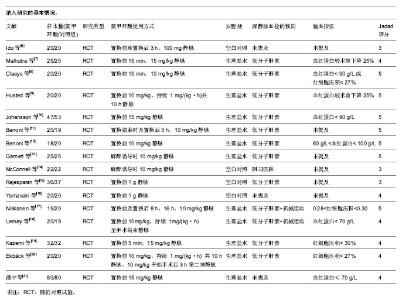
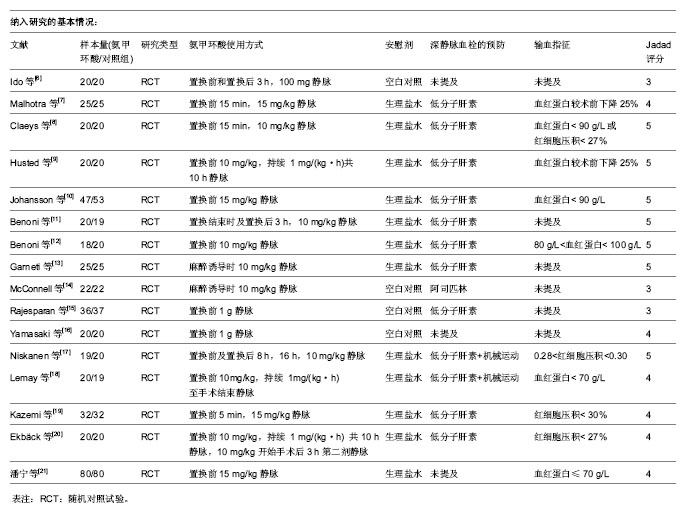
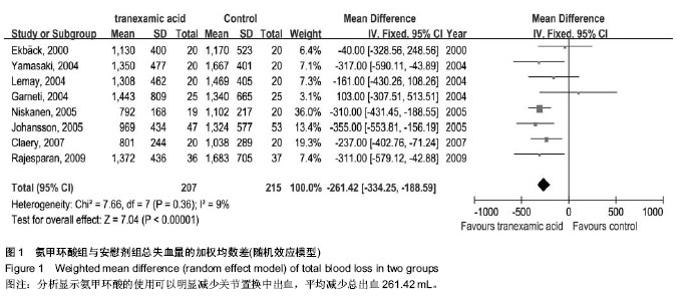
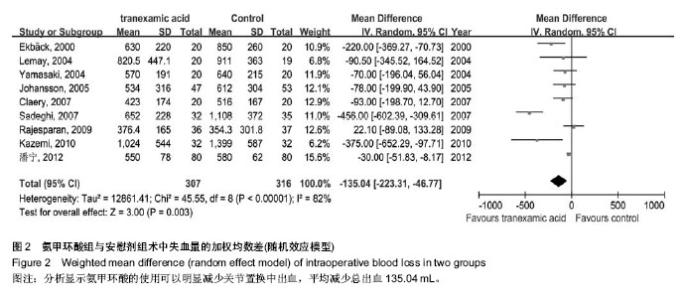
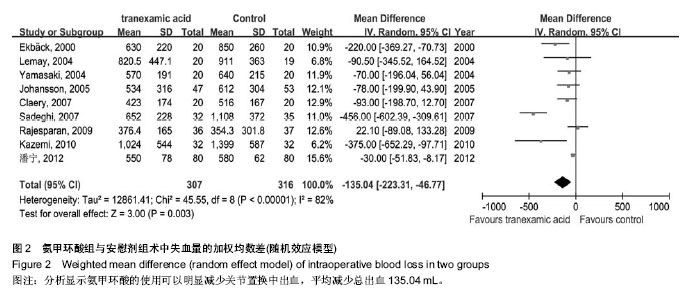
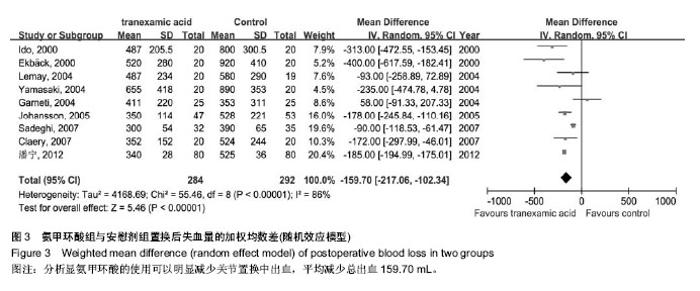
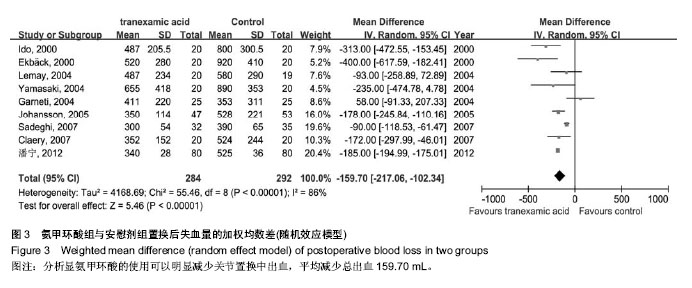
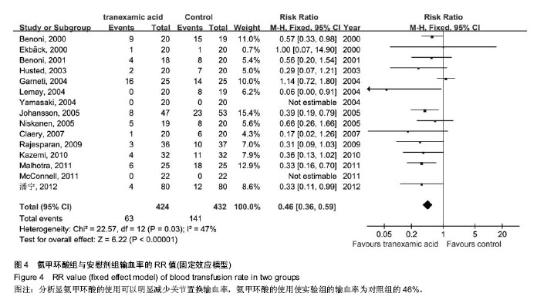
