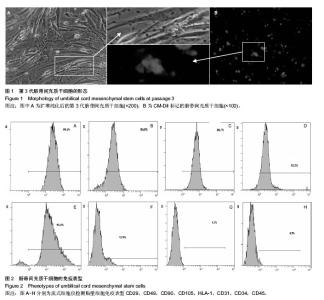
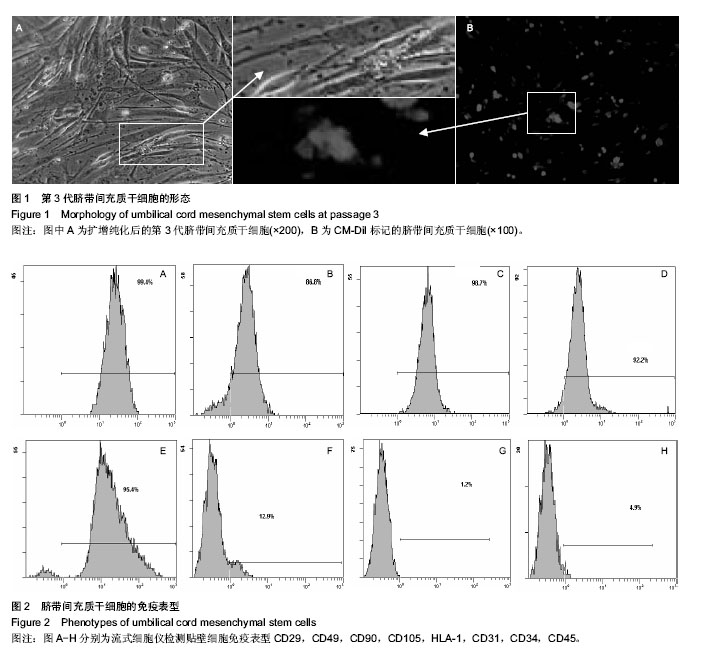
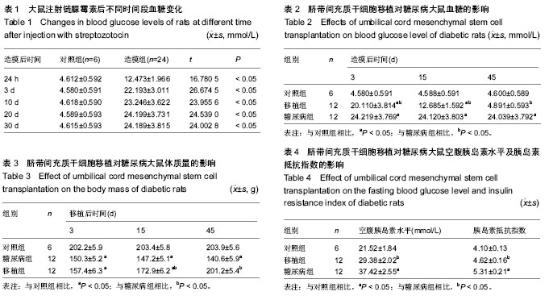
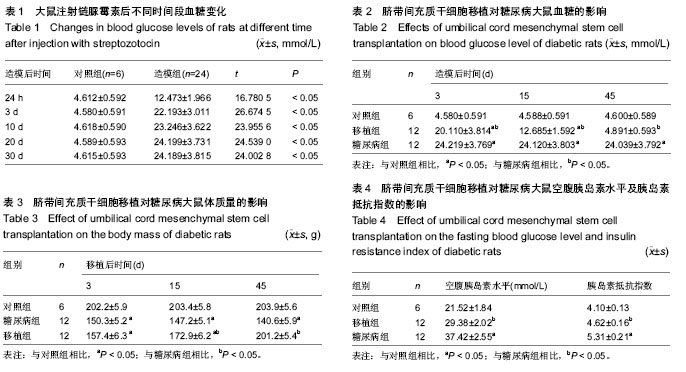
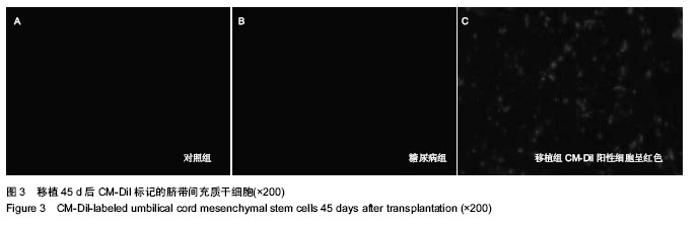
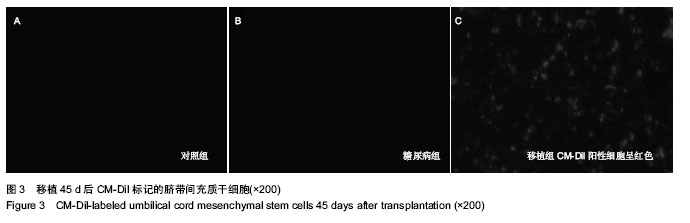
| [1] 何清华,周迎生,王征,等.干预脂毒性改善糖尿病大鼠胰岛素分泌及氧化应激的损害[J].中国实验动物学报,2009,2(1):123-124.
