率差异无显著性意义[5, 12, 23-25](图7,8)。"
| [1] Simic PM, Weiland AJ. Fractures of the distal aspect of the radius: changes in treatment over the past two decades. Instr Course Lect. 2003;52:185-195. [2] Gehrmann SV, Windolf J, Kaufmann RA. Distal radius fracture management in elderly patients: a literature review. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:421-429. [3] 郭柳生.锁钉钢板治疗桡骨远端骨折体会[J].求医问药:下半月刊, 2011,9(3):72. [4] 白玉明,马世云.桡骨远端骨折治疗进展[J].河北医药,2009, 31(18): 2477-2479. [5] Rein S, Schikore H, Schneiders W, et al. Results of dorsal or volar plate fixation of AO type C3 distal radius fractures: a retrospective study. J Hand Surg Am. 2007;32:954-961. [6] Huang JJ. Comparison between volar and dorsal plate positions in the treatment of unstable fracture of distal radius. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008;22:948-951. [7] BaratzME, Des Jardins J, Anderson DD, et al. Displaced intra articular fractures of the distal radius: the effect of fracture displacement on contact stresses in a cadaver model. J Hand Surg Am. 1996;21:183-188. [8] Leung F, Zhu L, Ho H, et al. Palmar plate fixation of AO type C2 fracture of distal radius using a locking compression plate biomechanical study in a cadaveric model. J Hand Surg Br. 2003;28:263-266. [9] Blythe M, Stoffel K, Jarrett P, et al. Volar versus dorsal locking plates with and without radial styloid locking plates for the fixation of dorsally comminuted distal radius fractures: a biomechanical study in cadavers. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31: 1587-1593. [10] Rozental TD, Blazar PE. Functional outcome and complications after volar plating for dorsally displaced, unstable fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 2006; 31:359-365. [11] Chappuis J, Boute´ P, Putz P. Dorsally displaced extra-articular distal radius fractures fixation: dorsal IM nailing versus volar plating. A randomized controlled trial. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97:471-478. [12] Chou YC, Chen AC, Chen CY, et al. Dorsal and volar 2.4-mm titanium locking plate fixation for AO type C3 dorsally comminuted distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2011; 36:974-981. [13] Matschke S, Wentzensen A, Ring D, et al. Comparison of angle stable plate fixation approaches for distal radius fractures. Injury. 2011;42:385-392. [14] Van Tulder M, Furlan A, Bombardier C, et al. Updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the cochrane collaboration back review group. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:1290-1299. [15] Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. 2000. [16] Jadad RA, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control clin trails. 1996;17:1-12. [17] Hartling L, Ospina M, Liang Y, et al. Risk of bias versus quality assessment of randomized controlled trials: corss sectional study. BMJ. 2009;339:b4012. [18] Begg CB, Mazumdar M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. 1994;50: 1088-1101. [19] Zettl RP, Ruchholtz S, Taeger G, et al. Postoperative morbidity in surgically treated extension fractures of the distal radius. A comparative study of dorsal and volar approach. Unfallchirurg. 2001;104:710-715. [20] Ruch DS, Papadonikolakis A. Volar versus dorsal plating in the management of intra-articular distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31:9-16. [21] Jakubietz RG, Gruenert JG, Kloss DF, et al. A randomised clinical study comparing palmar and dorsal fixed-angle plates for the internal fixation of AO C-type fractures of the distal radius in the elderly. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2008;33:600-604. [22] Nalbanto?lu U, Gereli A, Uç¸ ar Y, et al. Comparison between fixation with dorsal T-plate and palmar locking plate in the treatment of unstable displaced distal radius fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2008;42:365-372. [23] Zettl RP, Clauberg E, Nast-Kolb D, et al. Volar locking compression plating versus dorsal plating for fractures of the distal radius: a prospective, randomized study. Unfallchirurg. 2009;112:712-718. [24] Yu YR, Makhni MC, Tabrizi S, et al. Complications of low-profile dorsal versus volar locking plates in the distal radius: a comparative study. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36: 1135-1141. [25] Jakubietz MG, Gruenert JG, Jakubietz RG. Palmar and dorsal fixed-angle plates in AO C-type fractures of the distal radius: is there an advantage of palmar plates in the long term? J Orthop Surg Res. 2012;7:8. [26] 刘智.桡骨远端骨折治疗方法的合理选择[J].中国骨伤,2010, 23(8):57l-573. [27] 陈昌红,周荣魁.掌侧和背侧钢板内固定治疗背侧不稳定桡骨远端骨折的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(2):131-133. [28] 张兴平.桡骨远端骨折治疗方法的选择与思考[J].中国骨伤,2011, 24(11):887-889. [29] 王闯,张永久.掌侧入路锁定加压钢板治疗桡骨远端骨折28例体会[J].中国社区医师医学专业,2012,6(14):133. [30] Osada D, Tamai K, Iwamoto A, et al. Dorsal plating for comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius. Hand Surg. 2004;9:181-190. [31] Sen MK, Strauss N, Harvey EJ. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal radius fractures using a pronator sparing approach. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2008;12:2-6. [32] Ozer K, Toker S. Dorsal tangential view of the wrist to detect screw penetration to the dorsal cortex of the distal radius after volar fixed-angle plating. Hand (NY). 2011;6:190-193. [33] Tavakolian JD, Jupiter JB. Dorsal plating for distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2005;21:341-346. [34] Mignemi ME, Byram IR, Wolfe CC, et al. Radiographic outcomes of volar locked plating for distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38:40-48. [35] Tyllianakis ME, Panagopoulos AM, Saridis A. Long-term results of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures treated with the pi-plate: is hardware removal necessary? Orthopedics. 2011;34:e282-286. [36] Ring D, Jupiter JB, Brennwald J, et al. Prospective multicenter trial of a plate for dorsal fixation of distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1997;22:777-784. [37] Rozental TD, Beredjiklian PK, Bozentka DJ. Functional outcome and complications following two types of dorsal plating for unstable fractures of the distal part of the radius. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1956-1960. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||