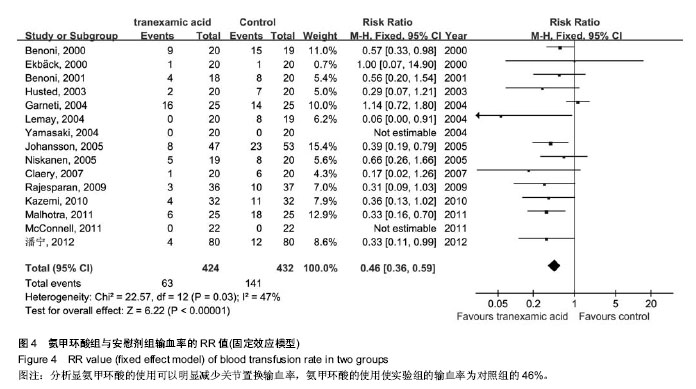
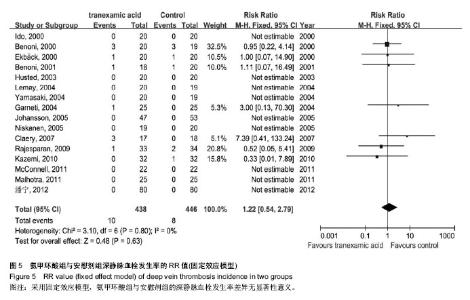
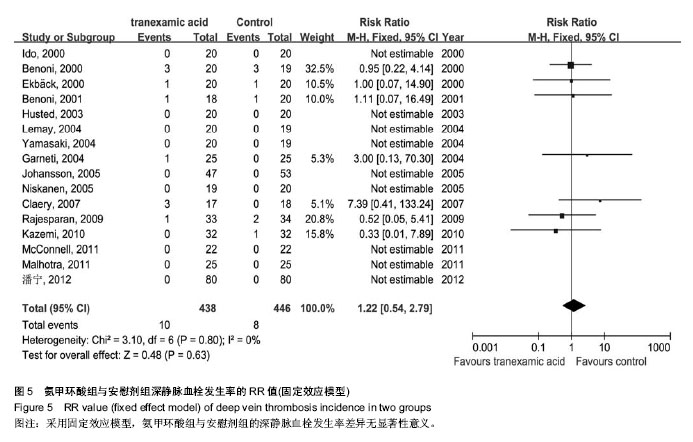
| [1] Bierbaum BE, Callaghan JJ, Galante JO, et al. An Analysis of Blood Management in Patients Having a Total Hip or Knee Arthroplasty.J Bone Jt Surg.1999;81:2-10.