[2] 付文亮,钟美蓉,和亚强,等.丝胶预处理对糖尿病大鼠睾丸IGF-1表达的影响[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2010,1(4):163- 165.
[3] 袁凤山,王长军,董飞,等.诱导回输胰岛素分泌细胞对大鼠糖尿病的疗效[J].中国生物工程杂志,2011,6(5):132-134.
[4] 肖醉萱,邓德明,孙爱萍.NF-κB、PKC与糖尿病及胰岛素的抗炎作用[J].长江大学学报(自然科学版)医学卷,2010,8(1):162-164.
[5] 李俊林,李德华,赵宝东,等.人脐带间充质干细胞体外向胰岛样细胞诱导分化及其治疗糖尿病效果[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(14):175-178.
[6] 高峰,周汉新,齐晖,等.骨髓间充质干细胞胰腺包膜下移植与静脉移植治疗大鼠糖尿病的效果比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,3(19):215-216.
[7] 禹亚彬,陈维,卞建民.体外定向诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛样细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,2(6):163-164.
[8] 于洪宇,马春宇,郑晓明.体外诱导人脐带间充质干细胞向胰岛β样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(19): 256-257.
[9] 洪敬欣,刘剑,李琳芳,等.地塞米松浓度与脐带间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,27(17):4204-4211.
[10] Faisal A, Saurin A, Gregory B, et al. The scaffold MyD88 acts to couple protein kinase Cepsilon to Toll-like receptors. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(27):18591-18600.
[11] 迟作华,陆琰,张洹. 体外诱导脐血间充质干细胞向胰岛β样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(49): 134-136.
[12] Hong SH, Lee JH, Lee JB, et al. ID1 and ID3 represent conserved negative regulators of human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cell hematopoiesis. J Cell Sci. 2011; 124(Pt 9):1445-1452.
[13] 李辛,刁克,张凤香,等.不同细胞接种浓度影响人脐带间充质干细胞生长及多向分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(14): 142-145.
[14] 刘峰,徐永胜,俞海燕,等.人脐带间充质干细胞作为维持人胚胎干细胞生长饲养层细胞的研究[J].中国实验动物学报,2011, 19(4): 271-276,10009.
[15] 荣靖,彭鑫磊,马岩岩,等.人脐带间充质干细胞向成骨细胞及脂肪细胞分化过程中nm23-H1基因的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19):3467-3471.
[16] 高璐,贾连顺.人脐带间充质干细胞及其治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(11):952-954.
[17] 窦慧慧,于丽,郭文君.人脐血单个核细胞和脐带间充质干细胞移植用于大鼠脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2010, 25(2):104-108.
[18] 单伟,王长辉,秦书俭,等.人脐带间充质干细胞修复大鼠坐骨神经损伤的实验研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2011,40(8):696-698, 702.
[19] 刘霞,陈寿康.以酮症酸中毒为首发症状的小儿糖尿病20例分析[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2010,2(1):48-50.
[20] 张冬梅,周智广,胡白瑛,等.自发酮症起病的肥胖糖尿病病人的临床特征[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2010,19(3):221-222.
[21] 朱鋐达,陈名道.酮症起病的糖尿病[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志., 2010,20(5):378-380.
[22] 周芬莉,张海鸥,吴军,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗糖尿病大鼠周围神经病变的研究[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2011,28(1):21-24.
[23] 苏仲春,陈家劲,王圳,等.诱导人脐带MSCs分化为胰岛样细胞团的促成熟方案及机制[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2013,29(2): 139-141.
[24] 董迎.胰岛素泵在糖尿病酮症酸中毒中的疗效比较[J].河北联合大学学报(医学版),2012,14(1):69-70.
[25] 梁黎,梁建凤,洪文澜,等.儿童糖尿病酮症酸中毒25年回顾分析[J].临床儿科杂志,2009,18(3):173-176.
[26] 杨柏梁,郭丽,任淑萍,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对糖尿病大鼠疗效观察[J].中国公共卫生,2009,25(8):973-974.
[27] 于文龙,徐薇,于江苏,等.人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗初发1型糖尿病鼠[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(19): 3474-3480.
[28] 李孔龙,段志胜,徐勉,等.脐血干细胞治疗1型糖尿病3例[J].中国医药指南,2013,26(11):1-3.