[2] 张江涛,尚延春,王战朝.局部应用氨甲环酸对膝关节置换术术后出血量的影响[J].中国现代药物应用,2013,7(14):120-121.
[3] Hardy JF, Bélisle S. Natural and synthetic antifibrinolytics: inert, poisonous or therapeutic agents? Can J Anaesth. 1997; 44:913.
[4] Massicotte L, Denault AY, Beaulieu D, et al. Aprotinin versus tranexamic acid during liver transplantation: impact on blood product requirements and survival. Transplantation.2011; 91:1273.
[5] Dhir A. Antifibrinolytics in cardiac surgery. Ann Card Anaesth. 2013;16:117-25.
[6] Ido K, Neo M, Asada Y, et al. Reduction of blood loss using tranexamic acid in total knee and hip arthroplasties. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2000;120:518.
[7] Malhotra R, Kumar V, Garg B. The use of tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss in primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology 2011;21:101.
[8] Claeys MA, Vermeersch N, Haentjens P. Reduction of blood loss with tranexamic acid in primary total hip replacement surgery. Acta Chir Belg.2007;107:397.
[9] Husted H, Blønd L, Sonne-Holm S, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and blood transfusions in primary total hip arthroplasty: a prospective randomized double-blind study in 40 patients. Acta Orthop Scand.2003;74:665.
[10] Johansson T, Pettersson LG, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty saves blood and money: a randomized, double-blind study in 100 patients. Acta Orthop.2005;76:314.
[11] Benoni G, Lethagen S, Nilsson P, et al. Tranexamic acid, given at the end of the operation, does not reduce postoperative blood loss in hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71:250.
[12] Benoni G, Fredin H, Knebel R, et al. Blood conservation with tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind study in 40 primary operations. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001;72:442.
[13] Garneti N, Field J. Bone bleeding during total hip arthroplasty after administration of tranexamic acid. J Arthroplasty.2004; 19:488.
[14] McConnell JS, Shewale S, Munro NA, et al. Reduction of blood loss in primary hip arthroplasty with tranexamic acid or fibrin spray. Acta Orthop.2011;82:660.
[15] Rajesparan K, Biant LC, Ahmad M,et al. The effect of an intravenous bolus of tranexamic acid on blood loss in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2009;91:776.
[16] Yamasaki S, Masuhara K, Fuji T. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss after cementless total hip arthroplasty-prospective randomized study in 40 cases. Int Orthop.2004;28:69.
[17] Niskanen RO, Korkala OL. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in cemented hip arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind study of 39 patients with osteoarthritis.Acta Orthop.2005; 76:829.
[18] Lemay E, Guay J, Côté C,et al. Tranexamic acid reduces the need for allogenic red blood cell transfusions in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Can J Anaesth.2004;51:31.
[19] Kazemi SM, Mosaffa F, Eajazi A, et al. The effect of tranexamic acid on reducing blood loss in cementless total hip arthroplasty under epidural anesthesia. Orthopedics.2010;33: 17.
[20] Ekbäck G, Axelsson K, Ryttberg L, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in total hip replacement surgery. Anesth Analg.2000;91:1124
[21] 潘宁,熊燕,熊君宇.氨甲环酸对老年全髋关节置换术患者的血液保护效果[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2012,32(5):548-550.
[22] Sukeik M, Alshryda S, Haddad FS,et al.Systematic review and meta -analysis of the use of tranexa mic acid in total hip replacement.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011;93:39-46. |