[29] 张弛,肖日军,张娜,等.脐血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病大鼠下肢缺血的实验研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志,2012,7(1):12-16.
[30] Finney MR, Fanning LR, Joseph ME, et al. Umbilical cord blood-selected CD133(+) cells exhibit vasculogenic functionality in vitro and in vivo. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(1): 67-78.
[31] 李晓玲,朱旅,宋光耀,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植对1型糖尿病大鼠模型血糖及肾脏病变的影响研究[J].解放军医药杂志,2013, 25(7):31-34.
[32] Fang Y, Tian X, Bai S, et al. Autologous transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress, pro-inflammatory cytokines and the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2012;30(1): 85-92.
[33] 王燕,赵霞,范斌,等.2型糖尿病血压控制与未来出现肾病终点的观察性研究[J].首都医科大学学 报,2012,33(4):472-476.
[34] Volarevic V, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML, et al. Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cell treatment of the complications of diabetes mellitus. Stem Cells. 2011;29(1):5-10.
[35] 郝永蕾,朱旅云,王更银,等.体外诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为胰岛样细胞实验研究[J].临床误诊误治,2010,23(9):804-807.
[36] Fang TC, Pang CY, Chiu SC, et al. Renoprotective effect of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in immunodeficient mice suffering from acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46504.
[37] Hills CE, Squires PE. The role of TGF-β and epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011;22(3):131-139.
[38] 陈镭,曲宗宁,张东强,等.人脐血源性间充质干细胞的体外培养及生物学鉴定[J].江苏医药,2005,31(7):481-483.
[39] 李倩倩,崔晓兰,时瀚,等.脐带间充质干细胞联合番茄红素的抗衰老作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,40(17):7040-7046.
[40] 迟作华,张桓,何冬梅,等.脐血间充质干细胞培养条件的优化[J].中国实用内科杂志,2006,26(5):372-375.
[41] 金玮,杨安怀,邢怡桥.人脐血间充质干细胞的体外培养及生物学特性[J].武汉大学学报:医学版,2007,28(4):488-491.
[42] Mansilla E, Díaz Aquino V, Zambón D, et al. Could metabolic syndrome, lipodystrophy, and aging be mesenchymal stem cell exhaustion syndromes? Stem Cells Int. 2011;2011: 943216.
[43] Duijvestein M, Wildenberg ME, Welling MM, et al. Pretreatment with interferon-γ enhances the therapeutic activity of mesenchymal stromal cells in animal models of colitis. Stem Cells. 2011;29(10):1549-1558.
[44] 常相萍,马艳,毕晓娟,等.冷冻前后脐带间充质干细胞造血支持能力的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,32(17):5765-5771.
[45] 李华,文峰,漆仲春,等.人脐带间充质干细胞与肝细胞共培养可分化为肝样细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,32(17):5765-5771.
[46] 雷鑫,陈彦,张建林,等.评价脐带间充质干细胞移植前细胞活性的指标[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,32(17):5847-5854.
[47] 唐欣,王岩,易海波,等.人脐带间充质干细胞诱导分化为心肌细胞的特异性基因表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,27(17):4988- 4991.
[48] 谢婷,欧阳建,陈军浩,等.犬骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为胰岛样细胞的研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2010,18(4):154-157.
[49] 单莎瑞,黄国志.干细胞抗衰老的理论研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,23(17):4347-4354.
[50] 雷川云,柯亭羽,徐勉.干细胞移植治疗2型糖尿病急眭心肌梗死的研究进展[J].中国医药科学,2013,19(3):36-38.
[51] 刘小银,莫朝晖.干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变的研究进展[J].医学综述,2013,19(17):3175-3179.
[52] 谭笑,汪年松.干细胞治疗糖尿病肾病的研究进展[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2013,19(8):738-740.
[53] 葛亮,赵建勇,孙诚谊,等.大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞体外转染为胰岛素分泌细胞的实验研究[J].中华消化外科杂志,2013,12(8):125.
[54] 陈崇岩,吴德全.干细胞分化为胰岛素分泌细胞研究进展[J].肝胆胰外科杂志,2013,25(4):347-349.
[55] Pievani A, Borleri G, Pende D, et al. Dual-functional capability of CD3+CD56+ CIK cells, a T-cell subset that acquires NK function and retains TCR-mediated specific cytotoxicity. Blood. 2011;118(12):3301-3310.
[56] 郑培,安沂华,王晓东,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的疗效观察[J].武警医学,2013,17(5):398-401. |